7、Navigation obstacle avoidance
7、Navigation obstacle avoidance7.1、Usage7.1.1、Start up7.1.2、Usage7.1.3、Dynamic parameter adjustment7.1.4、2D navigation by depth mapping alone7.2、navigation7.2.1、Introduction7.2.2、Setting tf7.3、move_base7.3.1、Introduction7.3.2、move_base communication mechanism1)Action 2)topic3)servies4)Parameter configuration7.3.3、Recovery Behavior1)Introduction2) Related feature packs4、costmap_params7.4.1、costmap_common7.4.2、global_costmap7.4.3、local_costmap7.4.4、costmap_2D1)Introduction7.5、planner_params7.5.1、global_planner7.5.2、local_planner7.6、AMCL7.6.1、Introduction
navigation:http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/
navigation/Tutorials:http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/RobotSetup
costmap_2d:http://wiki.ros.org/costmap_2d
nav_core:http://wiki.ros.org/nav_core
global_planner:http://wiki.ros.org/global_planner
dwa_local_planner:http://wiki.ros.org/dwa_local_planner
teb_local_planner:http://wiki.ros.org/teb_local_planner
move_base:http://wiki.ros.org/move_base
depthimage_to_laserscan:http://wiki.ros.org/depthimage_to_laserscan
Function package:~/rplidar/src/transbot_nav
7.1、Usage
Note: [R2] on the handle can cancel the target point.
7.1.1、Start up
Start the driver and start it according to your needs (note: the pure depth mapping navigation effect is not good, so it is not recommended).
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch transbot_nav usbcam_bringup.launch lidar_type:=a1 # mono + laser + Transbotroslaunch transbot_nav astra_bringup.launch # Astra + Transbotroslaunch transbot_nav laser_bringup.launch lidar_type:=a1 # laser + Transbotroslaunch transbot_nav transbot_bringup.launch lidar_type:=a1 # Astra + laser + TransbotStart the navigation obstacle avoidance function, you can set the parameters according to your needs, and you can also modify the launch file.
lidar_type parameter: the type of lidar used: [a1, a2, a3, s1, s2].
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch transbot_nav transbot_navigation.launch open_rviz:=true map:=house- open_rviz parameter: whether to open rviz.
- map: name of the map, the map to be loaded.
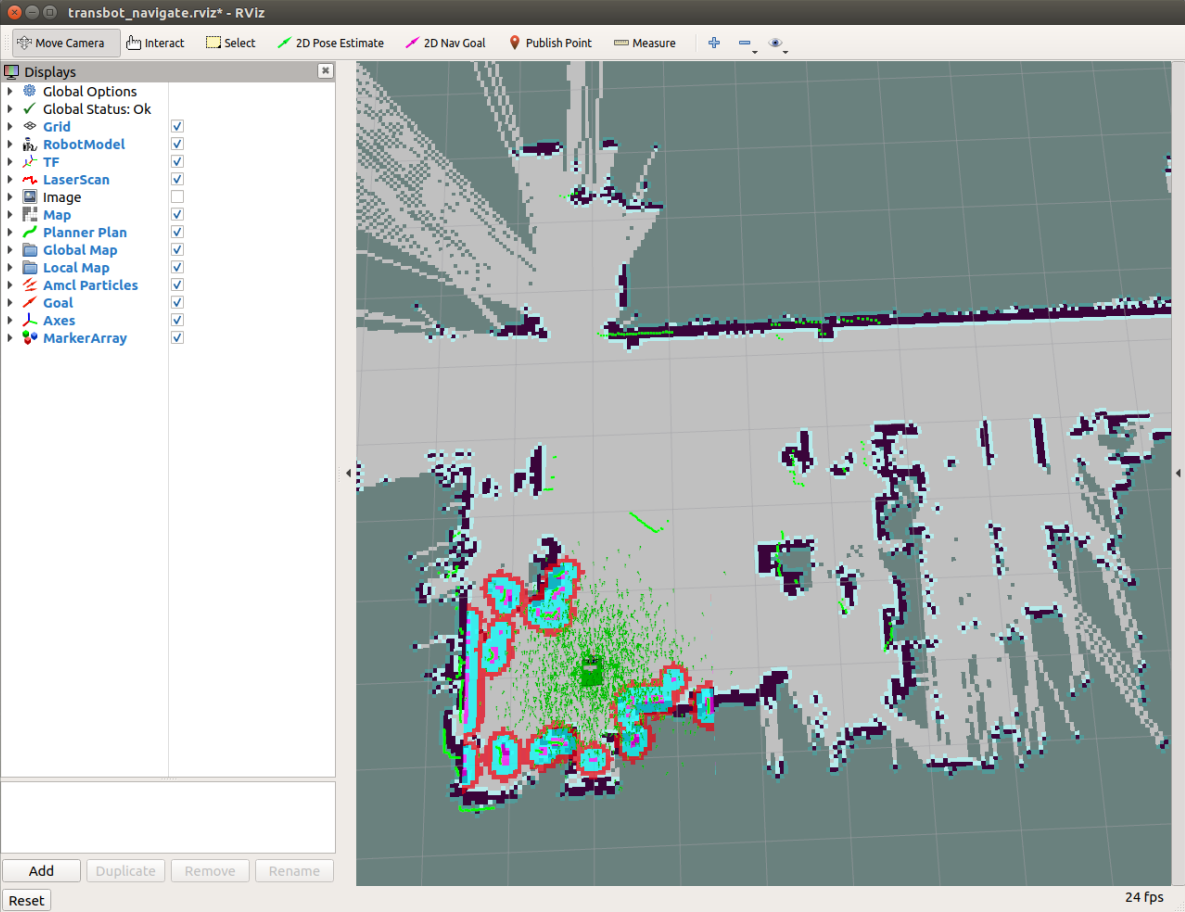
7.1.2、Usage
Place the robot at the origin. If the radar scanning edge does not coincide with the map, we need to use the 【2D Pose Estimate】of the 【rviz】 tool to set the initial pose. If the robot cannot find the pose in the map, it also needs to set the initial pose.
Single-point navigation:
Click the 【2D Nav Goal】 of the 【rviz】tool. Then use the mouse to select a target point on the map model where there are no obstacles. Release the mouse to start the navigation. Only one target point can be selected. Finally, robot car will move towards the target point form, after reaching the target point, the car will stop.
Multi-point navigation:
Click 【Publish Point】of the 【rviz】tool. Then select a target point where there are no obstacles on the map model, release the mouse to start navigation. You can click 【Publish Point】again, then select others point. Finally, robot car will cruise from point to point.
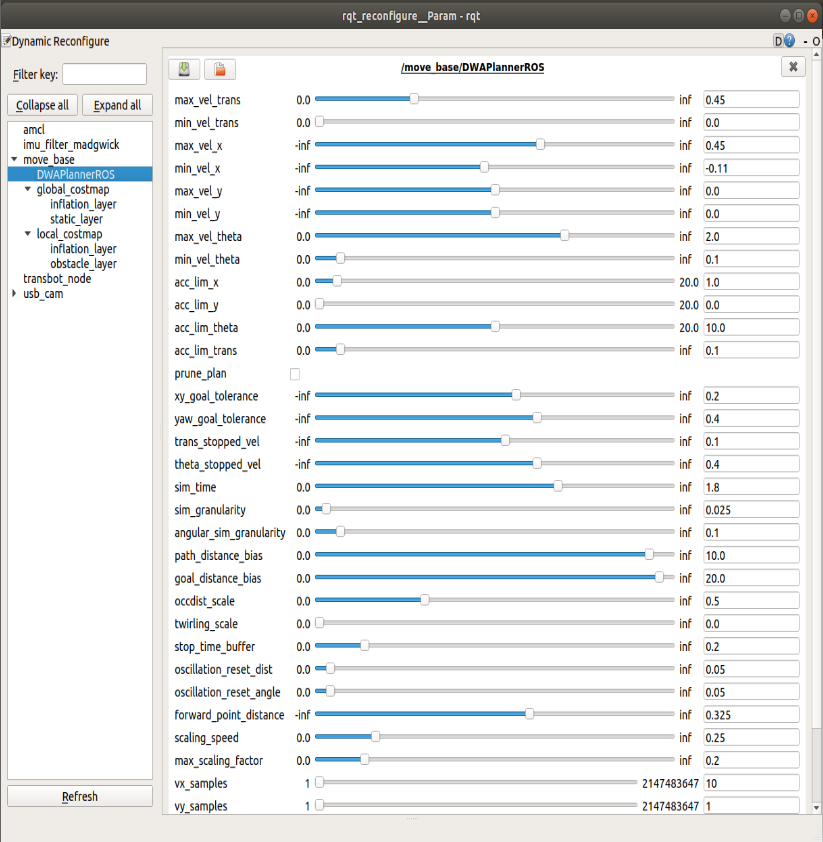
7.1.3、Dynamic parameter adjustment
xxxxxxxxxxrosrun rqt_reconfigure rqt_reconfigure
You can check the relationship between the node and the tf tree
xxxxxxxxxxrqt_graphrosrun rqt_tf_tree rqt_tf_tree
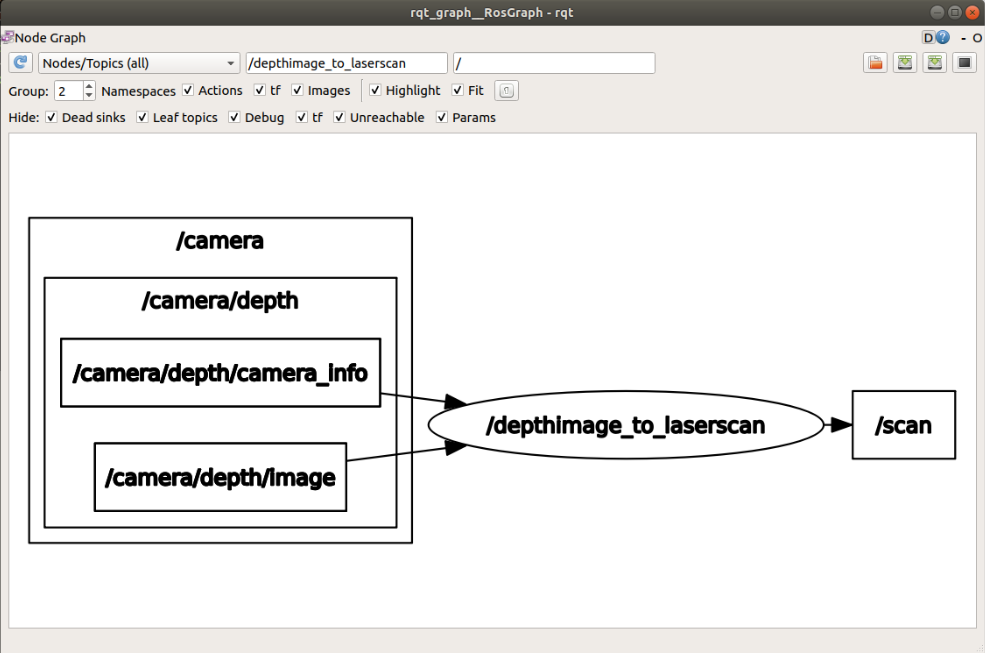
7.1.4、2D navigation by depth mapping alone
Start the driver reference【7.1.1】# Astra + Transbot; the command for starting the map is the same as【7.1.1】.
The function package depthimage_to_laserscan is mainly used to convert the depth image into lidar data. Its mapping function is the same as that of lidar.
Note: The scanning range of the depth camera is not 360°.
xxxxxxxxxxrqt_graph
7.2、navigation
7.2.1、Introduction
navigation is a 2D navigation obstacle avoidance function package of ROS.
7.2.2、Setting tf
The navigation function requires the robot to use tf to publish information about the relationship between coordinate systems.
Example: Lidar
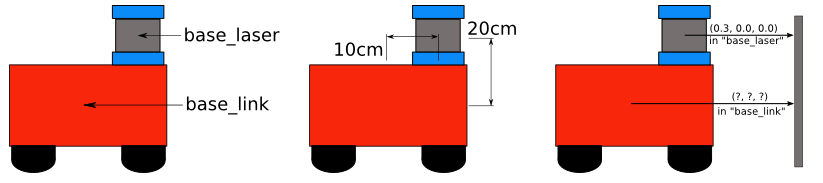
If we know that the lidar is installed at 10 cm and 20 cm above the center point of the mobile base.
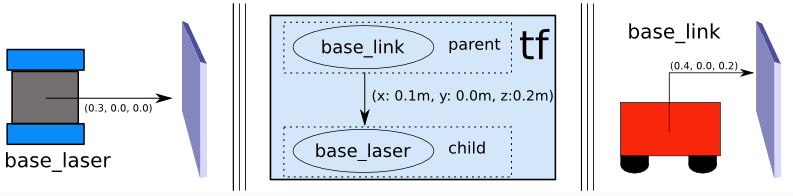
This gives us the translation offset that associates the "base_link" frame with the "base_laser" frame.
Specifically, we know that to get data from the "base_link" coordinate system to the "base_laser" coordinate system, we must apply the translation of (x: 0.1m, y: 0.0m, z: 0.2m) and move from the "base_laser" frame To the "base_link" frame, we must apply the opposite translation (x: -0.1m, y: 0.0m, z: -0.20m).
7.3、move_base
7.3.1、Introduction
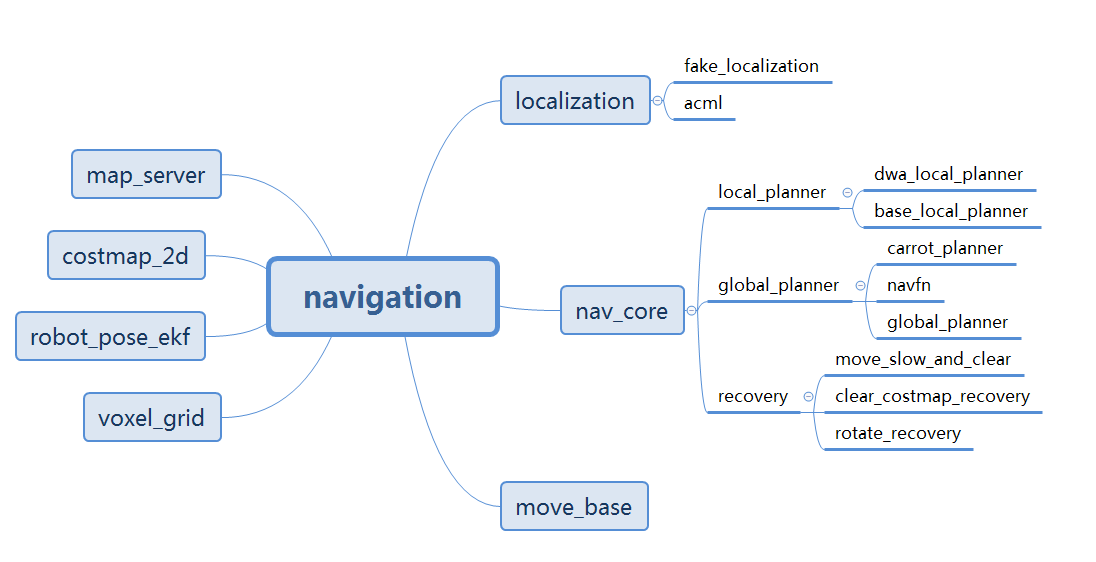
move_base provides the configuration, operation, and interactive interface of ROS navigation.
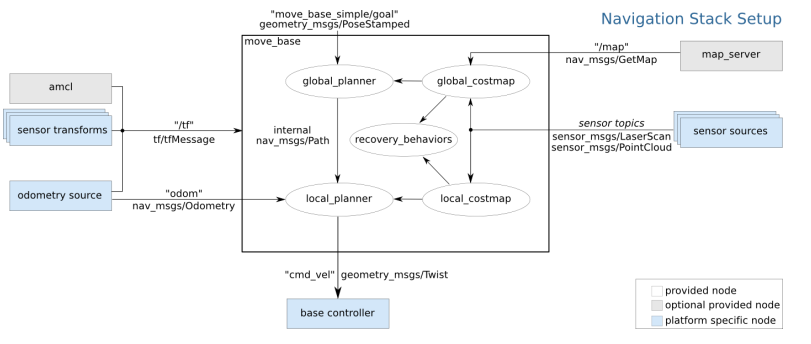
Realize the robot navigation function, it must be configured in a specific way, as shown in the figure above.
- White components are required components that have been implemented,
- Gray components are optional components that have been implemented,
- Blue component must be created for each robot platform.
7.3.2、move_base communication mechanism
1)Action
The move_base node provides an implementation of SimpleActionServer, which receives the target containing the geometry_msgs/PoseStamped message.
You can directly communicate with the move_base node through ROS, but if you are concerned about tracking the status of the target, it is recommended to use SimpleActionClient to send the target to move_base.
| Name | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| move_base/goal | move_base_msgs/MoveBaseActionGoal | move_base subscription will reach the target point. |
| move_base/cancel | actionlib_msgs/GoalID | move_base subscription cancels a request for a specific target |
| move_base/feedback | move_base_msgs/MoveBaseActionFeedback | publish contains the current position of the chassis. |
| move_base/status | actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray | publish the status information of the process of moving to the target point. |
| move_base/result | move_base_msgs/MoveBaseActionResult | post the final result of the move. |
2)topic
| Name | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| move_base_simple/goal | geometry_msgs/PoseStamped | Provides a non-action interface for not paying attention to the execution state of the tracking target. The move_base subscription will reach the target point. |
| cmd_vel | geometry_msgs/Twist | Release the speed of the car. |
3)servies
| Name | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| make_plan | nav_msgs/GetPlan | Allow external users to request a plan for a given posture from move_base without causing move_base to execute the plan. |
| clear_unknown_space | std_srvs/Empty | Allow external users to notify move_base to clear the unknown space around the robot. This is very useful when the costmaps of move_base are stopped for a long period of time and then restarted at a new location in the environment. |
| clear_costmaps | std_srvs/Empty | Allow external users to tell move_base to remove obstacles in the cost map used by move_base. This may cause the robot to hit something, so be careful when using it |
4)Parameter configuration
move_base_params.yaml
x# Set the plugin name of the global path planner for move_base#base_global_planner: "navfn/NavfnROS"base_global_planner: "global_planner/GlobalPlanner"#base_global_planner: "carrot_planner/CarrotPlanner"# Set the plugin name of the local path planner of move_base#base_local_planner: "teb_local_planner/TebLocalPlannerROS" # Implement DWA (Dynamic Window Method) local planning algorithmbase_local_planner: "dwa_local_planner/DWAPlannerROS" # Realize an online optimized local trajectory planner# Recovery behaviorrecovery_behaviors:- name: 'conservative_reset'type: 'clear_costmap_recovery/ClearCostmapRecovery'#- name: 'aggressive_reset'# type: 'clear_costmap_recovery/ClearCostmapRecovery'#- name: 'super_reset'# type: 'clear_costmap_recovery/ClearCostmapRecovery'- name: 'clearing_rotation'type: 'rotate_recovery/RotateRecovery'#- name: 'move_slow_and_clear'#type: 'move_slow_and_clear/MoveSlowAndClear'# Frequency of sending commands to the robot chassis cmd_velcontroller_frequency: 10.0 #default:20.0# The time that the path planner waits for a valid control command before the space cleanup operation is executedplanner_patience: 5.0 #default:5.0# Time the controller waits for a valid control command before the space clearing operation is executedcontroller_patience: 15.0 #default:15.0# Use this parameter only when the default recovery behavior is used for move_base.conservative_reset_dist: 3.0 #3.0,# Whether to enable move_base recovery behavior to try to clear space.recovery_behavior_enabled: true# Whether the robot uses in-situ rotation to clean up the space, this parameter is only used when the default recovery behavior is used.clearing_rotation_allowed: true# When move_base enters the inactive state, whether to disable the costmap of the nodeshutdown_costmaps: false #false# Allowed shock time before performing the recovery operation, 0 means never timeoutoscillation_timeout: 10.0 #0.0# The robot needs to move this distance before it can be considered as having no vibration. Reset timer parameters after movingoscillation_distance: 0.2 #0.5# The global path planner cycle rate.planner_frequency: 5.0 #0.0# The number of planned retries allowed before performing the recovery action. The value -1.0 corresponds to unlimited retries.max_planning_retries: -1.0
7.3.3、Recovery Behavior
1)Introduction
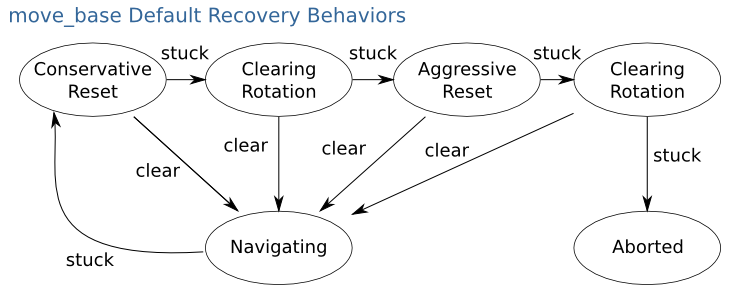
- conservative reset:Recover conservatively.
- clearing rotation:Rotate to clear.
- aggressive reset:Actively recover.
- aborted:Aborted.
2) Related feature packs
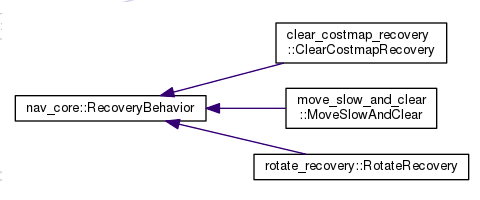
In the navigation function package set, there are 3 packages related to the recovery mechanism. They are: clear_costmap_recovery, move_slow_and_clear, rotate_recovery.
Three classes are defined in these three packages, all of which inherit the interface specifications in nav_core.
4、costmap_params
The navigation function uses two cost maps to store obstacle information.
7.4.1、costmap_common
Cost map public parameter configuration costmap_common_params.yaml
xxxxxxxxxxobstacle_range: 2.5raytrace_range: 3.0footprint: [[x0, y0], [x1, y1], ... [xn, yn]]# robot_radius: ir_of_robotinflation_radius: 0.55
observation_sources: laser_scan_sensor point_cloud_sensor
laser_scan_sensor: {sensor_frame: frame_name, data_type: LaserScan, topic: topic_name, marking: true, clearing: true}
point_cloud_sensor: {sensor_frame: frame_name, data_type: PointCloud, topic: topic_name, marking: true, clearing: true}
7.4.2、global_costmap
Global cost map parameter configuration global_costmap_params.yaml
xxxxxxxxxxglobal_costmap: global_frame: /map robot_base_frame: base_link update_frequency: 5.0 static_map: true
7.4.3、local_costmap
Local cost map parameter configuration local_costmap_params.yaml
xxxxxxxxxxlocal_costmap: global_frame: odom robot_base_frame: base_link update_frequency: 5.0 publish_frequency: 2.0 static_map: false rolling_window: true width: 6.0 height: 6.0 resolution: 0.05
7.4.4、costmap_2D
1)Introduction
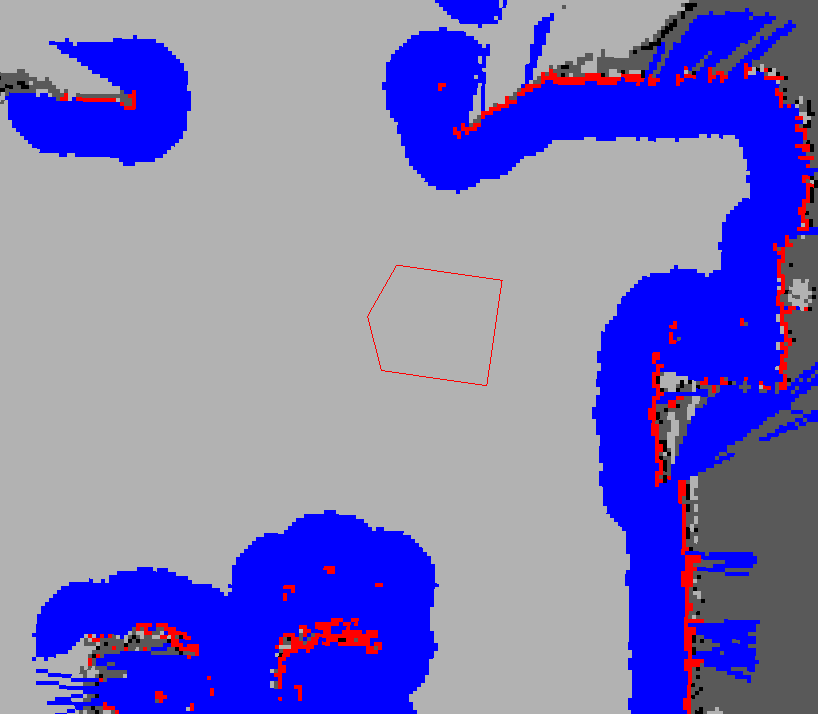
- Red represents obstacles in the cost map.
- Blue means that the robot is inscribed with an obstacle with an expanding radius,
- Red polygon represents the footprint of the robot.
- In order for the robot to avoid collisions, the outer shell of the robot must never intersect the red cell, and the center point of the robot must never intersect the blue cell.
7.5、planner_params
7.5.1、global_planner
global_planner_params.yaml
xxxxxxxxxxGlobalPlanner: allow_unknown: false default_tolerance: 0.2 visualize_potential: false use_dijkstra: true use_quadratic: true use_grid_path: false old_navfn_behavior: false lethal_cost: 253 neutral_cost: 50 cost_factor: 3.0 publish_potential: true orientation_mode: 0 orientation_window_size: 1
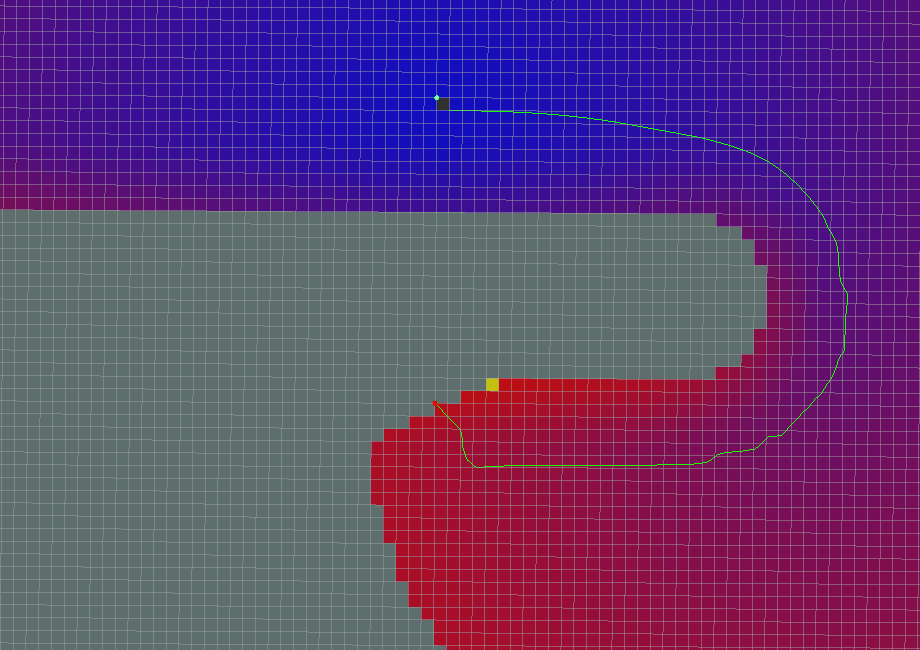
Global path planning algorithm renderings
- All parameters are default values
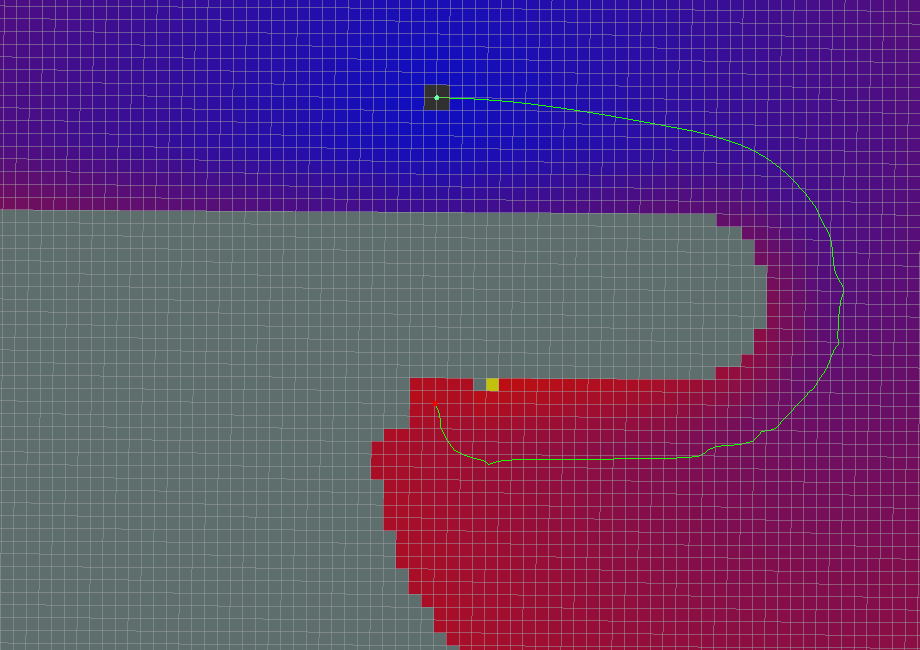
- use_grid_path=True
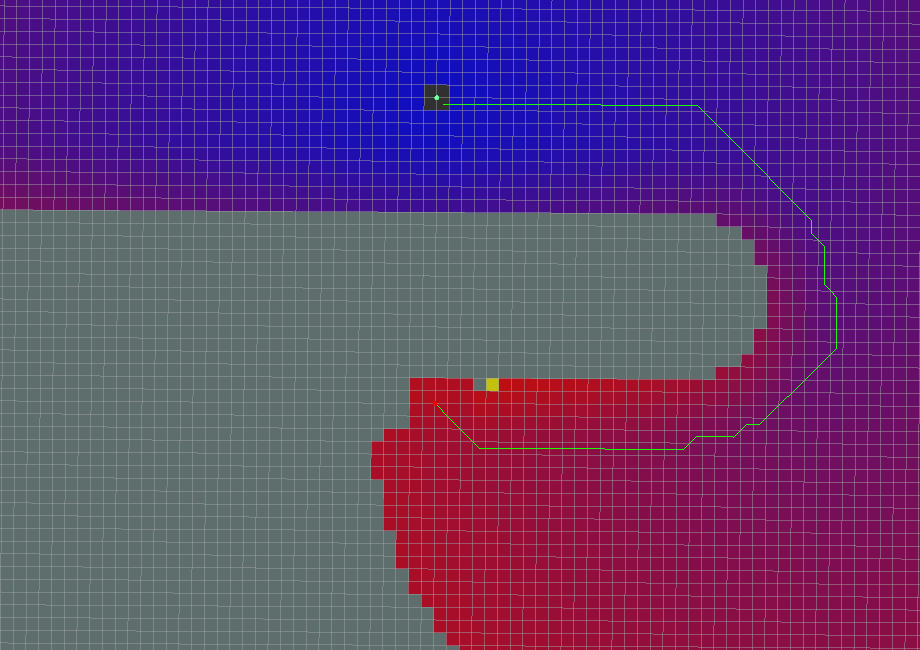
- use_quadratic=False
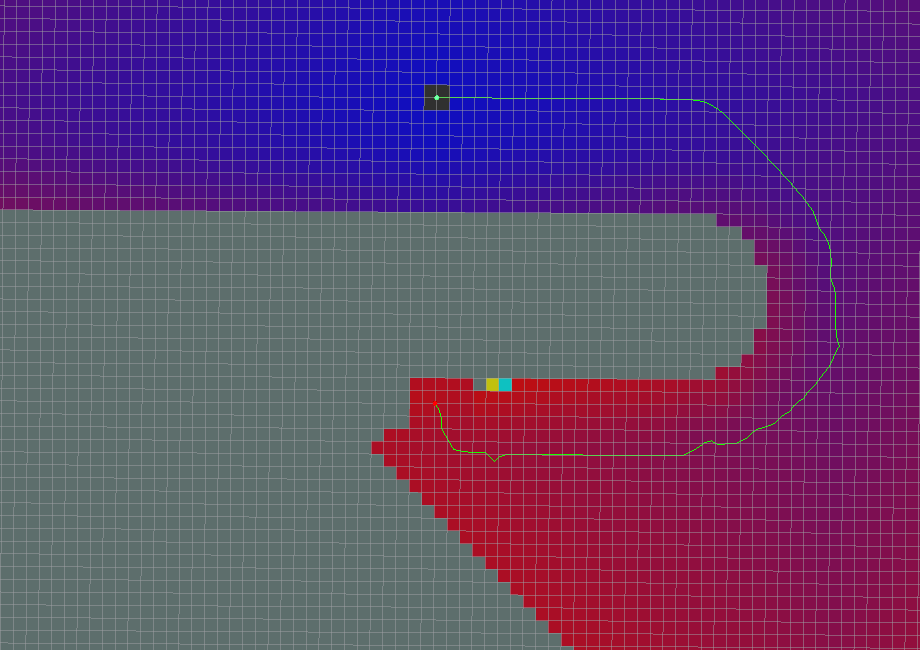
- use_dijkstra=False
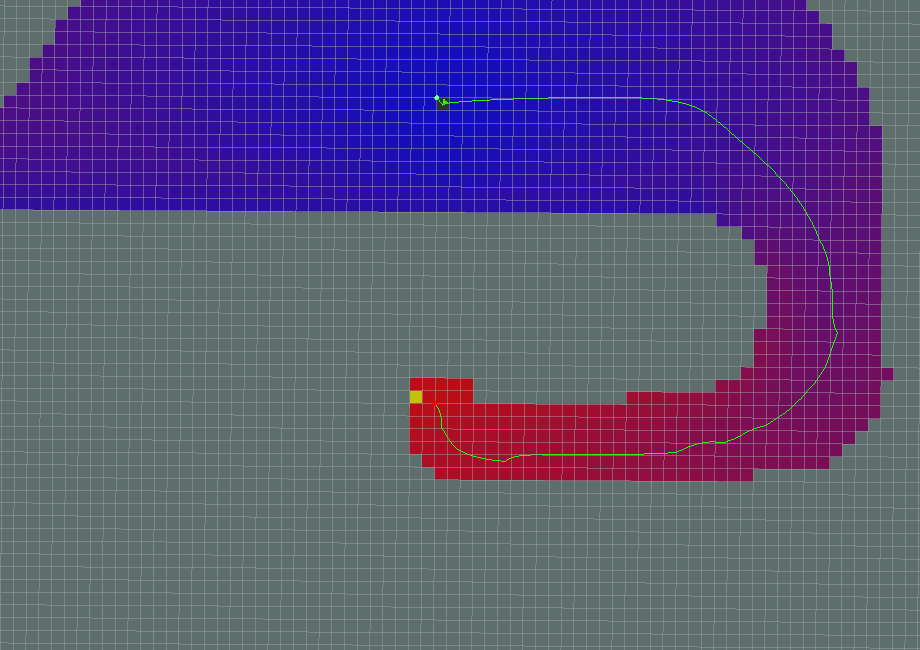
- Dijkstra
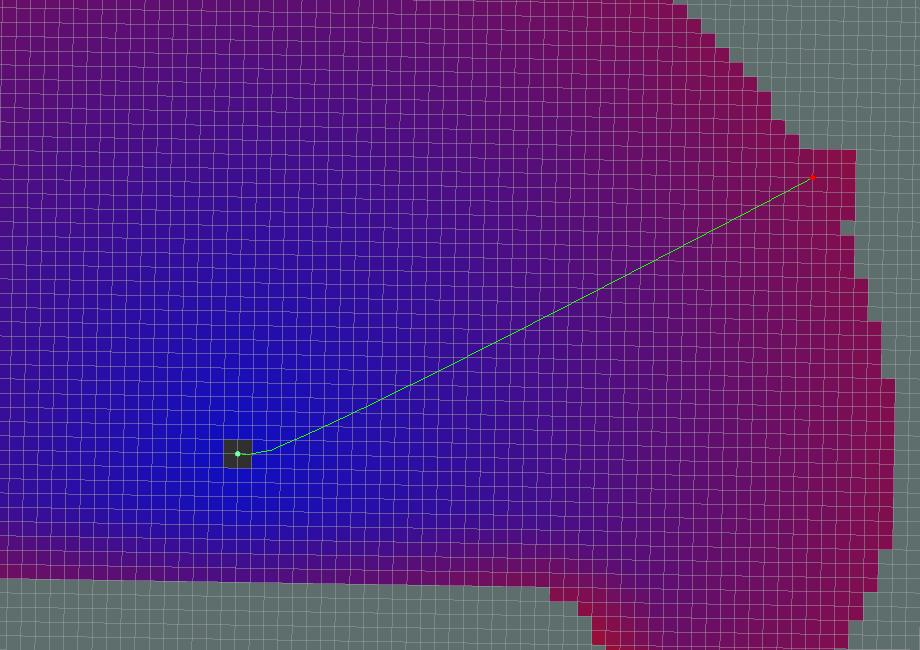
- A*
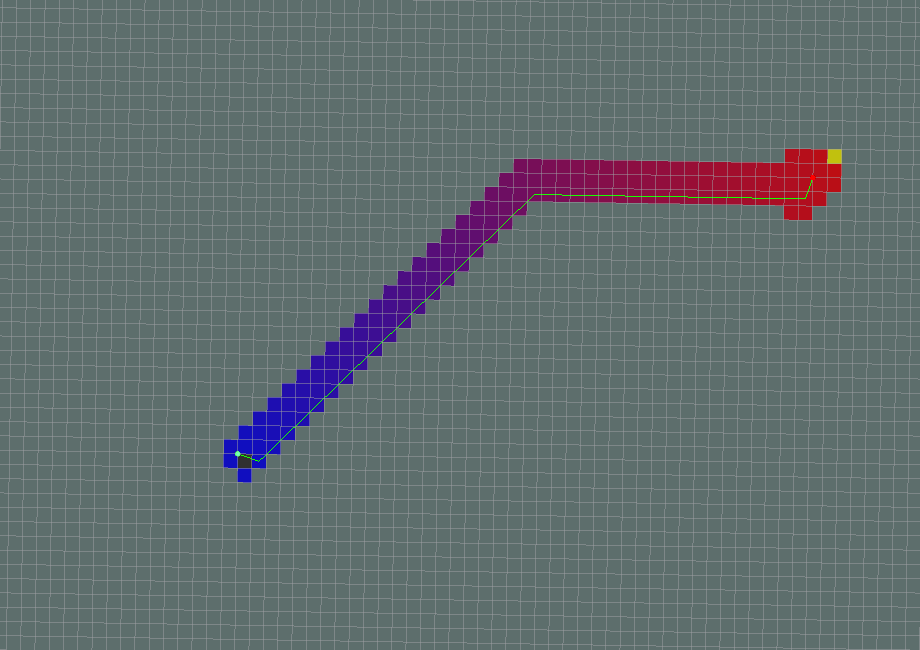
- old_navfn_behavior=True
If it appears at the very beginning:
xxxxxxxxxx[ERROR] [1611670223.557818434, 295.312000000]: NO PATH![ERROR] [1611670223.557951973, 295.312000000]: Failed to get a plan from potential when a legal potential was found. This shouldn't happen.
7.5.2、local_planner
nav_core::BaseLocalPlanner provides an interface for local path planners used in navigation.
xxxxxxxxxxDWAPlannerROS:# Robot Configuration Parameters acc_lim_x: 2.5 acc_lim_y: 2.5 acc_lim_th: 3.2 max_vel_trans: 0.55 min_vel_trans: 0.1 max_vel_x: 0.55 min_vel_x: 0.0 max_vel_y: 0.1 min_vel_y: -0.1 max_rot_vel: 1.0 min_rot_vel: 0.4 # Goal Tolerance Parameters yaw_goal_tolerance: 0.05 xy_goal_tolerance: 0.10 latch_xy_goal_tolerance: false# Forward Simulation Parameters sim_time: 2.0 sim_granularity: 0.025 vx_samples: 6 vy_samples: 1 vth_samples: 20 controller_frequency: 5.0# Trajectory Scoring Parameters path_distance_bias: 90.0 # 32.0 goal_distance_bias: 24.0 # 24.0 occdist_scale: 0.3 # 0.01 forward_point_distance: 0.325 # 0.325 stop_time_buffer: 0.2 # 0.2 scaling_speed: 0.20 # 0.25 max_scaling_factor: 0.2 # 0.2 publish_cost_grid: false# Oscillation Prevention Parameters oscillation_reset_dist: 0.05 # default 0.05# Global Plan Parameters prune_plan: false
teb_local_planner_params.yaml
xxxxxxxxxxTebLocalPlannerROS:# Miscellaneous Parameters map_frame:odom odom_topic: odom # Robot acc_lim_x: 0.5 acc_lim_theta: 0.5 max_vel_x: 0.4 max_vel_x_backwards: 0.2 max_vel_theta: 0.3 min_turning_radius: 0.0 footprint_model: type: "point"# GoalTolerance xy_goal_tolerance: 0.2 yaw_goal_tolerance: 0.1 free_goal_vel: False# Trajectory dt_ref: 0.3 dt_hysteresis: 0.1 min_samples: 3 global_plan_overwrite_orientation: True allow_init_with_backwards_motion: False max_global_plan_lookahead_dist: 3.0 global_plan_viapoint_sep: -1 global_plan_prune_distance: 1 exact_arc_length: False feasibility_check_no_poses: 5 publish_feedback: False # Obstacles min_obstacle_dist: 0.25 inflation_dist: 0.6 include_costmap_obstacles: True costmap_obstacles_behind_robot_dist: 1.5 obstacle_poses_affected: 15 dynamic_obstacle_inflation_dist: 0.6 include_dynamic_obstacles: True costmap_converter_plugin: "" costmap_converter_spin_thread: True costmap_converter_rate: 5# Optimization no_inner_iterations: 5 no_outer_iterations: 4 optimization_activate: True optimization_verbose: False penalty_epsilon: 0.1 obstacle_cost_exponent: 4 weight_max_vel_x: 2 weight_max_vel_theta: 1 weight_acc_lim_x: 1 weight_acc_lim_theta: 1 weight_kinematics_nh: 1000 weight_kinematics_forward_drive: 1 weight_kinematics_turning_radius: 1 weight_optimaltime: 1 # must be > 0 weight_shortest_path: 0 weight_obstacle: 100 weight_inflation: 0.2 weight_dynamic_obstacle: 10 weight_dynamic_obstacle_inflation: 0.2 weight_viapoint: 1 weight_adapt_factor: 2# Parallel Planning enable_homotopy_class_planning: True enable_multithreading: True max_number_classes: 4 selection_cost_hysteresis: 1.0 selection_prefer_initial_plan: 0.9 selection_obst_cost_scale: 100.0 selection_alternative_time_cost: False roadmap_graph_no_samples: 15 roadmap_graph_area_width: 5 roadmap_graph_area_length_scale: 1.0 h_signature_prescaler: 0.5 h_signature_threshold: 0.1 obstacle_heading_threshold: 0.45 switching_blocking_period: 0.0 viapoints_all_candidates: True delete_detours_backwards: True max_ratio_detours_duration_best_duration: 3.0 visualize_hc_graph: False visualize_with_time_as_z_axis_scale: False# Recovery shrink_horizon_backup: True shrink_horizon_min_duration: 10 oscillation_recovery: True oscillation_v_eps: 0.1 oscillation_omega_eps: 0.1 oscillation_recovery_min_duration: 10 oscillation_filter_duration: 107.6、AMCL
7.6.1、Introduction
Adaptive Monte Carlo localization is a probabilistic positioning system for two-dimensional mobile robots.