Control Serial Servo
Control Serial Servo 1. Experimental goal 2. Experiment preparation 3. Experimental effect 4. Program source code
1. Experimental goal
Control the movement of the serial port servo on the Rosmaster, control the serial port servo through the slider, and read the current angle value of the serial port servo.
2. Experiment preparation
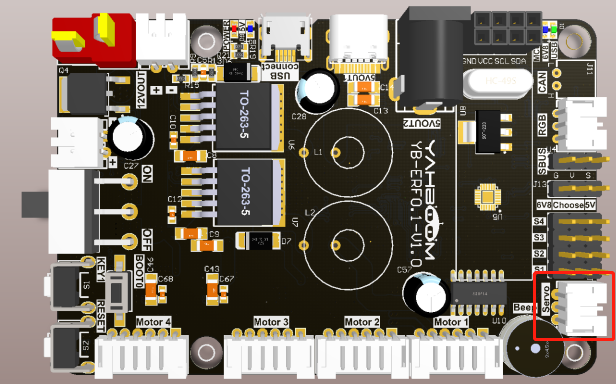
The position of the red box in the picture below is the interface of the serial servo. This interface has the function of anti-reverse connection. There is no need to worry about the problem of reverse insertion when using Rosmaster's servo cable.
For more information about serial servos, please check the following webpages:
The Rosmaster_Lib library functions needed to control the serial port servos have the following contents:
set_uart_servo_angle ( s_id , s_angle , run_time = 500 )
Parameter explanation: Control a serial servo, s_id: corresponding ID number: 1~6, run_time controls the running time of the servo, within the valid range, the smaller the time, the faster the servo rotates, the unit is milliseconds, and the minimum value is 0.
s_angle: corresponds to the angle value of the steering gear. The range is different according to the different s_id, 1~4:[0, 180], 5:[0, 270], 6:[30, 180]
Return value: None.
xxxxxxxxxxset_uart_servo_angle_array ( angle_s =[ 90 , 90 , 90 , 90 , 90 , 180 ], run_time = 500 )
Parameter explanation: control six serial servos, angle_s controls the angle value of six servos, the control range is the same as the above range, run_time controls the running time of the servos, within the effective range, the smaller the time, the faster the servos rotate. The unit is milliseconds, and the minimum value is 0.
Return value: None.
xxxxxxxxxxset_uart_servo_torque(enable)
Parameter explanation: close/open the torque force of the serial port servo, enable=[0, 1].
enable=0: Turn off the torque force of the steering gear, you can turn the steering gear by hand, but the command cannot control the rotation; enable=1: Turn on the torque force, the command can control the rotation, but you cannot turn the steering gear by hand.
Return value: none
xxxxxxxxxxget_uart_servo_angle(s_id)
Parameter explanation: read the angle of the serial servo, s_id indicates the ID number of the servo to be read, s_id=[1-6]
Return value: Returns the current angle of the input ID, and returns -1 for read errors.
xxxxxxxxxxget_uart_servo_angle_array()
Parameter explanation: read the angles of six servos at one time [xx, xx, xx, xx, xx, xx], if a servo is wrong, the digit is -1
Return value: [angle_1, angle_2, angle_3, angle_4, angle_5, angle_6].
3. Experimental effect
Check out the course accompanying video.
4. Program source code
Power on the Rosmaster robot, and open the browser of the Jetson Nano or remote computer to enter the Jupyter lab editor.
Reference code path: Rosmaster/Samples/9.arm_servo.ipynb