ROS application routine
ROS application routine1. ROS environment installation2. Bind the port3. IMU Ros package usage3.1 Compilation Workspace3.2 Modify parameter configuration3.3 Running the visual interface
1. ROS environment installation
This routine assumes that the system has already installed the ROS development environment by default. If the ROS environment is not installed, please install the ROS environment by yourself before running this routine.
Please run the corresponding command in the terminal
If you are using ubuntu 16.04, ROS kinetic, python2:
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-imu-tools ros-kinetic-rviz-imu-pluginsudo apt-get install python-visualIf you are using ubuntu 18.04, ROS Melodic, python2:
xxxxxxxxxxsudo apt-get install ros-melodic-imu-tools ros-melodic-rviz-imu-pluginIf you are using ubuntu 20.04, ROS Noetic, python3:
xxxxxxxxxxsudo apt-get install ros-noetic-imu-tools ros-noetic-rviz-imu-pluginpip3 install pyserialInstall ROS serial driver
xxxxxxxxxxsudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-serialThe following content takes ubuntu 18.04, ROS Melodic version as an example.
2. Bind the port
First connect the IMU module to the USB port of the computer, and then copy the sample program ros_imu_ws.zip in the data to the user directory. Run the following command to unzip:
xxxxxxxxxxunzip ros_imu_ws.zipcd ~/ros_imu_wssudo bash bind_usb.shRestart the computer to make the bound port take effect
xxxxxxxxxxsudo rebootAfter restarting, check whether the port has been bound.
xxxxxxxxxxll /dev/imu_usb
Note: This method is only suitable for the case that the external USB device has only one CP2102 serial port chip. If there are multiple USB devices driven by CP2102, please do not use this binding method.
3. IMU Ros package usage
3.1 Compilation Workspace
Open a command terminal and run the following command:
xxxxxxxxxx cd ~/ros_imu_ws/ catkin_make -j cd src/scripts/ sudo chmod 777 *.py echo "source ~/ros_imu_ws/devel/setup.sh" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc3.2 Modify parameter configuration
The baud rate is set according to the actual use. The default baud rate is 9600. If the user modifies the baud rate through the host computer, it needs to be modified accordingly to the modified baud rate.
Enter the workspace directory src/launch,
Open the configuration parameters in the rviz_and_imu.launch file.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros_imu_ws/src/launchvim rviz_and_imu.launch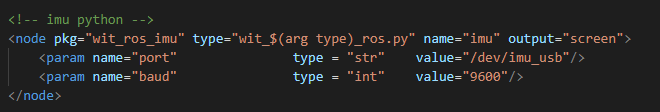
If you have already operated 2. Bind the port, skip to 3.3 to run the visual interface. If the 2. Binding port operation is not performed, you need to manually modify the USB device number corresponding to the module. The specific operations are as follows:
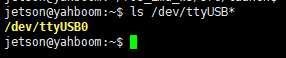
- Check the USB port number. Connect the inertial navigation module to the USB port of the computer through the USB-typeC data cable, and enter the following command in the terminal to detect the device port
xxxxxxxxxxls /dev/ttyUSB*If the computer is connected to multiple USB devices, you can check the port once without inserting the inertial navigation module.
After inserting the inertial navigation module, check the port again, and compare the port numbers printed out twice before and after.
The second time, the extra port number is the USB device number of the inertial navigation module.
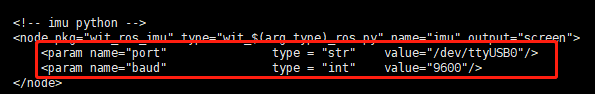
Modify parameter configuration. Parameters that need to be modified include the USB port number and baud rate.
Enter the workspace directory src/launch,
Open the configuration parameters in the rviz_and_imu.launch file.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros_imu_ws/src/launchvim rviz_and_imu.launchThe device number is /dev/ttyUSB0 (the code uses /dev/ttyUSB0 by default).
If the number recognized by your computer is not USB0, change it to the number recognized by your computer.
Note: If multiple USB serial devices are connected, it may be necessary to manually check and modify the corresponding serial number every time the device is turned on.
Save and exit after modification is complete.
If you are prompted that you do not have the USB permission, enter the following command in the terminal to increase the permission, or add the current user to the USB device permission list.
xxxxxxxxxxsudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0
3.3 Running the visual interface
- Open the terminal, run the launch file, pay attention to open it on the actual desktop, or VNC remote, not in the SSH remote terminal.
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch wit_ros_imu rviz_and_imu.launch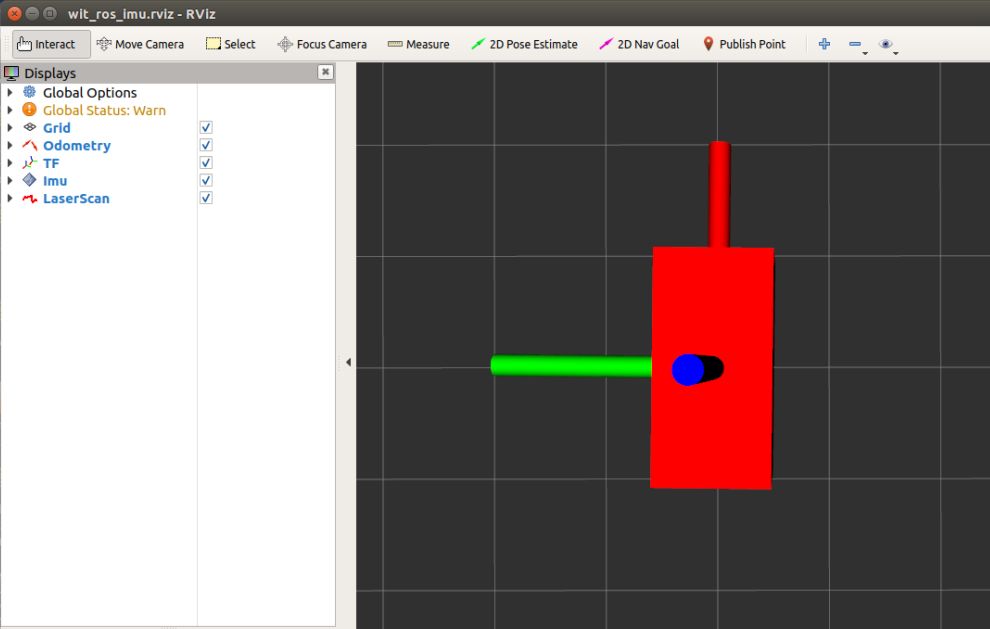
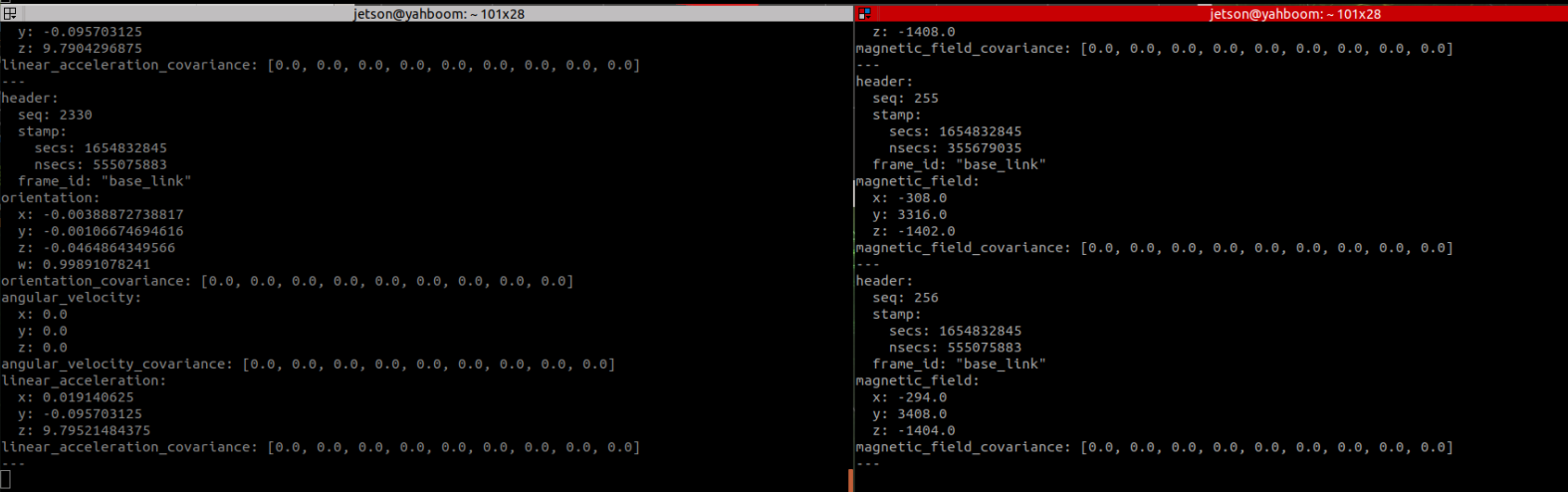
Open two new terminals and enter the following two lines of commands respectively to view the data.
xxxxxxxxxxrostopic echo /wit/imurostopic echo /wit/mag As shown below. Information output byrostopic echo