7.Client
In ROS communication, in addition to topic communication, there is also a type of service communication. Services include both client and server, where the client requests the service and the server provides the service. This section focuses on the client and explains how C++and Python can implement the client.
7.1 Preparation work
7.1.1 Establishing a Function Package
- Switch to~/catkin_ In the ws/src directory,
catkin_create_pkg learning_server std_msgs rospy roscpp geometry_msgs turtlesim
- Switch to~/catkin_ Under the ws directory,
xxxxxxxxxxcatkin_make
7.2. C++Language Implementation
7.2.1 Implementation steps
- Initialize ROS node
- Create handle
- Create a Client instance
- Initialize and publish service request data
- Wait for the response result after the server processes it
7.2.2. Switch to~/catkin_ ws/src/learning_ Create a new. cpp file under the server/src directory and name it a_ new_ Turtle, paste the following code inside
a_new_turtle.cpp
x#include <ros/ros.h>#include <turtlesim/Spawn.h>int main(int argc, char** argv){ros::init(argc, argv, "a_nes_turtle");// 初始化ROS节点ros::NodeHandle node;ros::service::waitForService("/spawn"); // 等待/spawn服务ros::ServiceClient new_turtle = node.serviceClient<turtlesim::Spawn>("/spawn");//创建一个服务客户端,连接名为/spawn的服务// 初始化turtlesim::Spawn的请求数据turtlesim::Spawn new_turtle_srv;new_turtle_srv.request.x = 6.0;new_turtle_srv.request.y = 8.0;new_turtle_srv.request.name = "turtle2";// 请求服务传入xy位置参数以及名字参数ROS_INFO("Call service to create a new turtle name is %s,at the x:%.1f,y:%.1f", new_turtle_srv.request.name.c_str(),new_turtle_srv.request.x,new_turtle_srv.request.y);new_turtle.call(new_turtle_srv);ROS_INFO("Spwan turtle successfully [name:%s]", new_turtle_srv.response.name.c_str());// 显示服务调用结果return 0;};
- Process Flow Chart
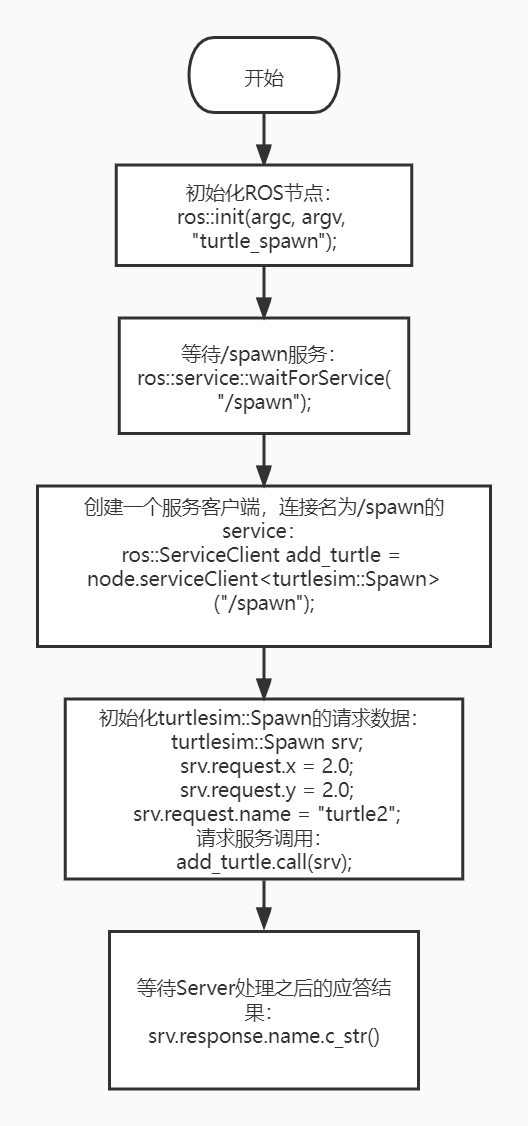
- Configure in CMakelist.txt, under the build area, add the following content
xxxxxxxxxxadd_executable(a_new_turtle src/a_new_turtle.cpp)target_link_libraries(a_new_turtle ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
- Compiling code under workspace directory
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/catkin_wscatkin_makesource devel/setup.bash
- run a program
xxxxxxxxxxroscorerosrun turtlesim turtlesim_noderosrun learning_server a_new_turtle
- Running effect screenshot
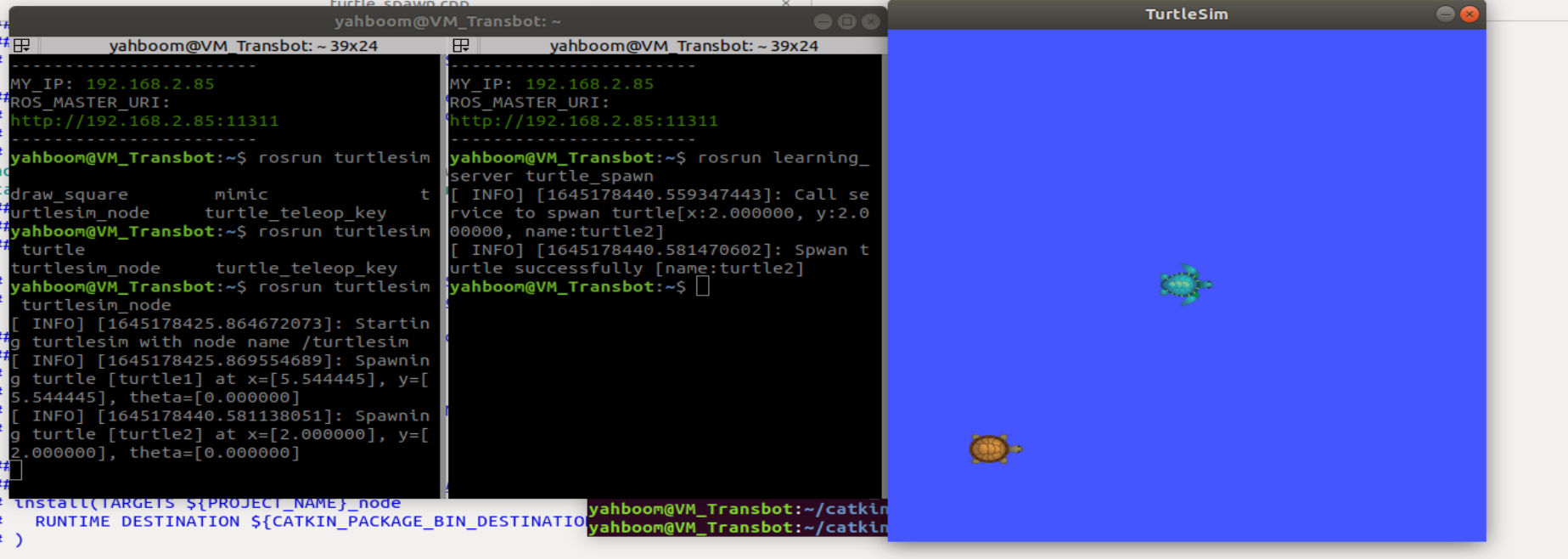
- Program Description
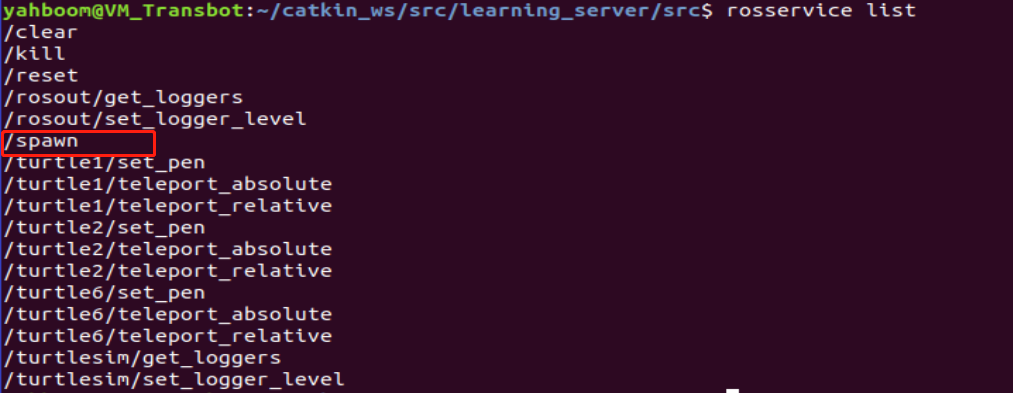
After starting the node of Little Turtle, run a_ new_ The Turtle program will find that there will be another small turtle appearing in the screen, because the turtle's node provides a service/spa wn, which will generate another small turtle Turtle2. To view the services provided by the turtle, you can use the rossservice list command, as shown in the following figure
You can view the parameters required for this service through rossservice info/spa, as shown in the following figure
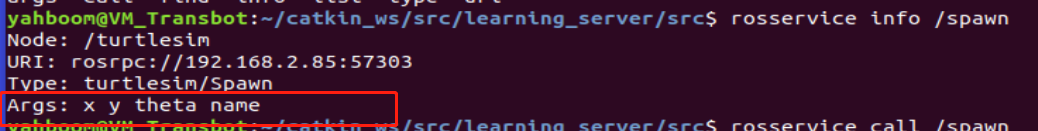
It can be seen that there are four parameters required: x, y, theta, and name, which are in a_ new_ There is initialization in turtle.cpp
xxxxxxxxxxsrv.request.x = 6.0;srv.request.y = 8.0;srv.request.name = "turtle2";
7.3. Python Language Implementation
7.3.1. Switch to~/catkin_ ws/src/learning_ Under the server directory, create a new script folder, cut it in, and create a new py file named a_ new_ Turtle, paste the following code inside
a_new_turtle.py
xxxxxxxxxx#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import sysimport rospyfrom turtlesim.srv import Spawndef turtle_spawn():rospy.init_node('new_turtle')# ROS节点初始化rospy.wait_for_service('/spawn')# 等待/spawn服务try:new_turtle = rospy.ServiceProxy('/spawn', Spawn)response = new_turtle(2.0, 2.0, 0.0, "turtle2")# 输入请求数据return response.nameexcept rospy.ServiceException, e:print "failed to call service : %s"%eif __name__ == "__main__":#服务调用并显示调用结果print "a new turtle named %s." %(turtle_spawn())
- Program flowchart
- run a program
xxxxxxxxxxroscorerosrun turtlesim turtlesim_noderosrun learning_server a_new_turtle.py
- The program operation effect and program description are consistent with the implementation effect of C++. Here, we mainly discuss how Python provides the parameters required for the service,
xxxxxxxxxxresponse = add_turtle(2.0, 2.0, 0.0, "turtle2")
The corresponding parameters are x, y, theta, and name.