3. QR code creation and identification
1. QR codes
1.1 Introduction of QR code
QR code is a two-dimensional bar code, QR from the English "Quick Response" abbreviation, that is, rapid response meaning, from the inventor hopes that the QR code can make its content quickly decoded. QR code not only has large information capacity, high reliability and low cost, but also can represent a variety of text information such as Chinese characters and images, and its security is strong and it is very convenient to use. What's more, the QR code technology is open source.
1.2 Structure of QR code
| Picture | Parsing |
|---|---|
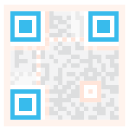 | Positioning markings: Indicate the direction of the QR code. |
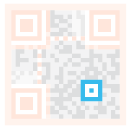 | Alignment markings: If the QR code is large, these additional elements help with positioning. |
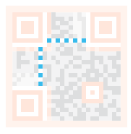 | Timing pattern: From these lines, the scanner can identify how large the matrix is. |
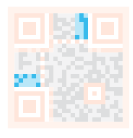 | Version information: This specifies the version number of the QR code being used, there are currently 40 different versions of QR codes. The version numbers used in the sales industry are usually 1-7. |
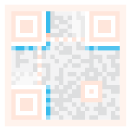 | Format information: The format pattern contains information about fault tolerance and data mask patterns, and makes it easier to scan code. |
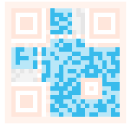 | Data and error correction keys: These schemas hold the actual data. |
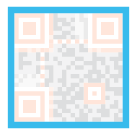 | Quiet zone: This area is very important for the scanner, its role is to separate itself from the surrounding. |
1.3 Features of QR code
The data values in the QR code contain duplicate information (redundant values). Therefore, even if up to 30% of the structure of the QR code is destroyed, the readability of the QR code is not affected. The QR code has a storage space of up to 7089 bits or 4296 characters, including punctuation and special characters, which can be written into the QR code. In addition to numbers and characters, you can encode words and phrases, such as web addresses. As more data is added to the QR code, the code size increases and the code structure becomes more complex.
1.4. Creation and recognition of QR code
1) Create a QR code
- Source path
~/orbbec_ws/src/yahboomcar_visual/simple_qrcode/QRcode_Create.py
Installation package
xxxxxxxxxxpython3 -m pip install qrcode pyzbarsudo apt-get install libzbar-devStartup
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/orbbec_ws/src/yahboomcar_visual/simple_qrcodepython QRcode_Create.pyAfter the program is run, it will prompt you to enter the generated content. Enter to confirm the content. As an example of creating a "yahboom" string,
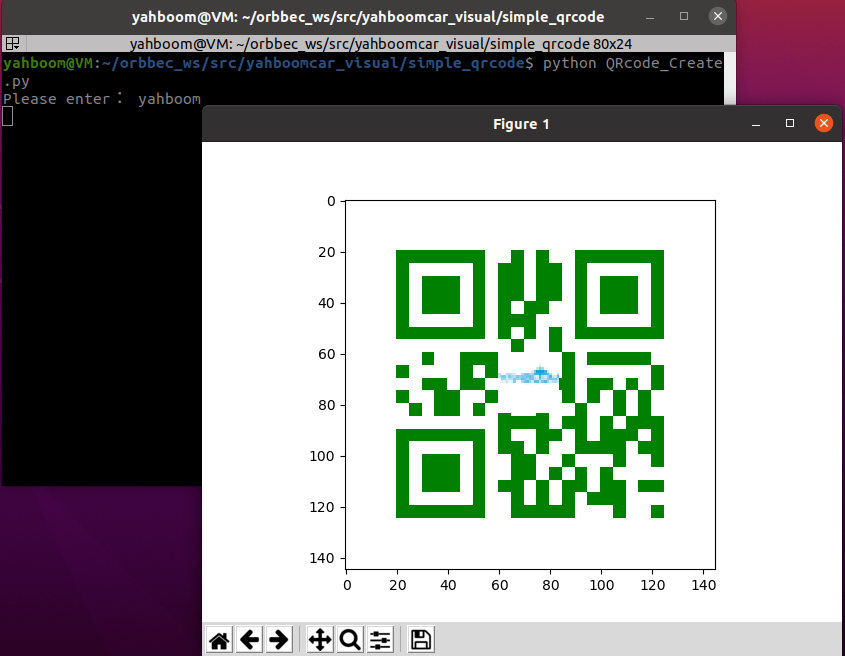
Core source code parsing
xxxxxxxxxx#创建qrcode对象# Create a qrcode objectqr = qrcode.QRCode(version=1,error_correction=qrcode.constants.ERROR_CORRECT_H,box_size=5,border=4,)#各参数含义# Meaning of each parameter'''version:值为1~40的整数,控制二维码的大小(最小值是1,是个12×12的矩阵)。如果想让程序自动确定,将值设置为 None 并使用 fit 参数即可。error_correction:控制二维码的错误纠正功能。可取值下列4个常量。ERROR_CORRECT_L:大约7%或更少的错误能被纠正。ERROR_CORRECT_M(默认):大约15%或更少的错误能被纠正。ROR_CORRECT_H:大约30%或更少的错误能被纠正。box_size:控制二维码中每个小格子包含的像素数。border:控制边框(二维码与图片边界的距离)包含的格子数(默认为4,是相关标准规定的最小值)version: The value is an integer ranging from 1 to 40, which controls the size of the two-dimensional code (the minimum value is 1, which is a 12×12 matrix).If you want the program to determine this automatically, set the value to None and use the fit argument.error_correction: Controls the error correction function of the two-dimensional code. It can take the following four constants.ERROR_CORRECT_L: Approximately 7% or less of errors can be corrected.ERROR_CORRECT_M (default) : Approximately 15% or less of errors can be corrected.ROR_CORRECT_H: About 30% or less of errors can be corrected.box_size: Controls the number of pixels contained in each small box in the QR code.border: Control the number of squares included in the border (the distance between the QR code and the image border) (default is 4, which is the minimum specified by the relevant standard)'''#qrcode二维码添加logo#qrcode Add logo to QR codemy_file = Path(logo_path)if my_file.is_file(): img = add_logo(img, logo_path)#添加数据# Add dataqr.add_data(data)# 填充数据# fill dataqr.make(fit=True)# 生成图片# generate imagesimg = qr.make_image(fill_color="green", back_color="white")
2) Identify the QR code
- Source path
xxxxxxxxxx~/orbbec_ws/src/yahboomcar_visual/yahboomcar_visual/QRcode_Parsing.py
Startup
xxxxxxxxxxros2 launch orbbec_camera gemini2.launch.xmlros2 run yahboomcar_visual QRcode_Parsing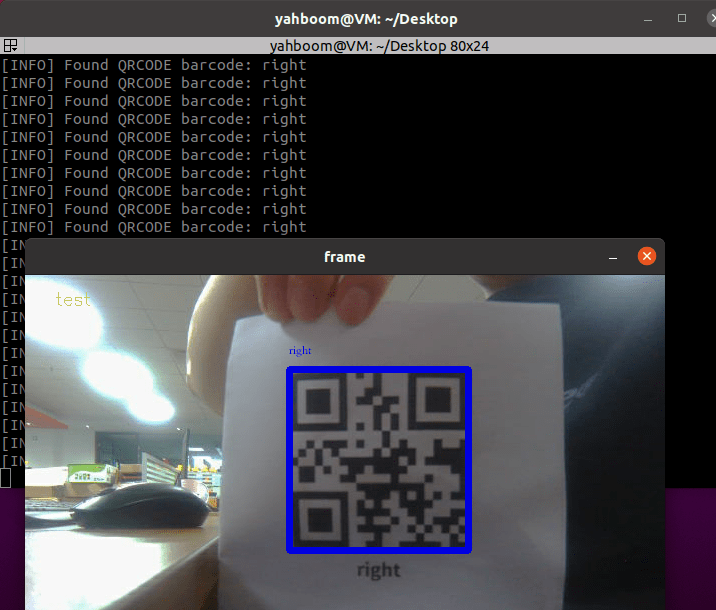
View the node communication diagram
xxxxxxxxxxros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph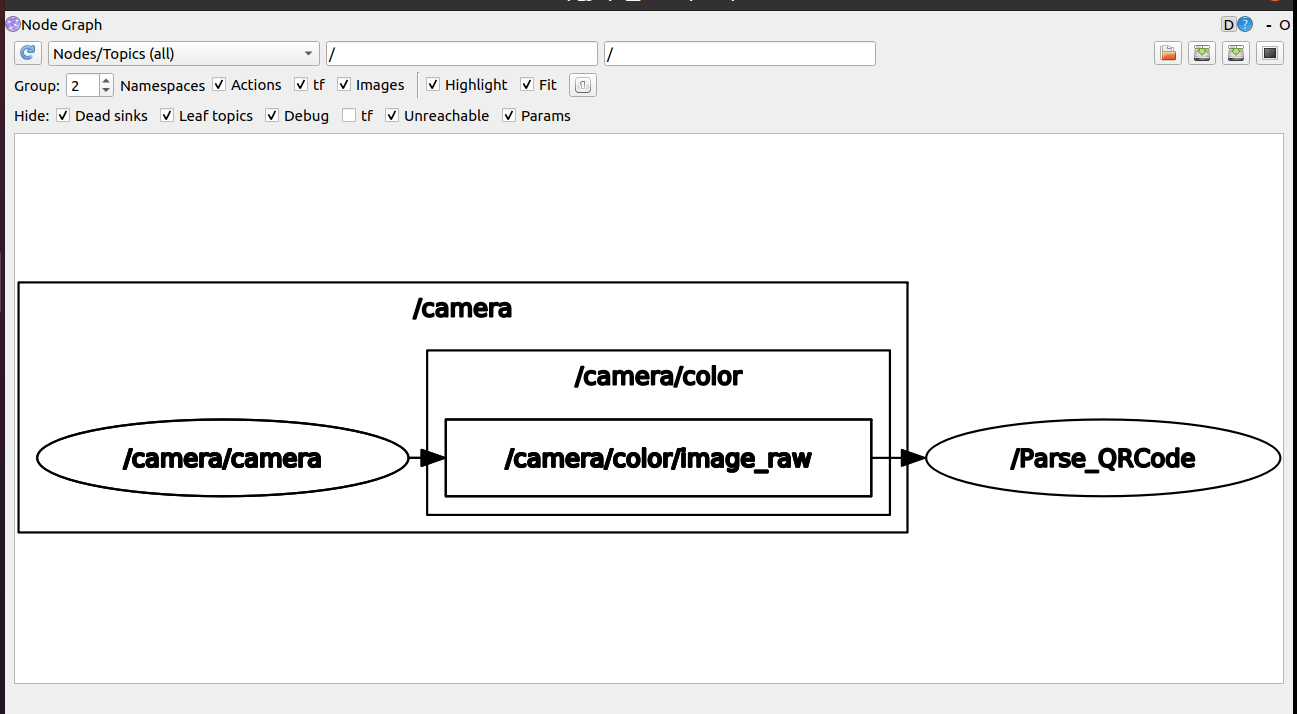
Core source code parsing
xxxxxxxxxx#订阅彩色图像信息# Subscribe to color image informationself.sub_img = self.create_subscription(CamImage,'/camera/color/image_raw',self.handleTopic,100)#在回调函数中把图像数据传递到解析图像函数中# Pass the image data in the callback function to the parsing image functionframe = self.decodeDisplay(frame)#解析图像# Parse the imagedef decodeDisplay(self,image):gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 需要先把输出的中文字符转换成Unicode编码形式# The output Chinese characters need to be converted to Unicode encoding firstbarcodes = pyzbar.decode(gray)for barcode in barcodes:# 提取二维码的边界框的位置# Extract the position of the boundary box of the TWO-DIMENSIONAL code# 画出图像中条形码的边界框# Draw the bounding box for the bar code in the image(x, y, w, h) = barcode.rectcv.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (225, 0, 0), 5)encoding = 'UTF-8'# 画出来,就需要先将它转换成字符串# to draw it, you need to convert it to a stringbarcodeData = barcode.data.decode(encoding)barcodeType = barcode.type# 绘出图像上数据和类型# Draw the data and type on the imagepilimg = Image.fromarray(image)# 创建画笔# create brushdraw = ImageDraw.Draw(pilimg) # 图片上打印 Print on picture# 参数1:字体文件路径,参数2:字体大小# parameter 1: font file path, parameter 2: font sizefontStyle = ImageFont.truetype("/home/yahboom/orbbec_ws/src/yahboomcar_visual/yahboomcar_visual/Block_Simplified.TTF", size=12, encoding=encoding)# # 参数1:打印坐标,参数2:文本,参数3:字体颜色,参数4:字体# Parameter 1: print coordinates, parameter 2: text, parameter 3: font color, parameter 4: fontdraw.text((x, y - 25), str(barcode.data, encoding), fill=(255, 0, 0), font=fontStyle)# # PIL图片转cv2 图片# PIL picture to CV2 pictureimage = np.array(pilimg)# 向终端打印条形码数据和条形码类型# Print barcode data and barcode type to terminalprint("[INFO] Found {} barcode: {}".format(barcodeType, barcodeData))return image
xxxxxxxxxx