3. ROS+Opencv foundation
3. ROS+Opencv foundation 3.1. Overview 3.2. Monocular camera/Raspberry PI CSI camera3.2.1. Start Monocular camera/Raspberry PI CSI camera3.2.2. Start the color map subscription node 3.3、Jetson CSI camera3.3.1. Start Jetson CSI camera3.2.2. Start the color map subscription node
This lesson takes the Astra camera as an example, which is similar to ordinary cameras.
3.1. Overview
Wiki: http://wiki.ros.org/cv_bridge/
Teaching: http://wiki.ros.org/cv_bridge/Tutorials
Source code: https://github.com/ros-perception/vision_opencv.git
Feature pack location: ~/yahboomcar_ws/src/yahboomcar_visual
ROS has already integrated versions above Opencv3.0 during the installation process, so the installation configuration hardly needs to be considered too much. ROS transmits images in its own sensor_msgs/Image message format and cannot directly process images, but the provided [CvBridge] ] Can perfectly convert and be converted image data formats. [CvBridge] is a ROS library, equivalent to a bridge between ROS and Opencv.
Opencv and ROS image data conversion is shown in the following figure:
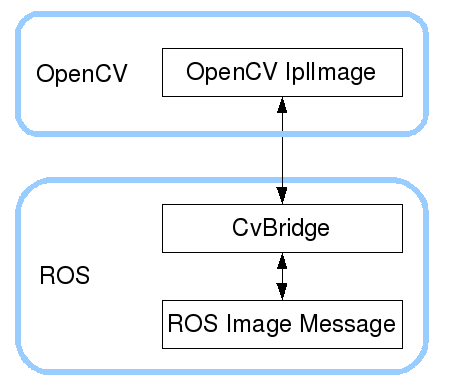
Although the installation configuration does not need to be considered too much, the use environment still needs to be configured, mainly the two files [package.xml] and [CMakeLists.txt]. This function package not only uses [CvBridge], but also needs [Opencv] and [PCL], so it is configured together.
- package.xml
Add the following
x < build_depend > sensor_msgs </ build_depend > < build_export_depend > sensor_msgs </ build_export_depend > < exec_depend > sensor_msgs </ exec_depend >
< build_depend > std_msgs </ build_depend > < build_export_depend > std_msgs </ build_export_depend > < exec_depend > std_msgs </ exec_depend > < build_depend > cv_bridge </ build_depend > < build_export_depend > cv_bridge </ build_export_depend > < exec_depend > cv_bridge </ exec_depend > < exec_depend > image_transport </ exec_depend > [cv_bridge]: Image conversion dependency package.
- CMakeLists.txt
There are many configuration contents in this file. For details, please refer to the source file.
3.2. Monocular camera/Raspberry PI CSI camera
3.2.1. Start Monocular camera/Raspberry PI CSI camera
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch usb_cam usb_cam-test.launchView threads
xxxxxxxxxxrostopic list You can see a lot of topics, just a few commonly used in this section
| topic name | type of data |
|---|---|
| /usb_cam/image_raw | sensor_msgs/Image |
| /usb_cam/image_raw/compressedDepth | sensor_msgs/Image |
| /usb_cam/image_raw/compressed | sensor_msgs/Image |
Check the encoding format of the topic: rostopic echo +[topic]+encoding, for example
xxxxxxxxxxrostopic echo /usb_cam/image_raw/encoding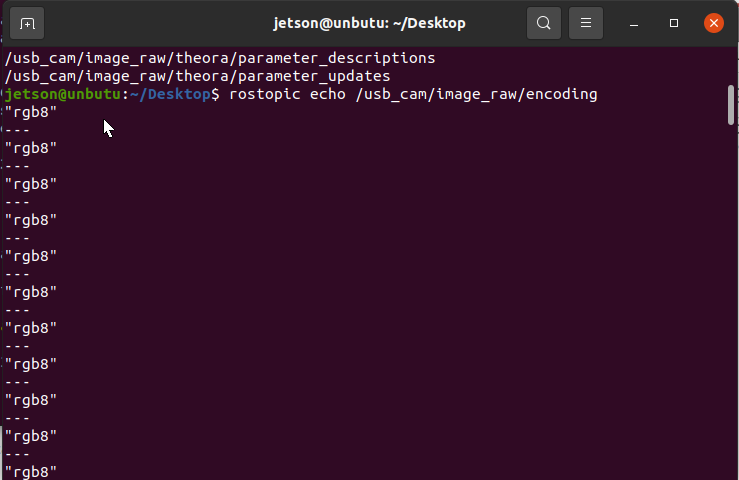
The topic with [compressed] or [compressedDepth] after the topic is a compressed topic. When ROS transmits images, data packets may be lost due to factors such as the network, the running speed of the host, the running memory of the host, and the huge amount of video stream data. off topic. So there is no way, I can only subscribe to the compressed topic. Open two images at the same time to subscribe to different topics for testing. If the device performance is good and the network is also good, there will be no change. Otherwise, you will find that the topics after image compression will be much smoother.
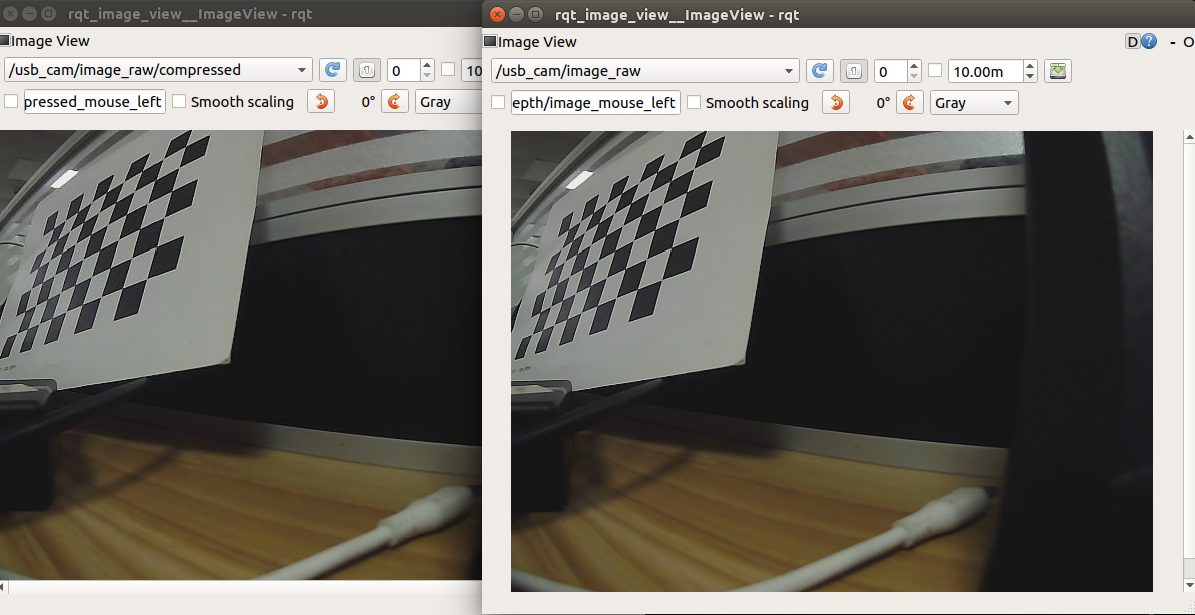
3.2.2. Start the color map subscription node
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch yahboomcar_visual usb_cam_flip.launch In this case, you need to change usb_cam_flip_usb.py to usb_cam_flip.py
py code analysis
Two subscribers and two publishers are created here, one for general image data and one for compressed image data.
- Create subscribers
The subscribed topic is ["/usb_cam/image_raw"], the data type is [Image], and the callback function [topic()].
The topic of subscription is ["/usb_cam/image_raw/compressed"], data type [CompressedImage], and callback function [compressed_topic()].
- Create a publisher
The published topic is ["/usb_cam/image_flip"], data type [Image], queue size [10].
The posted topic is ["/usb_cam/image_flip/compressed"], data type [CompressedImage], queue size [10].
xxxxxxxxxxsub_img = rospy.Subscriber("/usb_cam/image_raw", Image, topic)pub_img = rospy.Publisher("/usb_cam/image_flip", Image, queue_size=10)sub_comimg = rospy.Subscriber("/usb_cam/image_raw/compressed", CompressedImage, compressed_topic)pub_comimg = rospy.Publisher("/usb_cam/image_flip/compressed", CompressedImage, queue_size=10)- Callback function
xxxxxxxxxx# Normal image transfer processing def topic(msg): if not isinstance(msg, Image): return bridge = CvBridge() frame = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, "bgr8") frame = cv.resize(frame, (640, 480)) frame = cv.flip(frame, 1) # opencv mat -> ros msg msg = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(frame, "bgr8") pub_img.publish(msg)
# Compressed image transmission processing def compressed_topic(msg): if not isinstance(msg, CompressedImage): return bridge = CvBridge() frame = bridge.compressed_imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, "bgr8") frame = cv.resize(frame, (640, 480)) frame = cv.flip(frame, 1) # Create CompressedIamge msg = CompressedImage() msg.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now() msg.data = np.array(cv.imencode('.jpg', frame)[1]).tostring() pub_comimg.publish(msg)3.3、Jetson CSI camera
3.3.1. Start Jetson CSI camera
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch yahboomcar_visual yahboom_csi.launchView threads
xxxxxxxxxxrostopic list You can see a lot of topics, just a few commonly used in this section
| topic name | type of data |
|---|---|
| /usb_cam/image_raw | sensor_msgs/Image |
| /usb_cam/image_raw/compressed | sensor_msgs/Image |
Check the encoding format of the topic: rostopic echo +[topic]+encoding, for example
xxxxxxxxxxrostopic echo /csi_cam_0/image_raw/encoding
The topic with [compressed] or [compressedDepth] after the topic is a compressed topic. When ROS transmits images, data packets may be lost due to factors such as the network, the running speed of the host, the running memory of the host, and the huge amount of video stream data. off topic. So there is no way, I can only subscribe to the compressed topic. Open two images at the same time to subscribe to different topics for testing. If the device performance is good and the network is also good, there will be no change. Otherwise, you will find that the topics after image compression will be much smoother.
3.2.2. Start the color map subscription node
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch yahboomcar_visual usb_cam_flip.launch In this case, you need to change usb_cam_flip_usb.py to usb_cam_flip.py

py code analysis
Two subscribers and two publishers are created here, one for general image data and one for compressed image data.
- Create subscribers
The subscribed topic is ["/csi_cam_0/image_raw"], the data type is [Image], and the callback function [topic()].
The topic of subscription is ["/csi_cam_0/image_raw/compressed"], data type [CompressedImage], and callback function [compressed_topic()].
- Create a publisher
The published topic is ["/csi_cam_0/image_flip"], data type [Image], queue size [10].
The posted topic is ["/csi_cam_0/image_flip/compressed"], data type [CompressedImage], queue size [10].
xxxxxxxxxxsub_img = rospy.Subscriber("/csi_cam_0/image_raw", Image, topic)pub_img = rospy.Publisher("/csi_cam_0/image_flip", Image, queue_size=10)sub_comimg = rospy.Subscriber("/csi_cam_0/image_raw/compressed", CompressedImage, compressed_topic)pub_comimg = rospy.Publisher("/csi_cam_0/image_flip/compressed", CompressedImage, queue_size=10)- Callback function
xxxxxxxxxx# Normal image transfer processing def topic(msg): if not isinstance(msg, Image): return bridge = CvBridge() frame = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, "bgr8") frame = cv.resize(frame, (640, 480)) frame = cv.flip(frame, 1) # opencv mat -> ros msg msg = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(frame, "bgr8") pub_img.publish(msg)
# Compressed image transmission processing def compressed_topic(msg): if not isinstance(msg, CompressedImage): return bridge = CvBridge() frame = bridge.compressed_imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, "bgr8") frame = cv.resize(frame, (640, 480)) frame = cv.flip(frame, 1) # Create CompressedIamge msg = CompressedImage() msg.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now() msg.data = np.array(cv.imencode('.jpg', frame)[1]).tostring() pub_comimg.publish(msg)