6.Robot development environment construction
6.Robot development environment construction6.1. Use jupyter lab to access docker6.2. Use vscode to access docker6.2.1. Remote configuration6.2.2. Configure password-free login6.2.3. vscode configuration6.2.3.1. Download and install vscode6.2.3.2. vscode configures ssh remote login to the host6.2.3.3. Enter the robot container6.2.3.4. Configure the docker environment on the vscode remote host
6.1. Use jupyter lab to access docker
- Enter the container, see [5. Enter docker container], and execute the following command:
Note: When using jupyter lab in a docker container, you must run the docker container in host networking mode: add the "--net=host" parameter when running the container.
root@ubuntu:/# jupyter lab --allow-root[I 2023-04-24 09:27:45.265 ServerApp] Package jupyterlab took 0.0001s to import[I 2023-04-24 09:27:45.277 ServerApp] Package jupyter_server_fileid took 0.0096s to import[I 2023-04-24 09:27:45.297 ServerApp] Package jupyter_server_terminals took 0.0190s to import[I 2023-04-24 09:27:45.429 ServerApp] Package jupyter_server_ydoc took 0.1301s to import[I 2023-04-24 09:27:45.431 ServerApp] Package nbclassic took 0.0001s to import..................
- To view on other devices, open it in a windows or ubuntu browser (must be on the same LAN, 192.168.2.102 is the IP address in the docker container)
xhttp://192.168.2.102:8888/lab # Enter the jupyter lab of the host machinehttp://192.168.2.102:8889/lab # Enter jupyter lab inside the containerEnter the password: yahboom to enter jupyter lab
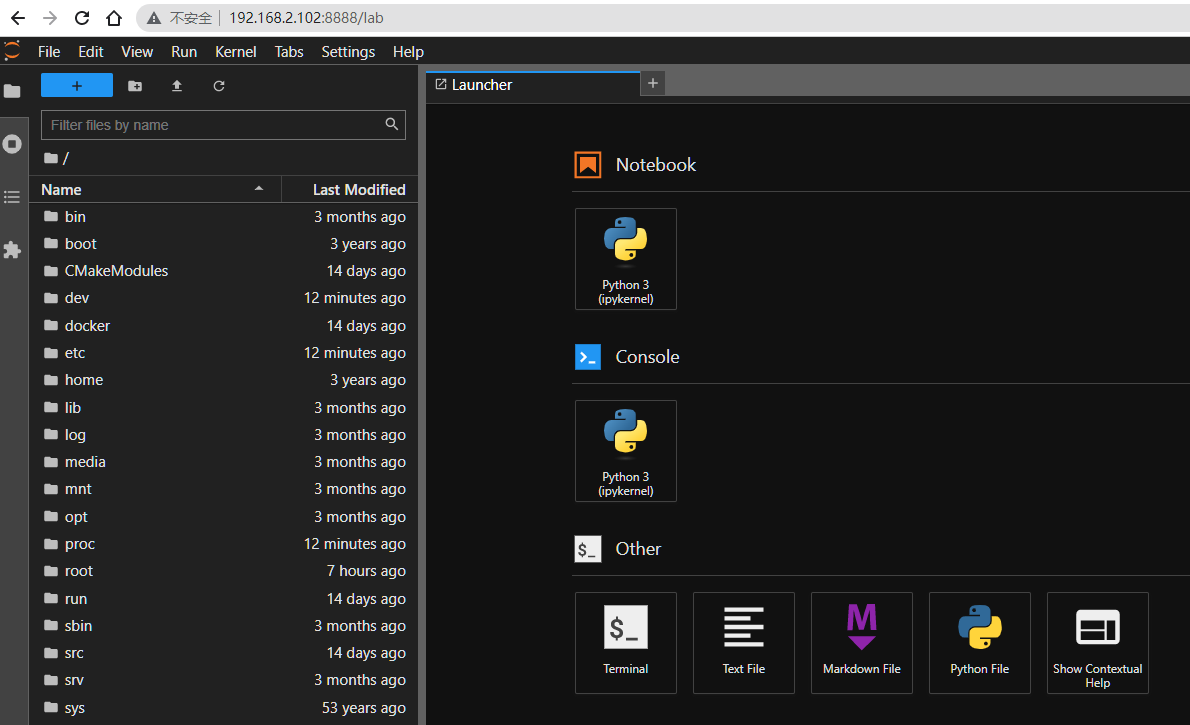
The following directory is the project path of the robot:
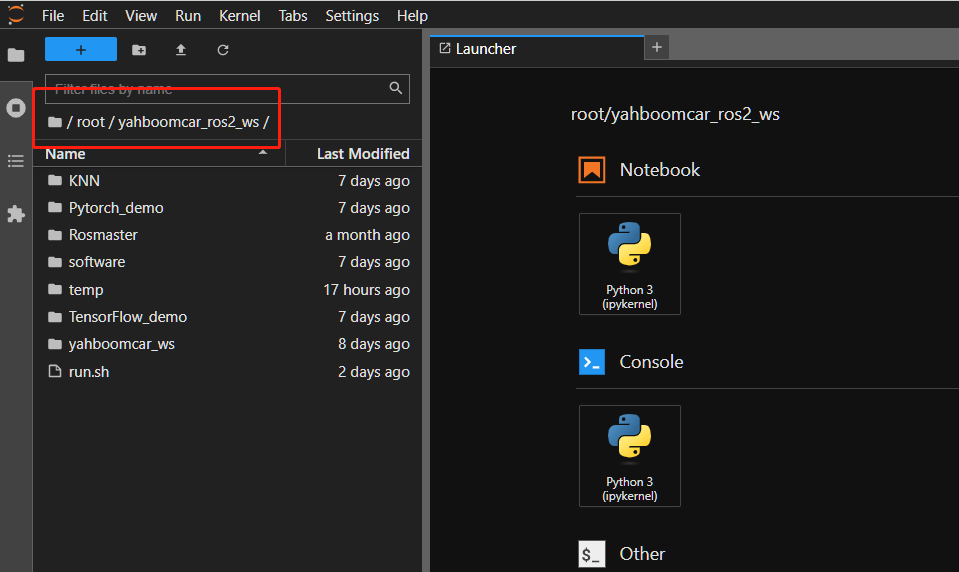
6.2. Use vscode to access docker
Here we take configuring vscode to access the docker container in windows as an example to explain. The steps to access docker in ubuntu are basically the same.
6.2.1. Remote configuration
Make sure that windows can remotely log in to the docker host [car]:
xxxxxxxxxxOpen cmd in windows and input ssh command to test:ssh jetson@192.168.2.102 (Change the username and IP to your own)Or use remote tools: putty, xshell, securecrt, winscp, mobaxterm, finalshell, etc. Mobaxterm is recommended.
6.2.2. Configure password-free login
Some of the above steps may require you to enter the host's password. Let's optimize it again and configure password-free login.
- First, test opening the cmd command on Windows and using ssh to log in to the host [car]. The instructions are as follows:
xxxxxxxxxxssh jetson@192.168.2.102 (Change the username and IP to your own)
At this time you will find that you need to enter the host password
- Next configure password-free login
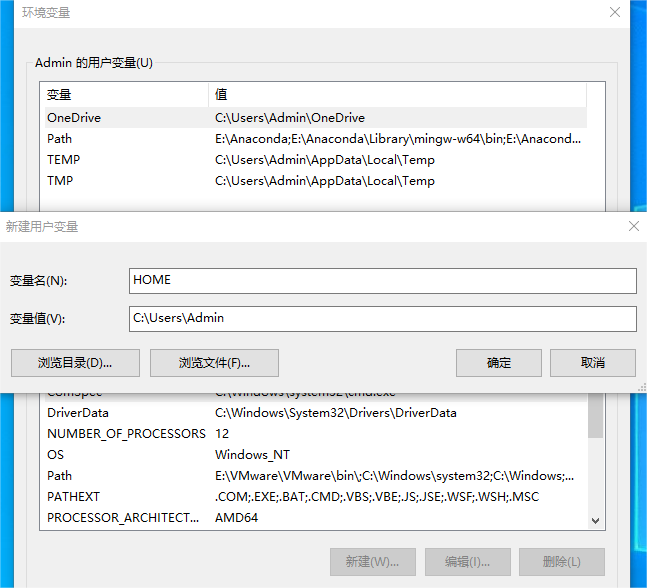
(1) Add environment variables
Taking Windows 10 as an example, open: This PC---Properties---Advanced system settings---Environment variables, and open the environment variable properties page. Click New in the user variables section. The variable is HOME and the value is C:\Users\name, where name is the user name. You can check the user name of your computer by yourself. The key pair generated will be saved in this directory by default.
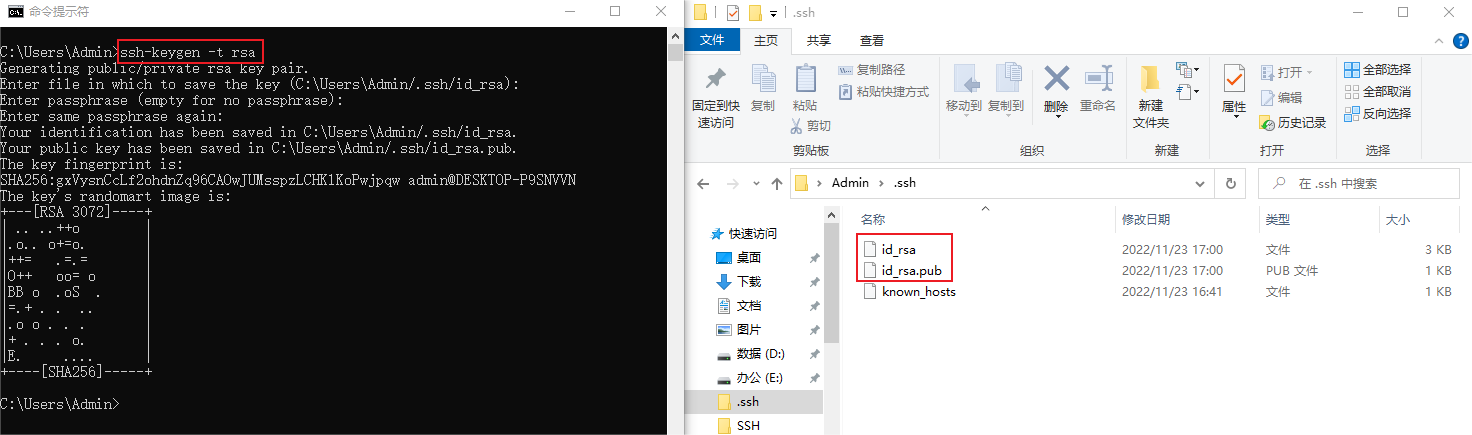
(2) Generate key pair
Open the cmd command line and run it in the directory where the ssh program is located, or after adding the system environment, run [ssh-keygen -t rsa] anywhere. This command is used to generate a key, and then press Enter all the way. When you see a rectangular diagram generated, Then the key generation is successful. At this time, there will be two more files in the .ssh folder in the user directory, namely id_rsa (private key) and id_rsa.pub (public key)
(3) Add the public key to the host machine
First, check whether the .ssh directory already exists in the user root directory of the host. If it does not exist, perform the above "(2) Generate key pair" step to add the .ssh directory.
Secondly, check whether there is an authorized_keys file in the .ssh directory. If not, execute the following two commands to add:
xxxxxxxxxxtouch ~/.ssh/authorized_keyschmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysThen, open the Windows cmd command line and enter
xxxxxxxxxxssh username@host "cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys" < C:\Users\name\.ssh\id_rsa.pubNote: The above "C:\Users\name\.ssh\id_rsa.pub" path is modified according to your own Windows computer path
#For example: Modify according to your own situationssh jetson@192.168.2.102 "cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys" < C:\Users\Admin\.ssh\id_rsa.pub This command first logs in to the host machine, and then adds the local public key under Windows to the personal directory of the host account to achieve password-free login. Note that this step requires entering the password for the host account.
(4) Verification
Test again. Open the cmd command on Windows and use SSH to log in to the host [car]. The instructions are as follows:
xxxxxxxxxxssh jetson@192.168.2.102 (Change the username and IP to your own)
At this time, you will find that you no longer need to enter a password.
6.2.3. vscode configuration
6.2.3.1. Download and install vscode
vscode official website: https://code.visualstudio.com/, just download and install the windows version
6.2.3.2. vscode configures ssh remote login to the host
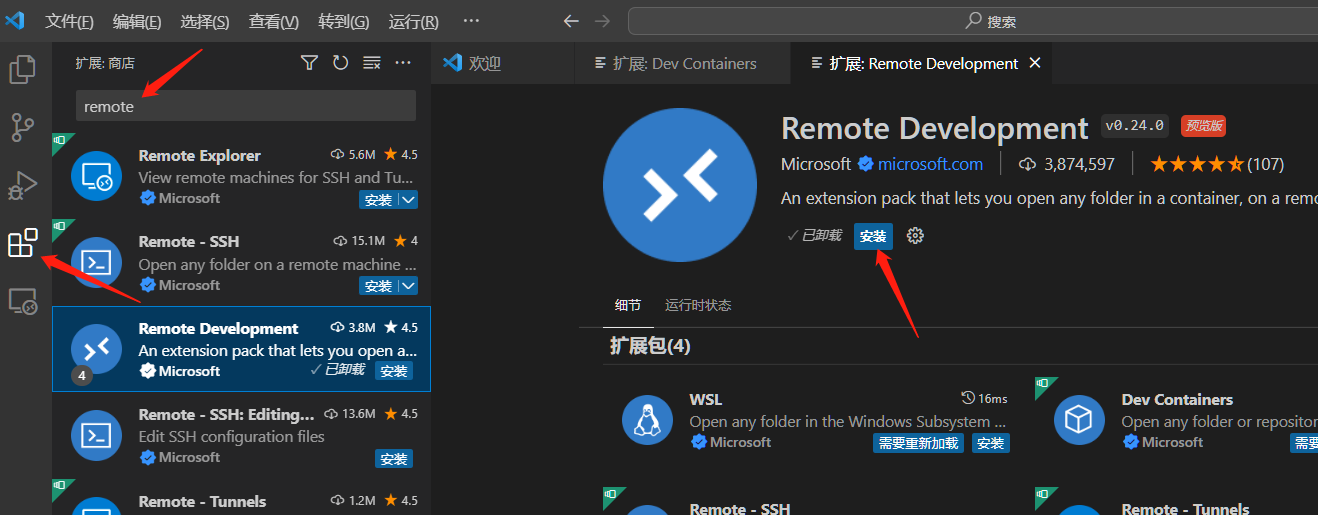
- Open vscode, click the icon with the arrow below on the left, then enter remote in the search box, select the Remote Development plug-in, and click Install to install the plug-in.
After vscode is installed by default, it is the English version. You can install the Chinese plug-in to localize it:
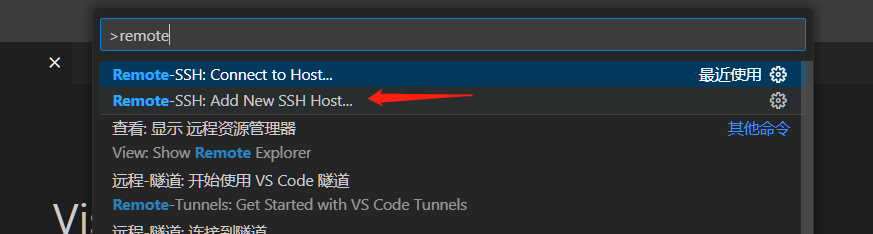
- Press the shortcut key [ctrl + shift + p] in vscode to open the command input window, enter: remote, and then follow the instructions in the figure below to log in to the remote host [car].
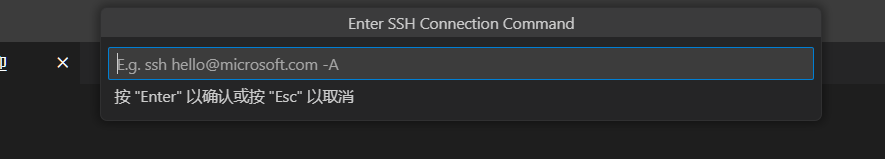
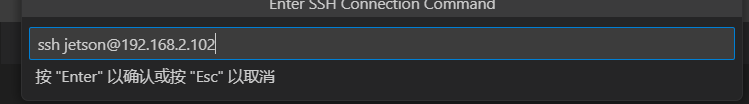
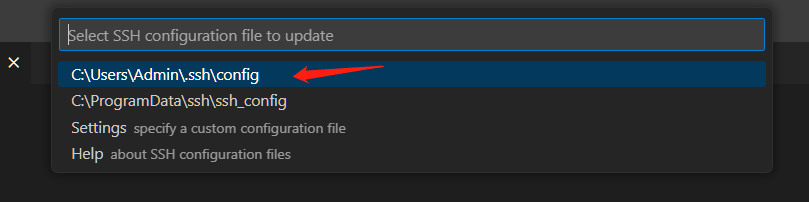
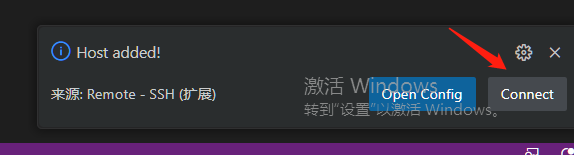
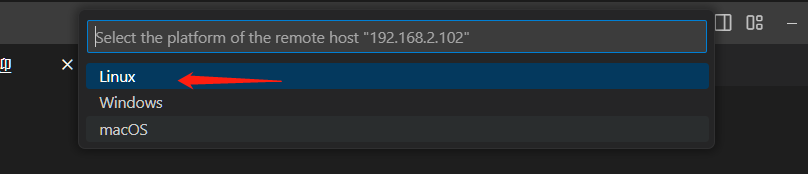
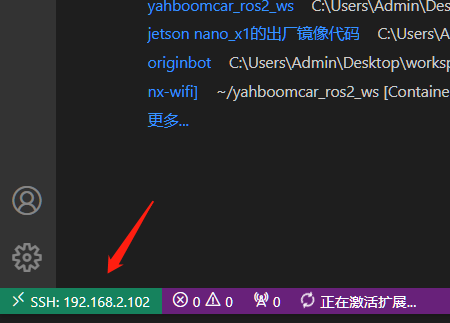
If you see the screen above, it means you have successfully logged in to the host computer remotely.
6.2.3.3. Enter the robot container
See the tutorial in Chapter [5.Enter docker container] to enter.
6.2.3.4. Configure the docker environment on the vscode remote host
- Install the docker plug-in on the remote host [car]
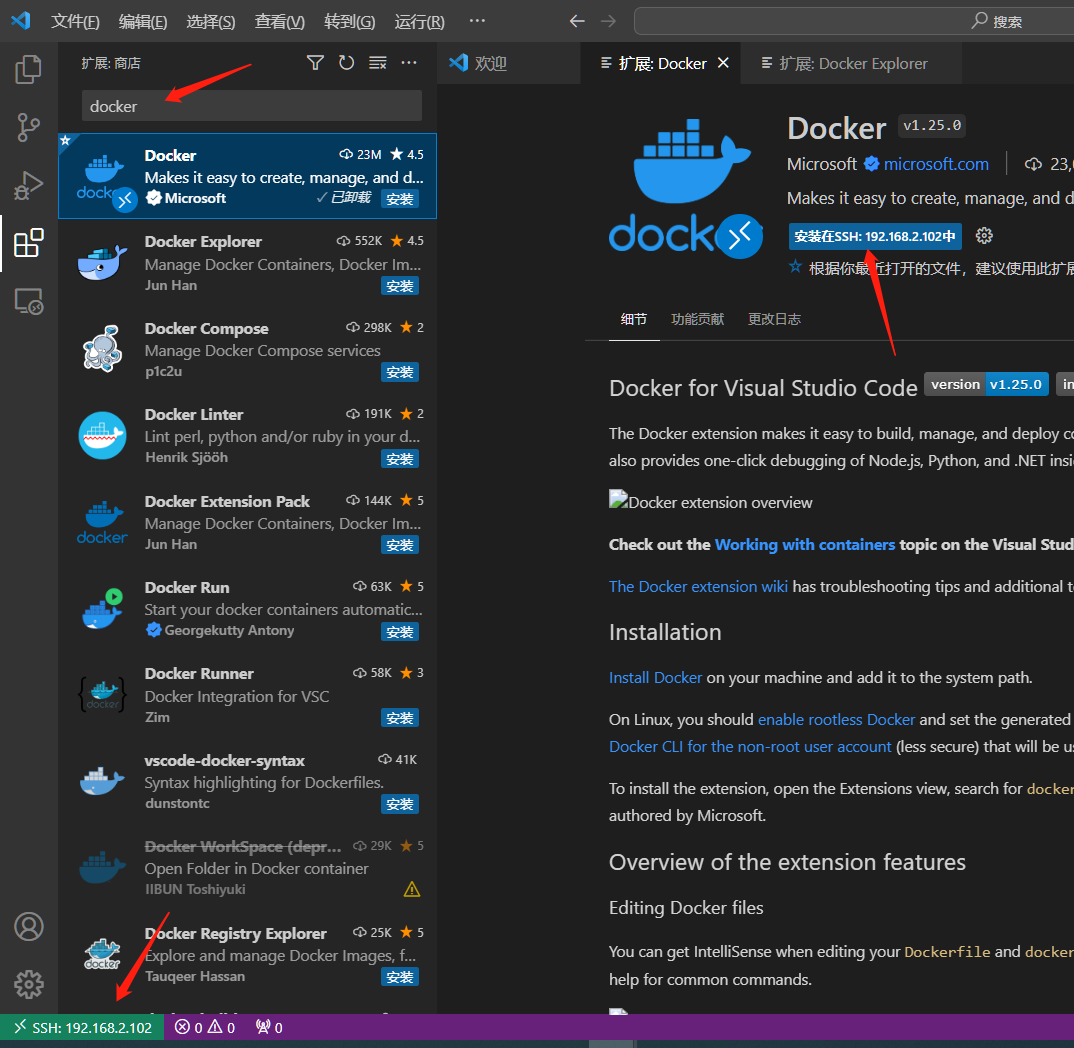
- After the installation is complete, a docker icon will appear in the left navigation bar.
- Click the docker icon
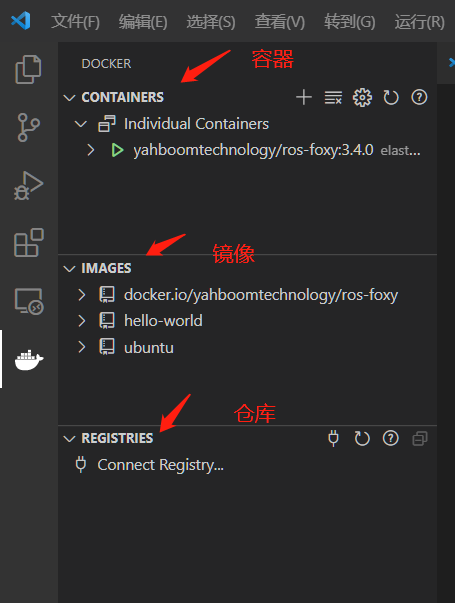
- Right-click on the running container and follow the steps below:
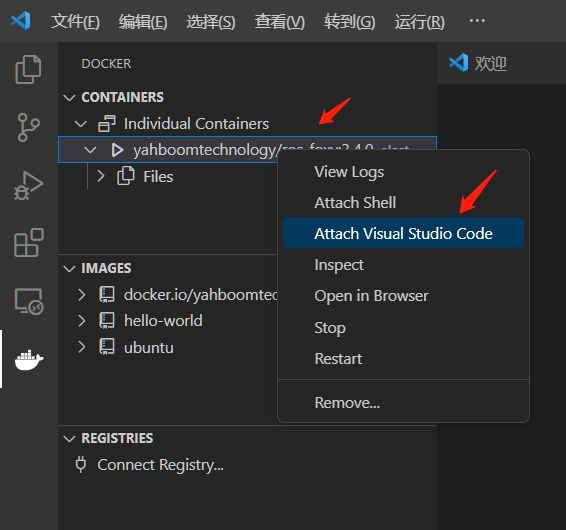
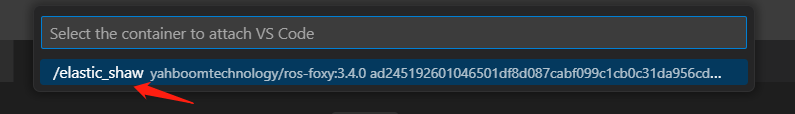
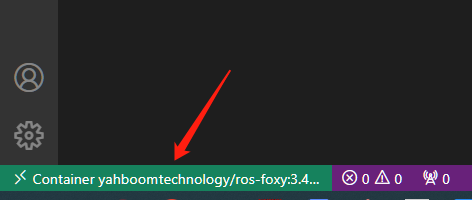
- A new window will open. When you see the following, you have entered the container.
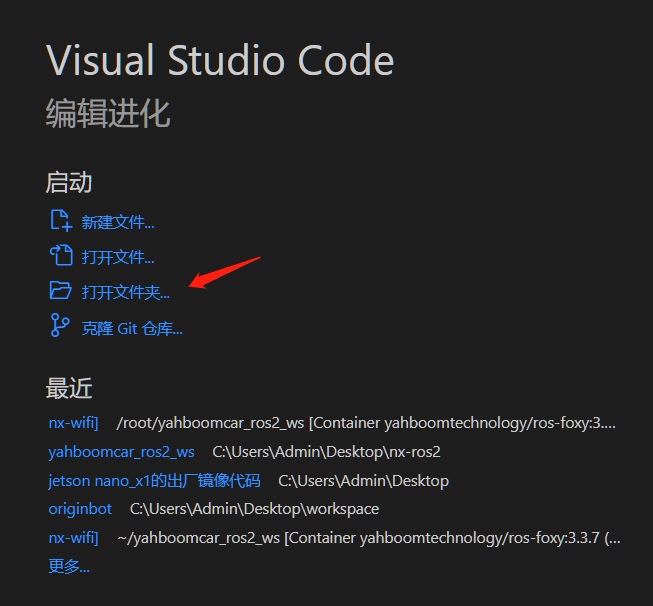
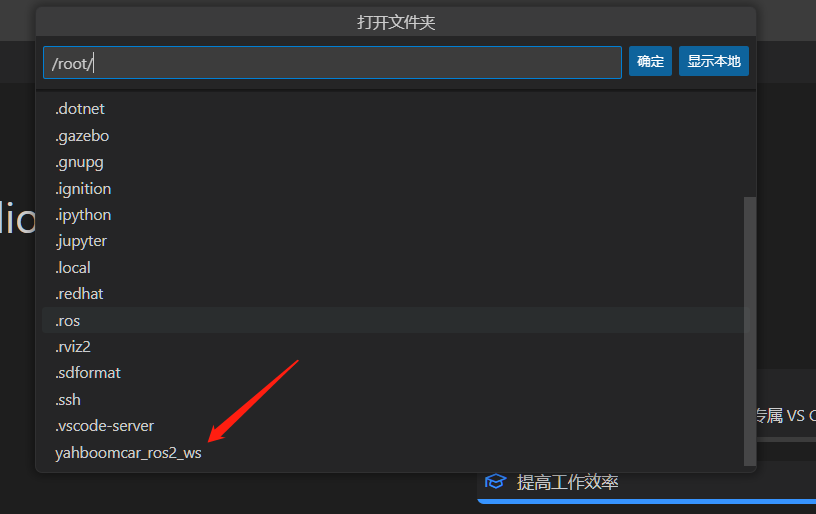
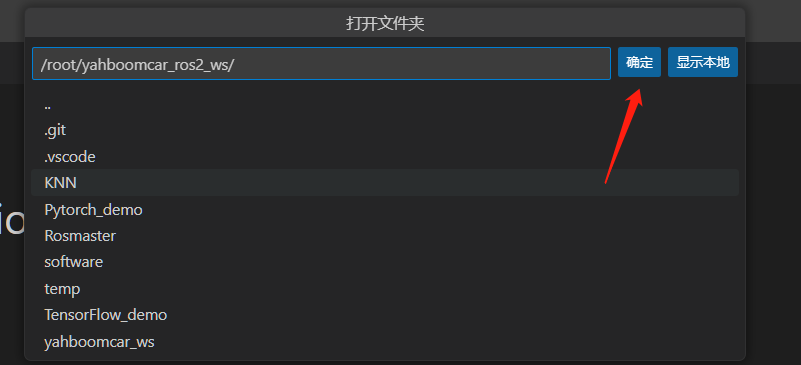
- Open the folder
xxxxxxxxxx/root/yahboomcar_ros2_ws # This is the project path of the robot
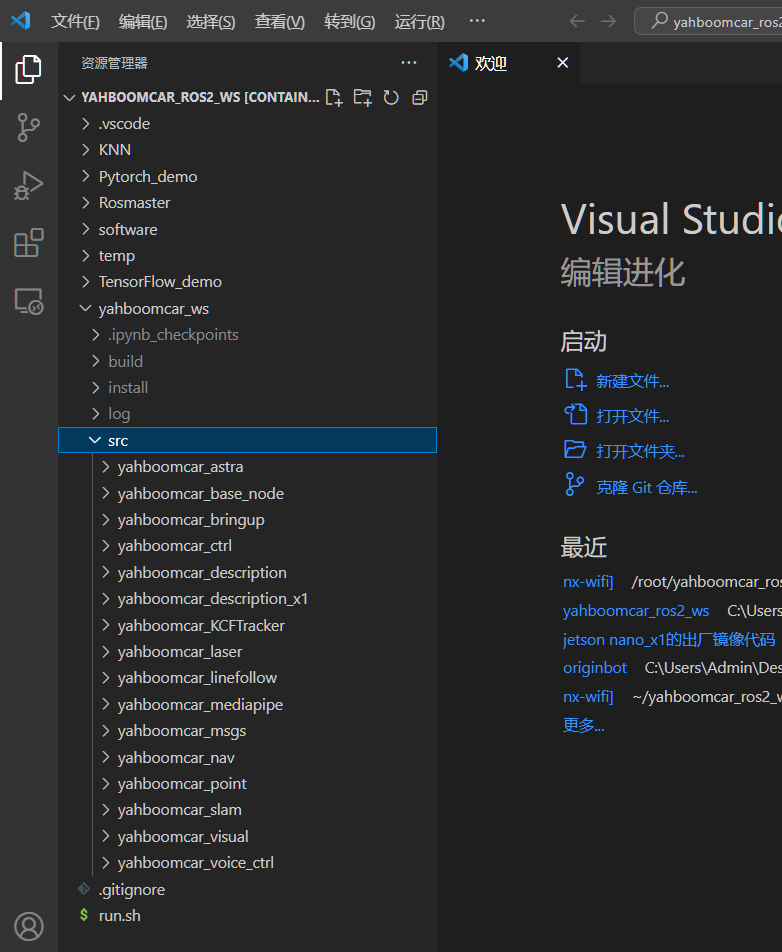
- Similarly, we can also install the plug-ins we need in the container to facilitate our development.
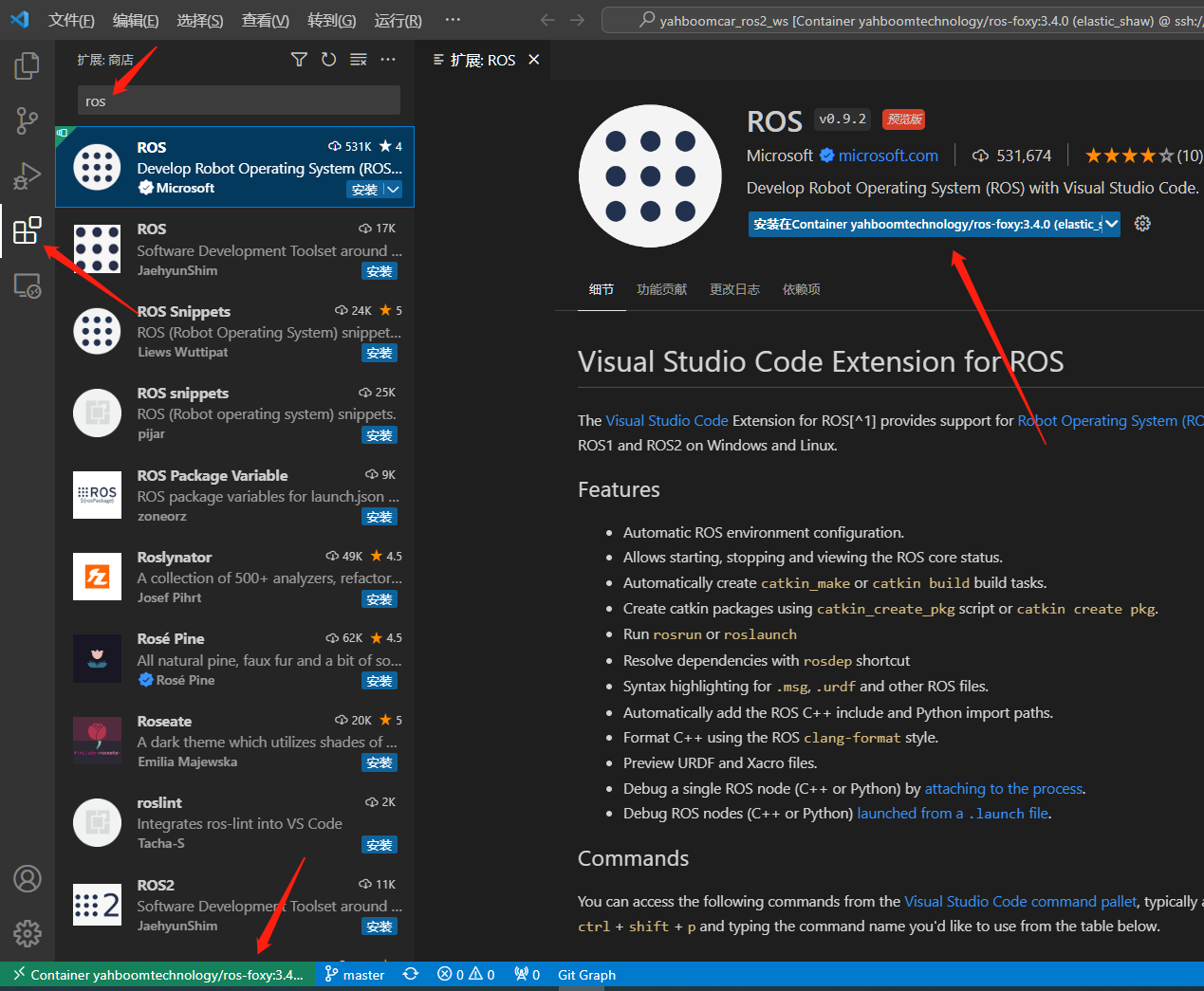
In addition to ros, the recommended plug-ins to install here are:
After completing the above steps, you can operate the code files in the container to develop and learn.