7. rrt_exploration mapping algorithm
The following workspace contains the function packages in the entire rplidar_ws. If you need to transplant it to your own development board, you need to copy all the function packages to the src of the workspace for compilation, and install the relevant environment.
Note: This course uses Rosmaster-X3 as an example. Users need to modify it according to their own motion model.
Different from the handheld lidar mapping content, this mapping adds odom data, so if you use your own motion model, you also need to have odom data.
Function package path: ~/rplidar_ws/src/yahboomcar_nav
7.1 Start
Input following command:
roslaunch yahboomcar_nav laser_bringup.launchroslaunch yahboomcar_nav rrt_exploration.launch use_rviz:=true
[use_rviz] parameter: whether to enable rviz visualization.
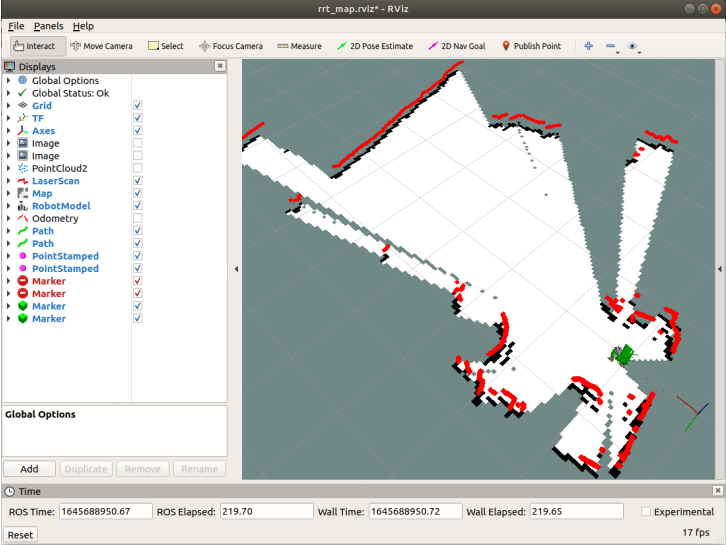
Start Mapping
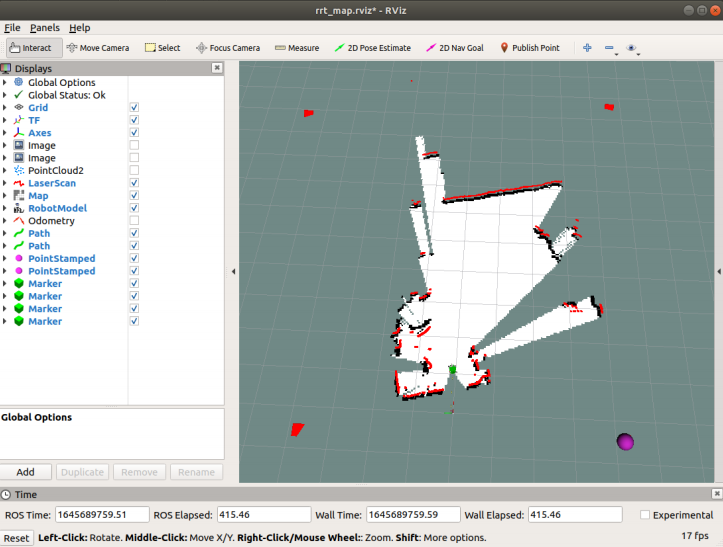
Click [Publish Point] on the [rviz] interface, and then click on the map. Each time you click a point on the map, you must first select [Publish Point]. the clockwise or counterclockwise last point is near the car. After selecting five points as required, the robot begins to explore and build a map.
Save Map
After the mapping is completed, the map is automatically saved and returned to zero. The map is saved to the folder ~/yahboomcar_ws/src/yahboomcar_nav/maps with the name rrt_map, which can be modified in the [simple.launch] file.
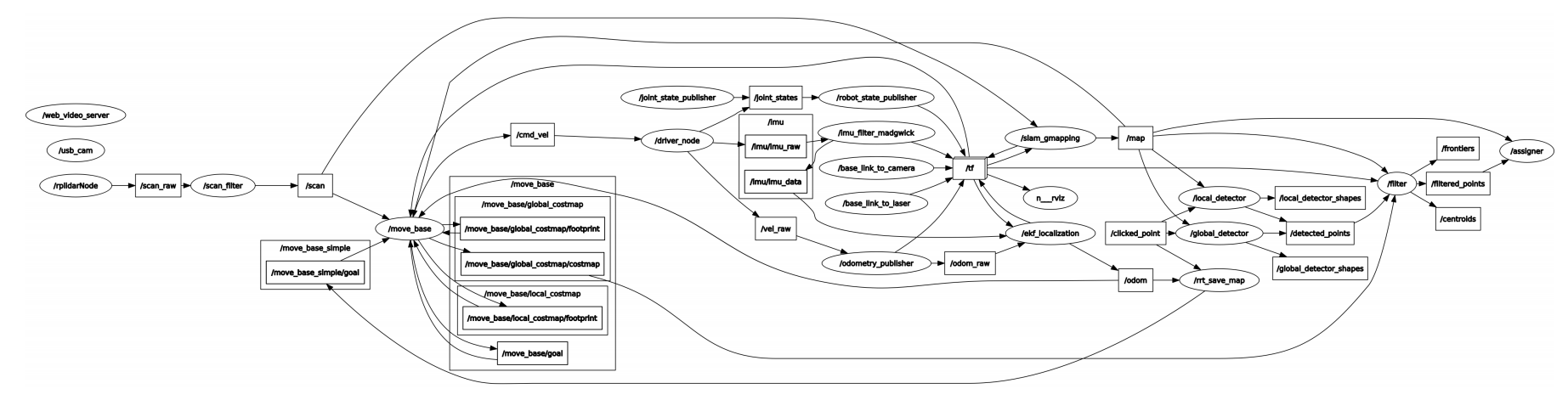
View nodes:
xxxxxxxxxxrqt_graph
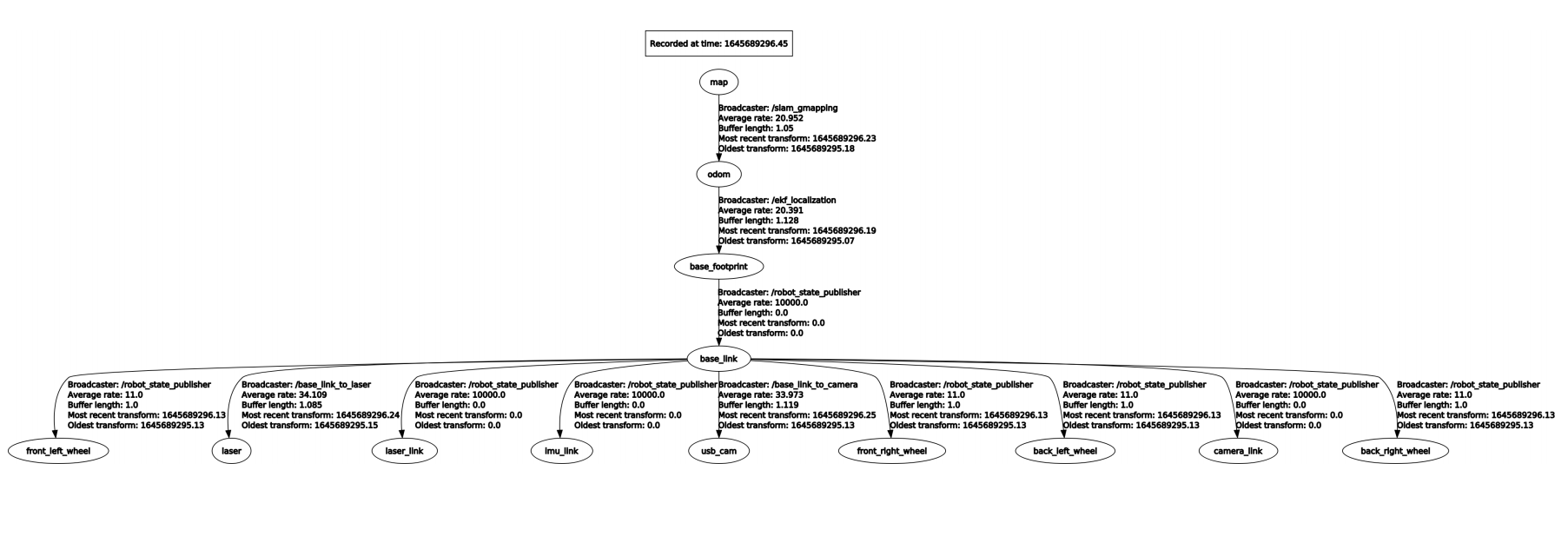
View TF tree:
xxxxxxxxxxrosrun rqt_tf_tree rqt_tf_tree
7.2 Introduction
The framework of the Rapid Exploration Random Tree (RRT) algorithm is as follows:
- Global RRT frontier point detector node.
- Local RRT frontier point detector node.
- OpenCV-based frontier detector node.
- Filter node.
- Assigner node.
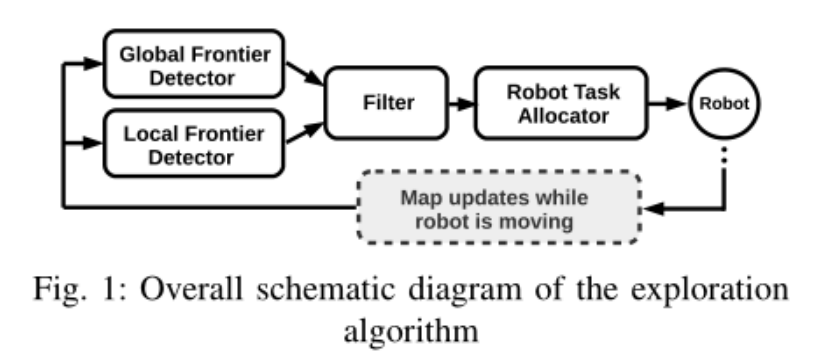
7.2.1 Global RRT frontier point detector node.
1)Introduction
The global_rrt_frontier_detector node takes an occupancy grid and finds frontier points(i.e. exploration targets) in it. It publishes detected points so that filter nodes can process them. In a multi-robot configuration, only one instance of the node is running. If desired, running additional instances of the global boundary detector can increase the speed of boundary point detection.
2)Topics and Services
| Subscribe to topics | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| map | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | Topic names are defined by the ~map_Topic parameter. It is the name of the topic that the node receives. |
| clicked_point | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | The area to be probed by the global_rrt_frontier_detector node. This topic is where the node receives the five points that define the area. The first four points are the four points that define the square area to be explored, and the last point is the starting point of the tree. After these five points are announced, the RRT will begin to probe the border points. |
| Post a topic | type | describe |
| detected_points | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | Post the topic of detected boundary points. |
| shapes | visualization_msgs/Marker | Post RRT hypothetical linetypes to view with Rviz. |
3) Configuration parameters
| parameter | type | Defaults | describe |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~map_topic | string | "/robot_1/map" | This node receives the map topic map name |
| ~ eta | float | 5.0 | This parameter controls the growth rate of the RRT used to detect boundary points, in meters. This parameter should be set according to the map size, a very large value will cause the tree to grow faster and thus detect border points faster, but a larger growth rate also means that the tree will lose small corner points in the map |
7.2.2 Local RRT frontier point detector node
1. Introduction
This node is similar to global_rrt_frontier_detector. However, it works differently because here the tree keeps getting reset every time a boundary point is detected. This node will run along the Global Boundary Detector node, which is responsible for quickly detecting boundary points located near the robot.
In a multi-robot configuration, each robot runs a local probe instance. So for a team of 3 robots, there will be 4 nodes for detecting boundary points; 3 local detectors and 1 global detector. If needed, running additional instances of the local boundary detector can increase the speed of boundary point detection. All detectors will publish detected boundary points("/detected_points") on the same topic.
2. Topics and Services
| Subscribe to topics | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| map | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | The name of the map topic to which this node is subscribed. |
| clicked_point | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | Similar to global_rrt_frontier_detector node |
| Post a topic | type | describe |
| detected_points | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | Post the topic of detected boundary points. |
| shapes | visualization_msgs/Marker | Post RRT hypothetical linetypes to view with Rviz. |
3. Configuration parameters
parametertypeDefaultsdescribe~/robot_1/base_linkstring"/robot_1/base_link"Connect to the frame of the robot. Every time the RRT tree is reset, it will start from the current robot position obtained in this coordinate system.~map_topicstring"/robot_1/map"This node receives the map topic map name~ etafloat5.0This parameter controls the growth rate of the RRT used to detect boundary points, in meters. This parameter should be set according to the map size, a very large value will cause the tree to grow faster and thus detect border points faster, but a larger growth rate also means that the tree will lose small corner points in the map
7.2.3 OpenCV-based frontier detector node.
1. Introduction
This node is another edge detector, but it is not based on RRT. This node uses OpenCV tools to detect boundary points. It is designed to run alone, in a multi-bot configuration, only one instance should be running(running other instances of this node will not make any difference).
Originally, this node was implemented for comparison with RRT-based boundary detectors. Running this node along the RRT detectors(local and global) can increase the speed of boundary point detection.
Note: You can run any type and number of detectors, all of which will be published on the same topic that the filter node(explained in the next section) subscribes to. The filter, on the other hand, passes the filtered boundary points to the assignor in order to command the robot to explore these points.
2. Topics and Services
| Subscribe to topics | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| map | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | The name of the map topic to which this node is subscribed. |
| Post a topic | type | describe |
| detected_points | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | Post the topic of detected boundary points. |
| shapes | visualization_msgs/Marker | Post RRT hypothetical linetypes to view with Rviz. |
3. Configuration parameters
| parameter | type | Defaults | describe |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~map_topic | string | "/robot_1/map" | This node receives the map topic map name |
7.2.4 Filter node
1. Introduction
This node is similar to global_rrt_frontier_detector. However, it works differently because here the tree keeps getting reset every time a boundary point is detected. This node will run along the Global Boundary Detector node, which is responsible for quickly detecting boundary points located near the robot.
In a multi-robot configuration, each robot runs a local probe instance. So for a team of 3 robots, there will be 4 nodes for detecting boundary points; 3 local detectors and 1 global detector. If needed, running additional instances of the local boundary detector can increase the speed of boundary point detection. All detectors will publish detected boundary points("/detected_points") on the same topic.
2. Topics and Services
| Subscribe to topics | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| map | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | Topic names are defined by the ~map_Topic parameter. It is the name of the topic that the node receives. |
| robot_x/move_base_node /global_costmap/costmap | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | x is the number of the robot. This node subscribes to the topic of all costmaps for all robots, so costmaps are required. Normally, costmaps should be published by navigation(there will be one costmap per robot when navigation is turned on on a robot). For example, if n_robots=2, the nodes will subscribe to: robot_1/move_base_node/global_costmap/costmap and robot_2/move_base_node/global_costmap/costmap. The costmap is used to remove invalid points. Note: The namespace of all nodes corresponding to robots should start with robot_x. |
| detected_points | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | The topic name defined by ~goals_topic. It is the topic on which the filter node receives boundary detection points. |
| Post a topic | type | describe |
| frontiers | visualization_msgs/Marker | The filter node only publishes topics of filtered boundary points. |
3. Configuration parameters
| parameter | type | Defaults | describe |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~map_topic | string | "/robot_1/map" | This node receives the map topic map name |
| ~costmap_clearing_threshold | float | 70.0 | Costmap cleanup threshold |
| ~info_radius | float | 1.0 | The information radius used to calculate the information gain of the boundary point. |
| ~goals_topic | string | /detected_points | Defines the topic the node receives to detect boundary points |
| ~n_robots | float | 1.0 | Number of robots |
| ~namespace | string | Namespaces | |
| ~namespace_init_count | float | 1.0 | index of namespace |
| ~rate | float | 100.0 | Node cycle rate(in Hz). |
7.2.5 Assigner node.
1. Introduction
This node receives target detection targets, i.e. filtered boundary points issued by the filtering node, and commands the robot accordingly. The evaluator node commands the robot via move_base_node. That's why navigation is initiated on the robot.
2. Topics and Services
| Subscribe to topics | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| map | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | Topic names are defined by the ~map_Topic parameter. It is the name of the topic that the node receives. |
| frontiers_topic | nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid | The topic name is defined by the ~frontiers_topic parameter |
3. Configuration parameters
| parameter | type | Defaults | describe |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~map_topic | string | "/robot_1/map" | This node receives the map topic map name |
| ~info_radius | float | 1.0 | The information radius used to calculate the information gain of the boundary point. |
| ~info_multiplier | float | 3.0 | The unit is meters. This parameter is used to emphasize the importance of the information gain of the boundary point relative to the cost (expected travel distance to the boundary point). |
| ~hysteresis_radius | float | 3.0 | The unit is meters. This parameter defines the lag radius. |
| ~hysteresis_gain | float | 2.0 | The unit is meters. This parameter defines the hysteresis gain. |
| ~frontiers_topic | string | /filtered_points | This node receives topics for boundary points. |
| ~n_robots | float | 1.0 | Number of robots |
| ~namespace | string | Namespaces | |
| ~namespace_init_count | float | 1.0 | Starting indexing of bot names. |
| ~delay_after_assignement | float | 0.5 | The unit is seconds. It defines the amount of delay after each robot assignment. |
| ~global_frame | string | "/map" | for the global coordinate system. In a single bot, it is the same as the "map_topic" parameter. In the case of multiple robots, the coordinate system name corresponds to the global coordinate system name. |