12.Bind device ID
12.Bind device ID1.Device view command2. Establish port mapping relationship2.1. Device binding2.2. Introduction to rule file syntax3. Verify view4. Bind USB port
When the robot uses two or more USB serial devices, the corresponding relationship between the device name and the device is not fixed, but is assigned in sequence according to the order in which the devices are connected to the system.
Inserting one device first and then another device can determine the relationship between the device and the device name, but it is very troublesome to plug and unplug the device every time the system starts. The serial port can be mapped to a fixed device name. Regardless of the insertion order, the device will be mapped to a new device name. We only need to use the new device name to read and write the device.
1.Device view command
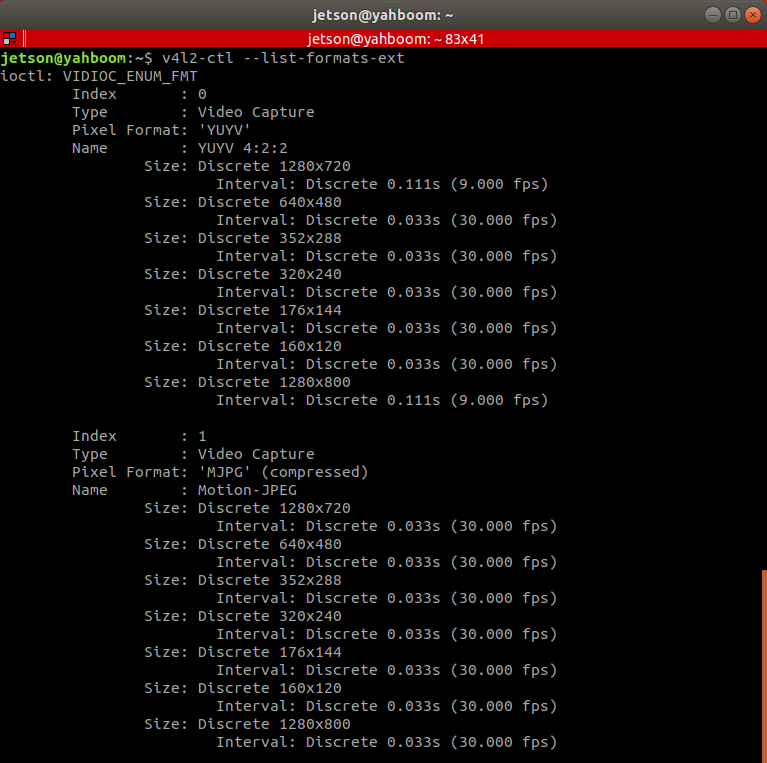
View camera device parameters
Enter the following command in the terminal to view the corresponding relationship between the camera's pixel size and frame rate.
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
View device ID
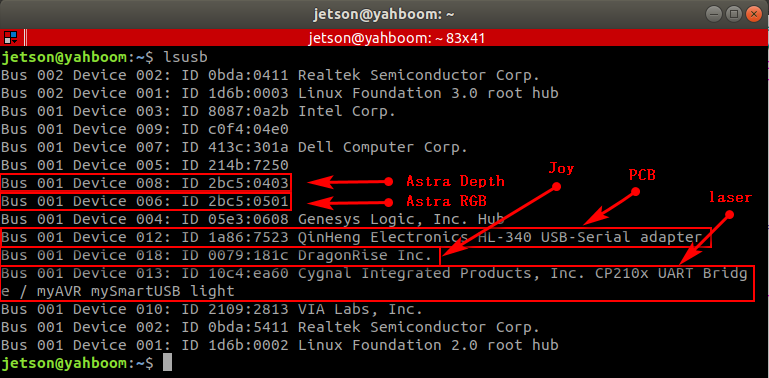
xxxxxxxxxxlsusb
As can be seen from the picture below, Astra depth camera has an official document for binding the device to the ID number of each device. Generally, the controller does not need to be bound, and it can mainly be bound to the PCB and radar.
View device ID
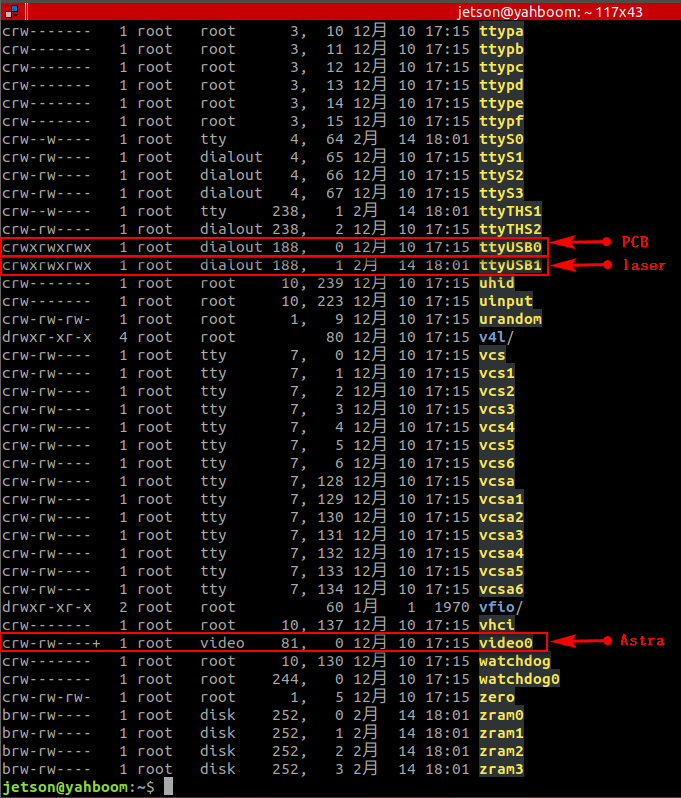
xxxxxxxxxxll /dev/
2. Establish port mapping relationship
2.1. Device binding
- Astra binding
There is a create_udev_rules file in the scripts folder under the astra_camera function package.
Run this file to automatically bind it.
Run the command as follows
xxxxxxxxxx./create_udev_rulesEnter rules.d directory
xxxxxxxxxxcd /etc/udev/rules.d/You can find the 56-orbbec-usb.rules file, which is the Astra camera device binding file.
- PCB and lidar binding
Enter rules.d directory
xxxxxxxxxxcd /etc/udev/rules.d/Create a new rplidar.rules file
xxxxxxxxxxsudo touch rplidar.rulessudo chmod 777 rplidar.rulesOpen the rplidar.rules file
xxxxxxxxxxsudo vim rplidar.rules
Write the following content
xxxxxxxxxxKERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTRS{idProduct}=="7523", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="myserial"KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="10c4", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ea60", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="rplidar"
Exit for the rules to take effect
xxxxxxxxxxsudo udevadm triggersudo service udev reloadsudo service udev restart
2.2. Introduction to rule file syntax
xxxxxxxxxxKERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTRS{idProduct}=="7523", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="myserial"KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="10c4", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ea60", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="rplidar"
Analyze
x
KERNEL #The device name matching the eventATTR{filename} # Match the sysfs attributes of the event device.idVendor # Manufacturer numberidProduct # Product numberSYMLINK # Generate symbolic links for device files under /dev/. Just give this device an alias.MODE # Set permissions for the device。From [6.1], we can see that the PCB device number is [ttyUSB0] and is easy to change. The ID number is [1a86, 7523] and is fixed. [ttyUSB*] means that no matter the device number becomes [ttyUSB] in the future, it will be followed by [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,...] are all bound to [myserial]; the radar device [ttyUSB1] is the same; the same is true for other devices that need to be bound.
3. Verify view
View device number
xxxxxxxxxxll /dev/
PCB
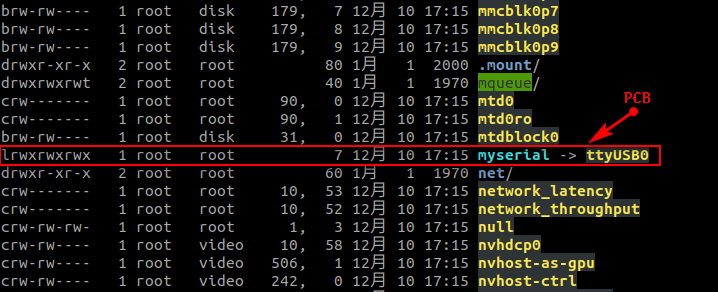
laser
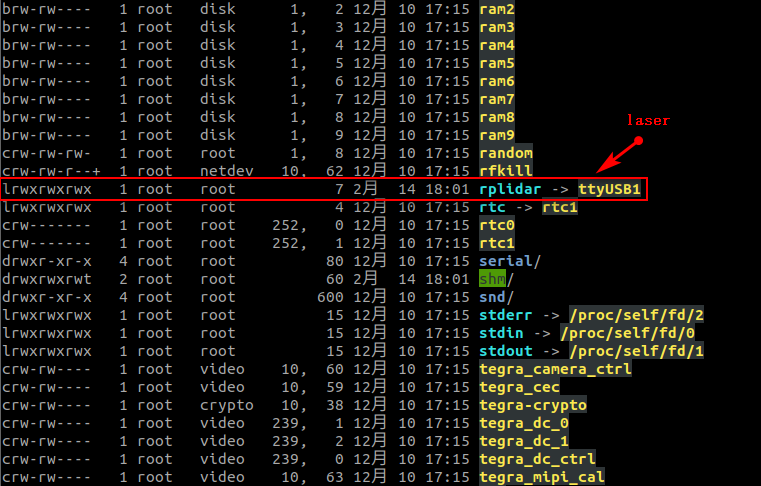
4. Bind USB port
The above situations are all different ID numbers. If the ID numbers of the radar and PCB are the same, or there are two or more PCBs (radars) with the same ID, the above binding will be confusing.
Then, we need to bind the USB port. After binding, the USB port cannot be changed at will. Each device can only be connected to a fixed USB port.
Binding method, take [ttyUSB0] as an example to check the port of the device at this time
xxxxxxxxxxudevadm info --attribute-walk --name=/dev/ttyUSB0 |grep KERNELS
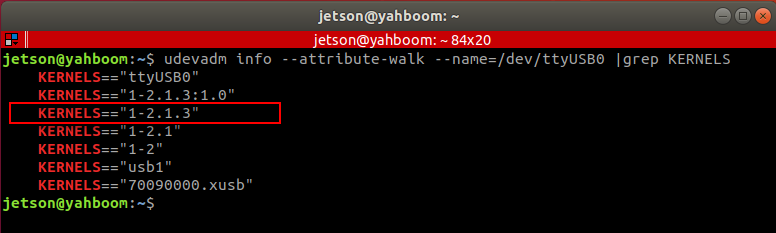
We need is to modify it in the rules file
x
# KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTRS{idProduct}=="7523", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="myserial" # before modifyKERNELS=="1-2.1.3", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTRS{idProduct}=="7523", MODE:="0777", SYMLINK+="myserial" # after modify