04. Multi-computer communication configuration
04. Multi-computer communication configuration4.1. Concepts4.2 Implementation4.2.1 Default implementation4.2.2. Distributed network grouping4.3 Notes4.4 Calculation rules for DDS domain ID values
The operating environment and hardware and software reference configuration are as follows:
- Reference model: ROSMASTER X3
- Robot hardware configuration: Arm series main control, Silan A1 Lidar, AstraPro Plus depth camera.
- Robot system: Ubuntu (version not required) + docker (version 20.10.21 and above)
- PC virtual machine: Ubuntu (20.04) + ROS2 (Foxy)
- Usage scenario: use on a relatively clean 2D plane
4.1. Concepts
Multi-computer communication, i.e. distributed communication, is a communication strategy that allows data interaction between different hosts over a network.
ROS2 itself is a distributed communication framework, which can easily realize the communication between different devices. The middleware that ROS2 is based on is DDS, and when in the same network, distributed communication can be realized through the domain ID mechanism (ROS_DOMAIN_ID) of DDS, and the general process is: before starting a node, you can set the value of the domain ID, and different nodes can freely discover and communicate with each other if they have the same domain ID. are the same, then they can freely discover and communicate, and vice versa, if the domain ID values are different, it cannot be realized. By default, the domain ID used for all nodes to start up is 0. In other words, as long as you ensure that you are on the same network, you don't need to do any configuration for different nodes on different ROS2 devices to realize distributed communication.
Distributed communication is used in a wide range of scenarios, such as unmanned vehicle formations, drone formations, remote control, and so on, all of which rely on distributed communication for data interaction.
4.2 Implementation
4.2.1 Default implementation
Distributed communication is already realized by simply having the host and the slave [there can be more than one] in the same network. For example, the host and the slave are connected to the same WiFi or the same router.
The virtual machine in Windows is in the same network as the host by setting the network to [bridge mode].
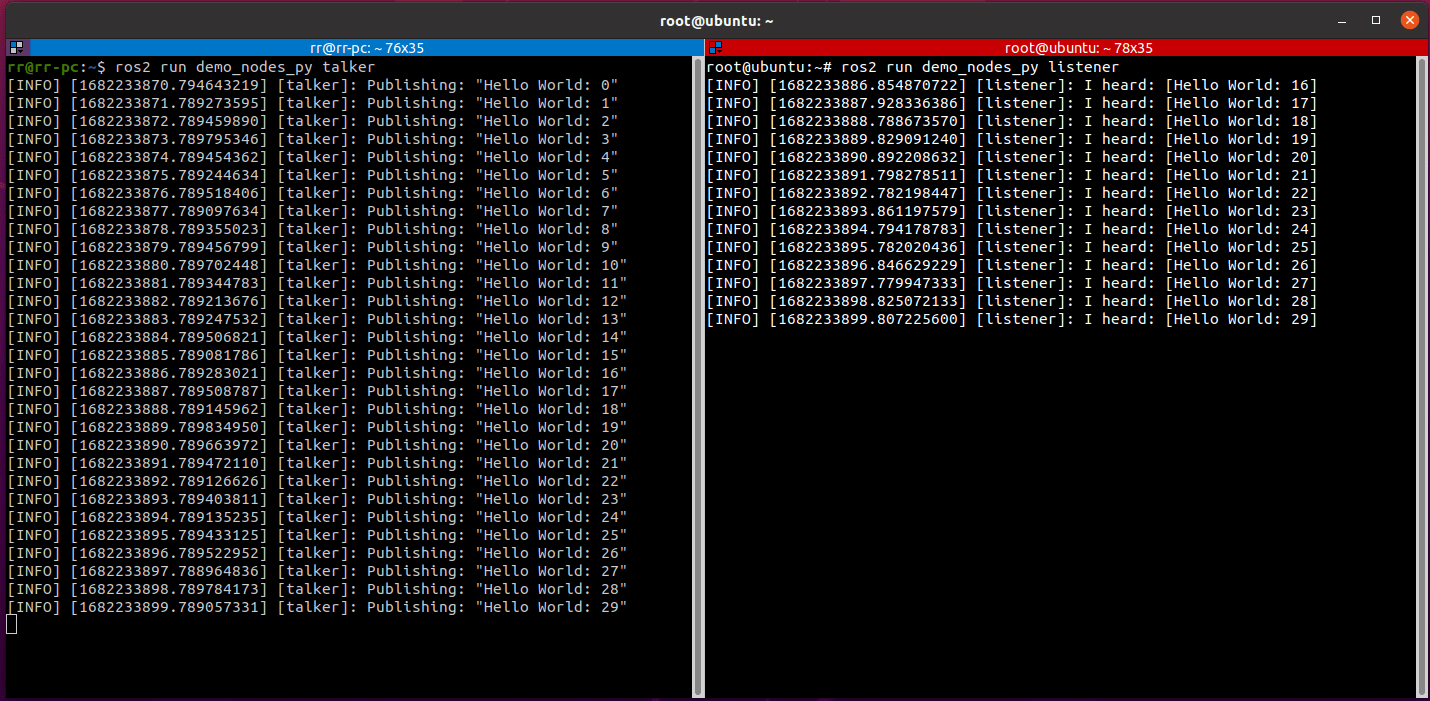
Test:
1, the host side of the [cart] execution:
Demonstration here is the cart in docker, docker uses the network mode is host mode, host mode is simply and the cart share a network, so with the cart on the implementation of no difference.
xxxxxxxxxxros2 run demo_nodes_py talker
- while the slave side [VM] is executed:
xxxxxxxxxxros2 run demo_nodes_py listener
If the following is displayed: the topic published by the host can be subscribed to by the slave in time, it means that multi-computer communication has been realized
4.2.2. Distributed network grouping
Assuming that there are other robots in use in the network you are in now, in order not to be interfered by other robots, you can also set up a grouping for your robots.
ROS2 provides a DOMAIN mechanism, similar to grouping, in the same DOMAIN in the computer to communicate, we can be in the host side of the [trolley] and the slave side of the [virtual machine] of the .bashrc to add such a sentence in the configuration, you can assign the two to a group:
xxxxxxxxxx$ export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=<your_domain_id>
If the IDs assigned to the host side [cart] and the slave side [VM] are different, the two cannot communicate for the purpose of grouping.
Test:
1, the host side [cart] execution:
Demonstrated here is the cart is in docker, docker uses the network mode is host mode, host mode is simply and the cart share a network, so with the cart on the implementation of no difference.
xxxxxxxxxxecho "export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=6" >> ~/.bashrc # 这里的6是ROS_DOMAIN_ID, 不一定要用6,符合ROS_DOMAIN_ID的规则即可# The 6 here is the ROS_DOMAIN_ID, it doesn't have to be a 6, just the ROS_DOMAIN_ID rule.source ~/.bashrcros2 run demo_nodes_py talker
- while the slave side [VM] is executed:
xxxxxxxxxxecho "export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=6" >> ~/.bashrc # 这里和主机端的值保持一致# It's consistent with the values on the host sidesource ~/.bashrcros2 run demo_nodes_py listener
If the following is displayed: the topic posted by the host can be subscribed to by the slave in time, it means that grouped multi-computer communication has been realized
4.3 Notes
The value of ROS_DOMAIN_ID is not arbitrary, there are some constraints:
- It is recommended that the value of ROS_DOMAIN_ID is between [0,101], including 0 and 101;
- the total number of nodes within each domain ID is limited and needs to be less than or equal to 120;
- if the domain ID is 101, then the total number of nodes in the domain needs to be less than or equal to 54.
4.4 Calculation rules for DDS domain ID values
The rules related to the calculation of the domain ID value are as follows:
- DDS is based on TCP/IP or UDP/IP network communication protocol, network communication needs to specify the port number, which is represented by a 2-byte unsigned integer and its value range is between [0,65535];
- The allocation of port number also has its own rules, not arbitrary use, according to the DDS protocol to 7400 as the starting port, that is, the port can be used for [7400,65535], and is known in accordance with the DDS protocol by default, each domain ID occupies 250 ports, then the number of domain ID: (65535-7400)/250 = 232 (a), corresponding to the range of values is [0,65535], and its value range is [0,65535]. The number of domain IDs is: (65535-7400)/250 = 232 (ports), which corresponds to a range of [0,231];
- The operating system will also set up some reserved ports, when using ports in the DDS, you also need to avoid these reserved ports, so as to avoid conflicts in the use of different operating systems reserved ports and there are differences in the end result is that, in Linux, the available domain ID [0,101] and [215-231], in Windows and Mac available domain ID [0, 166], in summary, the available domain ID [0, 166], the available domain ID [0, 166], the available domain ID [0, 166], the available domain ID [0, 166], the available domain ID [0, 166]. 166]. In summary, for compatibility with multiple platforms, it is recommended that the domain IDs take values in the range of [0,101]. 4.
- Each domain ID occupies 250 ports by default, and each ROS2 node needs to occupy two ports. In addition, according to the DDS protocol within the port segment of each domain ID, the 1st and 2nd ports are Discovery Multicast ports and User Multicast ports, and the 11th and 12th ports are the Discovery Unicast ports and User Multicast ports for the first node of the domain, and the 11th and 12th ports are the Discovery Unicast ports and User Multicast ports for the first node of the domain. Discovery Unicast port and User Unicast, and the ports occupied by the subsequent nodes are in order, then the maximum number of nodes in a domain ID is: (250-10)/2 = 120 (pcs);
- Special case: when the domain ID value is 101, the second half of its ports belong to the reserved ports of the operating system, and the maximum number of its nodes is 54.
The above calculation rules can be understood.