1.ROS introduction
1.ROS introduction1.1 Main features of ROS1.2 Overall architecture of ROS1.2.1 Calculation graph level1.2.2 File system level1.2.3 Open source community level1.3 Communication mechanism1.3.1、Topic1.3.2、Service1.3.3、Action1.4 Common components1.5 Release version
ROS wiki : http://wiki.ros.org/
ROS (Robot Operating System, referred to as "ROS") is an open source operating system suitable for robots. It provides the services that an operating system should have, including hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of common functions, inter-process message passing, and package management. It also provides the tools and library functions needed to obtain, compile, write, and run code across computers.
The main goal of ROS is to provide support for code reuse for robotics research and development. ROS is a framework of distributed processes (also known as "nodes") that are encapsulated in packages and function packages that are easy to share and publish. ROS also supports a federated system similar to a code repository, which can also enable project collaboration and release. This design allows the development and implementation of a project to be completely independent from the file system to the user interface (not restricted by ROS). At the same time, all projects can be integrated by ROS basic tools.
1.1 Main features of ROS
(1) Distributed architecture (each working process is regarded as a node and is managed uniformly using the node manager),
(2) Multi-language support (such as C++, Python, etc.),
(3) Good scalability (you can write one node, or organize many nodes into a larger project through roslaunch),
(4) Open source code (ROS follows the BSD protocol and is completely free for individual and commercial applications and modifications).
1.2 Overall architecture of ROS
Open source community level: mainly includes developer knowledge, code, and algorithm sharing.
File system level: used to describe the code and executable programs that can be found on the hard disk.
Computational graph level: reflects the communication between processes and processes and systems.
1.2.1 Calculation graph level
Node
Nodes are the main computing execution processes. ROS is composed of many nodes. After multiple nodes are started, you can use the following command to view the topic communication between each node.
rqt_graph
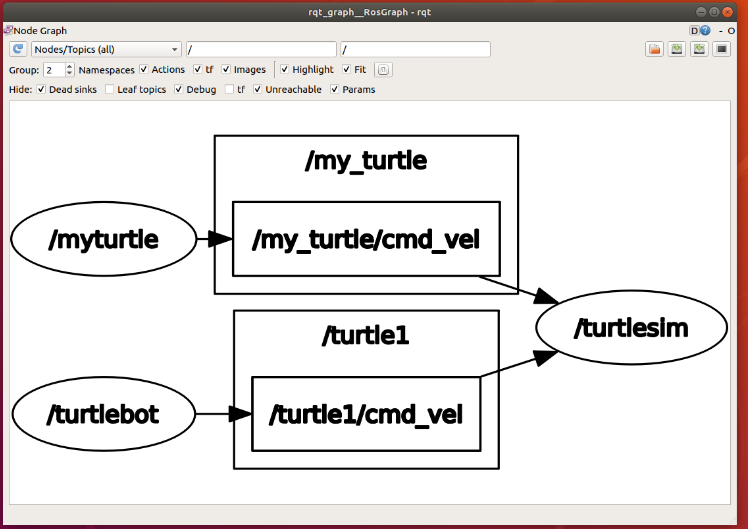
Information
Nodes realize logical connections and data exchange with each other through messages.
Topic (theme)
Topics are a way of delivering messages (publish/subscribe). Each message must be published to the corresponding topic, and each topic is strongly typed. ROS topic messages can be transmitted using TCP/IP or UDP. The default transmission method used by ROS is TCP/IP. Transmission based on TCP is called TCPROS, which is a long connection method; transmission based on UDP is called UDPROS, which is a low-latency, high-efficiency transmission method, but it is easy to lose data and is suitable for remote operations.
Services
Services are used in the request-reply model and must also have a unique name. When a node provides a service, all nodes can communicate with it through code written using ROS clients.
Message record package
Message recording package is a file format used to save and playback ROS message data, which is saved in .bag file. It is an important mechanism for storing data.
Parameter server
The parameter server is a shared multi-variable dictionary accessible over the network, stored by key on the node manager.
Node Manager (Master)
The node manager is used for registration and search of topics and service names, etc. If there is no node manager in the entire ROS system, there will be no communication between nodes.
1.2.2 File system level
Dependencies can be configured between function packages. If function package A depends on function package B, then when building the system in ROS, B must be built earlier than A, and A can use the header files and library files in B.
The file system level concepts are as follows:
Function pack list:
This list indicates the dependencies of the function package, source file compilation flag information, etc. The package.xml file in the function package is a function package list.
Function pack:
Function packages are the basic form of software organization in the ROS system, including running nodes and configuration files.
Comprehensive feature package
Several functional packages are organized together to form a comprehensive functional package.
Message type
When sending messages between nodes in ROS, a message description is required in advance. ROS provides standard types of messages, which can also be defined by yourself. The description of the message type is stored in the msg file under the function package.
Service type
Defines the data structure provided by each process in the ROS system regarding service requests and responses.
1.2.3 Open source community level
- Distribution: ROS distribution is a series of comprehensive function packages that can be installed independently and have version numbers. ROS distributions serve a similar role as Linux distributions. This makes it easier to install ROS software and maintain consistent versions through a collection of software.
- Software repository (Repository): ROS relies on websites or hosting services that share open source code and software libraries, where different organizations can publish and share their own robot software and programs.
- ROS Wiki: The ROS Wiki is the primary forum for recording information about the ROS system. Anyone can register an account, contribute their own files, provide corrections or updates, write tutorials, and other actions.
- Bug Ticket System: If you find a problem or want to propose a new feature, ROS provides this resource to do this.
- Mailing list: The ROS user mailing list is the main communication channel about ROS. It can exchange various questions or information from ROS software updates to ROS software use like a forum.
- ROS Answer: Users can use this resource to ask questions
1.3 Communication mechanism
1.3.1、Topic
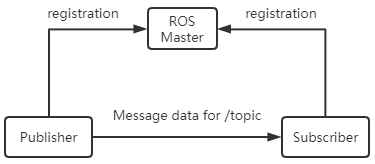
The asynchronous publish-subscribe communication mode is widely used in ros. Topic is generally used for one-way, message flow communication. Topics generally have strong type definitions: a topic of one type can only accept/send messages of a specific data type (message type). Publisher is not required to have type consistency, but when accepting, subscriber will check the md5 of the type and report an error.
1.3.2、Service
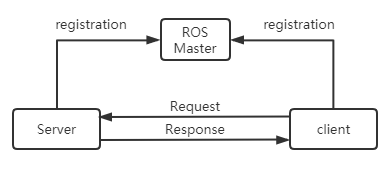
Service is used to handle synchronous communication in ros communication, using server/client semantics. Each service type has two parts: request and response. For the server in the service, ros will not check the name conflict. Only the last registered server will take effect and establish a connection with the client.
1.3.3、Action
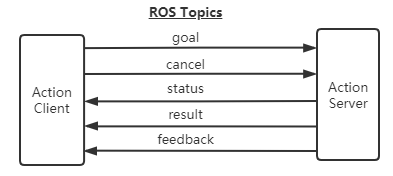
Actions are composed of multiple topics and are used to define tasks. Task definitions include goals (Goal), task execution process status feedback (Feedback), and results (Result). Compiling action will automatically generate 7 structures: Action, ActionGoal, ActionFeedback, ActionResult, Goal, Feedback, and Result structures.
Features of Action:
- A question and answer communication mechanism
- With continuous feedback
- Can be terminated during a mission
- Implementation of message mechanism based on ROS
Action interface:
- goal: publish task goal
- cancel: Request to cancel the task
- status: Notify the client of the current status
- feedback: Monitoring data for periodic feedback task running
- result: Send the execution result of the task to the client and only publish it once.
Comparison of communication mode features
| Features | Topic | Service | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response mechanism | None | Result response | Progress response, result response |
| Synchronicity | Asynchronous | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
| Communication model | Publisher,Subscriber | Client,Server | Client,Server |
| Node correspondence | Many to many | Many(Client)to one(Server) | Many(Client)to one(Server) |
1.4 Common components
launch startup file; TF coordinate transformation; Rviz; Gazebo; QT toolbox; Navigation; MoveIt!
launch:Launch File is a way to start multiple nodes at the same time in ROS.It can also automatically start the ROS Master node manager, and can implement various configurations of each node, providing great convenience for the operation of multiple nodes.
TF coordinate transformation: There are often a large number of component elements in the robot body and the robot's working environment. The positions and postures of different components are involved in robot design and robot applications. TF is a function package that allows users to track multiple coordinate systems over time , which uses a tree data structure to buffer and maintain coordinate transformation relationships between multiple coordinate systems based on time, which can help developers complete coordinate transformations such as points and vectors between coordinate systems at any time.
QT toolbox: In order to facilitate visual debugging and display, ROS provides a Qt-based background graphics tool suite - rqt_common_plugins,It contains many practical tools: log output tool (rqt_console), calculation graph visualization tool (rqt_graph), data drawing tool (rqt_plot), parameter dynamic configuration tool (rqt_reconfigure)
Rviz: rviz is a 3D visualization tool that is well compatible with various robot platforms based on the ROS software framework. In rviz, you can use XML to describe the size, quality, position, material, joints and other attributes of any physical objects such as robots and surrounding objects, and present them in the interface. At the same time, rviz can also display robot sensor information, robot motion status, changes in the surrounding environment, etc. in a graphical manner in real time.
Gazebo: Gazebo is a powerful three-dimensional physics simulation platform with a powerful physics engine, high-quality graphics rendering, convenient programming and graphics interfaces, and most importantly, it is open source and free. Although the robot model in Gazebo is the same as the model used by rviz, the physical properties of the robot and the surrounding environment, such as mass, friction coefficient, elastic coefficient, etc., need to be added to the model. The robot's sensor information can also be added to the simulation environment in the form of plug-ins and displayed in a visual manner.
Navigation: Navigation is a two-dimensional navigation function package of ROS. Simply put, it calculates safe and reliable robot speed control instructions through the navigation algorithm based on the information flow of the input odometer and other sensors and the global position of the robot.
Moveit:Moveit!Function package is the most commonly used tool package, mainly used for trajectory planning. Move it! The configuration assistant is used to configure some files that need to be used in planning, which is very important.
1.5 Release version
Reference link:http://wiki.ros.org/Distributions
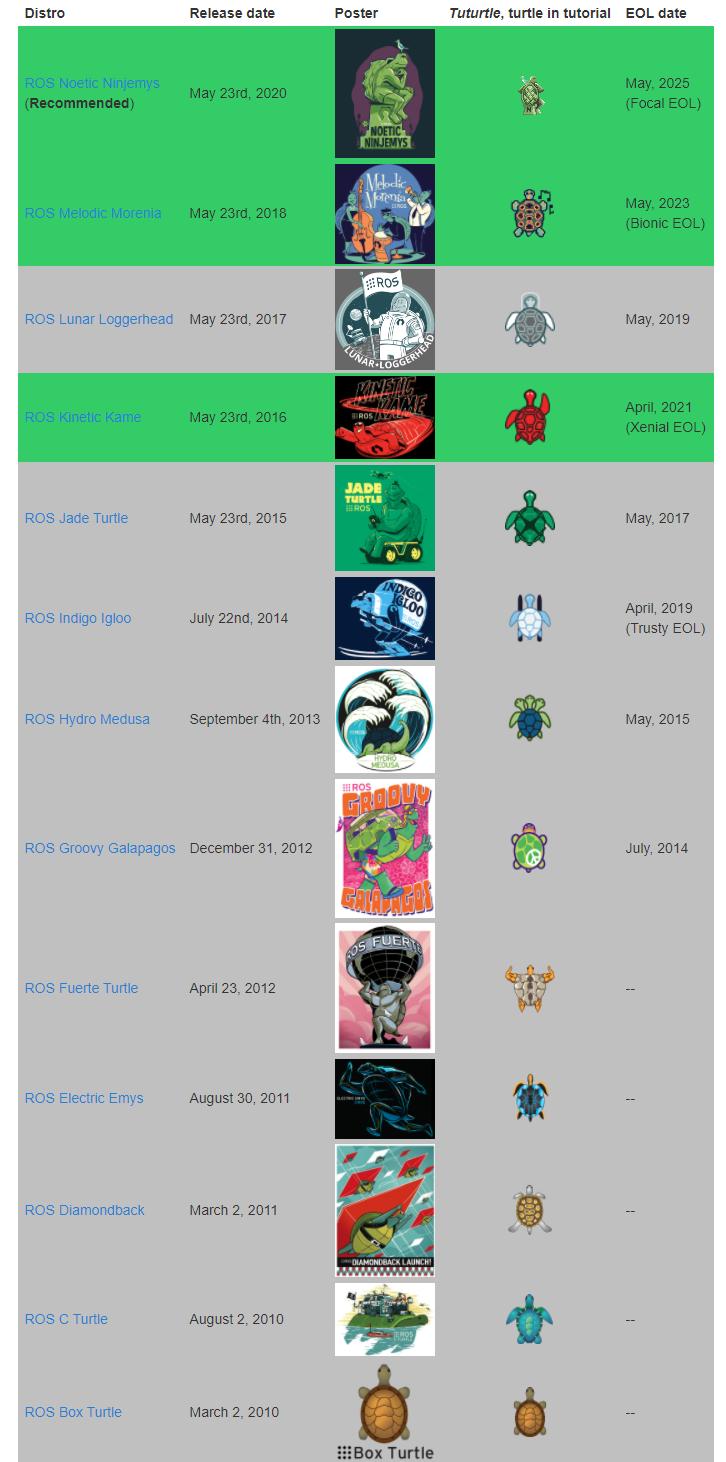
ROS distribution refers to the version of the ROS software package.The concept of it and Linux distribution version (such as Ubuntu) similar.The purpose of a ROS distribution is to allow developers to work with a relatively stable codebase until they are ready to upgrade everything.Therefore, after each release version is launched, ROS developers usually only fix the bugs in this version and provide a small number of improvements to the core software package.As of October 2019, the version names, release times and version life cycles of major ROS releases are as shown in the following table:
| Version name | Release date | Version lifecycle | Operating system platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROS Noetic Ninjemys | May 2020 | May 2023 | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| ROS Melodic Morenia | May 23, 2018 | May 2023 | Ubuntu 17.10, Ubuntu 18.04, Debian 9, Windows 10 |
| ROS Lunar Loggerhead | May 23, 2017 | May 2019 | Ubuntu 16.04, Ubuntu 16.10, Ubuntu 17.04,Debian 9 |
| ROS Kinetic Kame | May 23, 2016 | April 2021 | Ubuntu 15.10, Ubuntu 16.04, Debian 8 |
| ROS Jade Turtle | May 23, 2015 | May 2017 | Ubuntu 14.04, Ubuntu 14.10, Ubuntu 15.04 |
| ROS Indigo Igloo | July 22, 2014 | April 2019 | Ubuntu 13.04, Ubuntu 14.04 |
| ROS Hydro Medusa | September 4, 2013 | May 2015 | Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 12.10, Ubuntu 13.04 |
| ROS Groovy Galapagos | December 31, 2012 | July 2014 | Ubuntu 11.10, Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 12.10 |
| ROS Fuerte Turtle | April 23, 2012 | -- | Ubuntu 10.04, Ubuntu 11.10, Ubuntu 12.04 |
| ROS Electric Emys | August 30, 2011 | -- | Ubuntu 10.04, Ubuntu 10.10, Ubuntu 11.04, Ubuntu 11.10 |
| ROS Diamondback | March 2, 2011 | -- | Ubuntu 10.04, Ubuntu 10.10, Ubuntu 11.04 |
| ROS C Turtle | August 2, 2010 | -- | Ubuntu 9.04, Ubuntu 9.10, Ubuntu 10.04, Ubuntu 10.10 |
| ROS Box Turtle | March 2, 2010 | -- | Ubuntu 8.04, Ubuntu 9.04, Ubuntu 9.10, Ubuntu 10.04 |