Light up the LED
Light up the LED1. Learning objectives2. Hardware construction3. Experimental steps1. Open the SYSCONFIG configuration tool2. Parameter settings2.1 Set port parameters2.2 Set pin parameters2.3 Save and update the configuration file3. Write the program4. Compile4. Program Analysis5. Experimental phenomenon
1. Learning objectives
- Learn the basic use of the pins of the MSPM0G3507 motherboard.
- Understand how to control the onboard LED lights.
2. Hardware construction
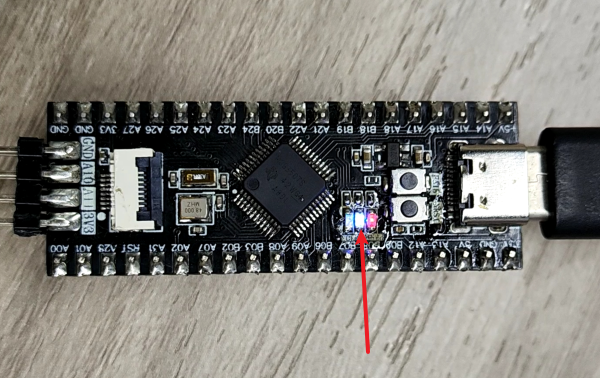
This course does not require additional hardware equipment, and can directly use the onboard LED lights on the MSPM0G3507 motherboard.
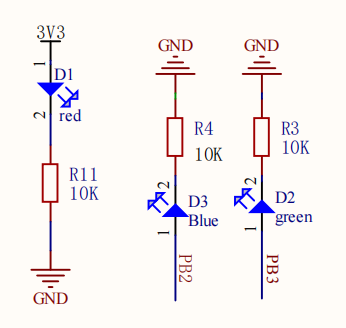
We set up two LED user lights on the motherboard, and users can DIY their functions. Take LED1 as an example below.
MSPM0G3507 main control diagram
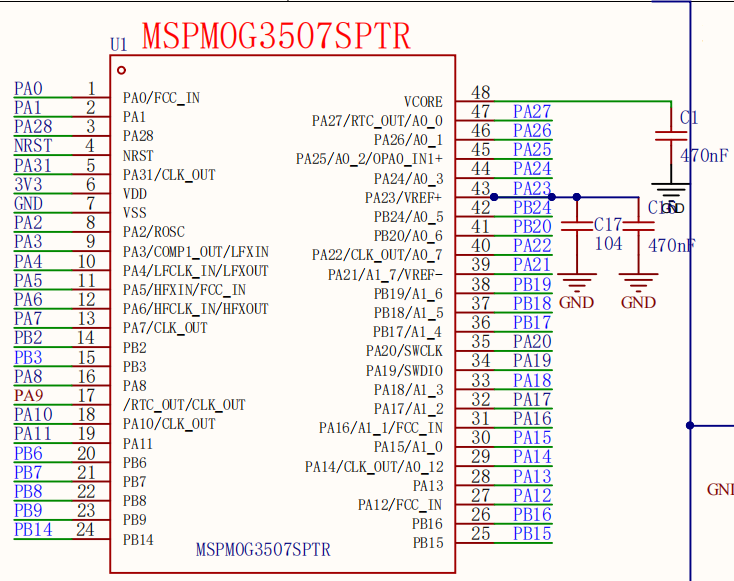
LED part schematic diagram
3. Experimental steps
1. Open the SYSCONFIG configuration tool
Open the blank project empty in the SDK in KEIL.
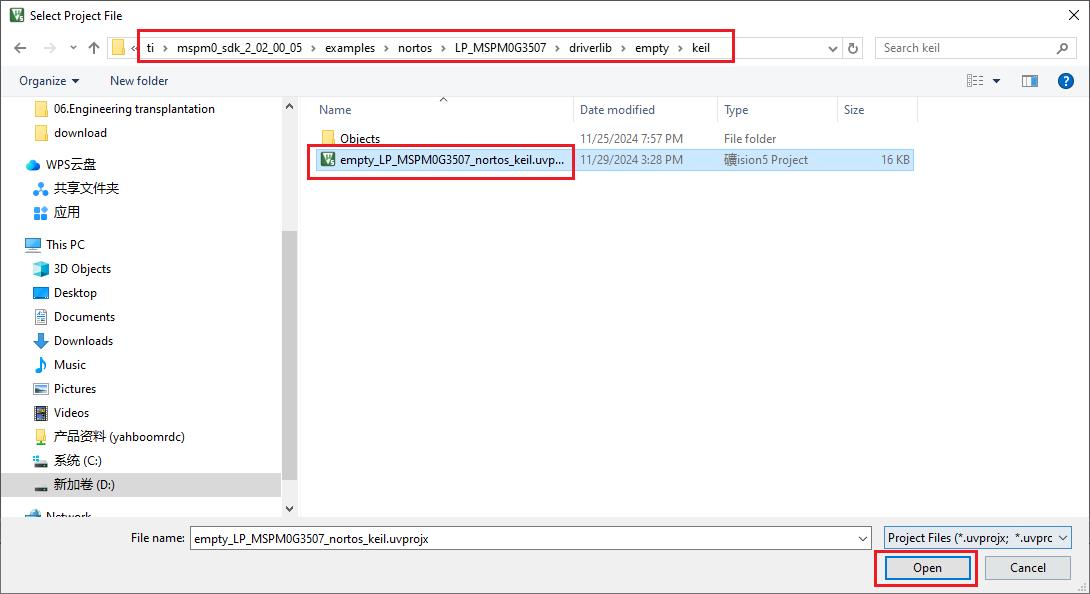
Open after selecting, open the empty.syscfg file in the keil interface, when the empty.syscfg file is open, then select to open the SYSCONFIG GUI interface in the Tools bar.
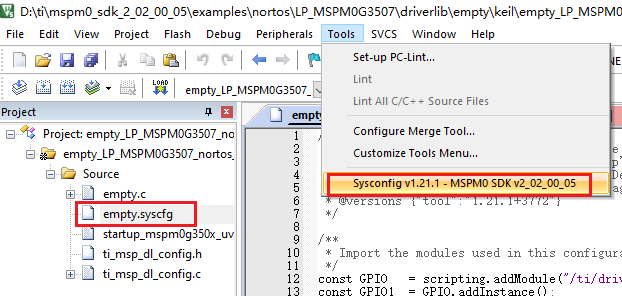
In SYSCONFIG, select MCU peripherals on the left, find the GPIO option and click to enter. Click ADD in GPIO to add a group of GPIO.
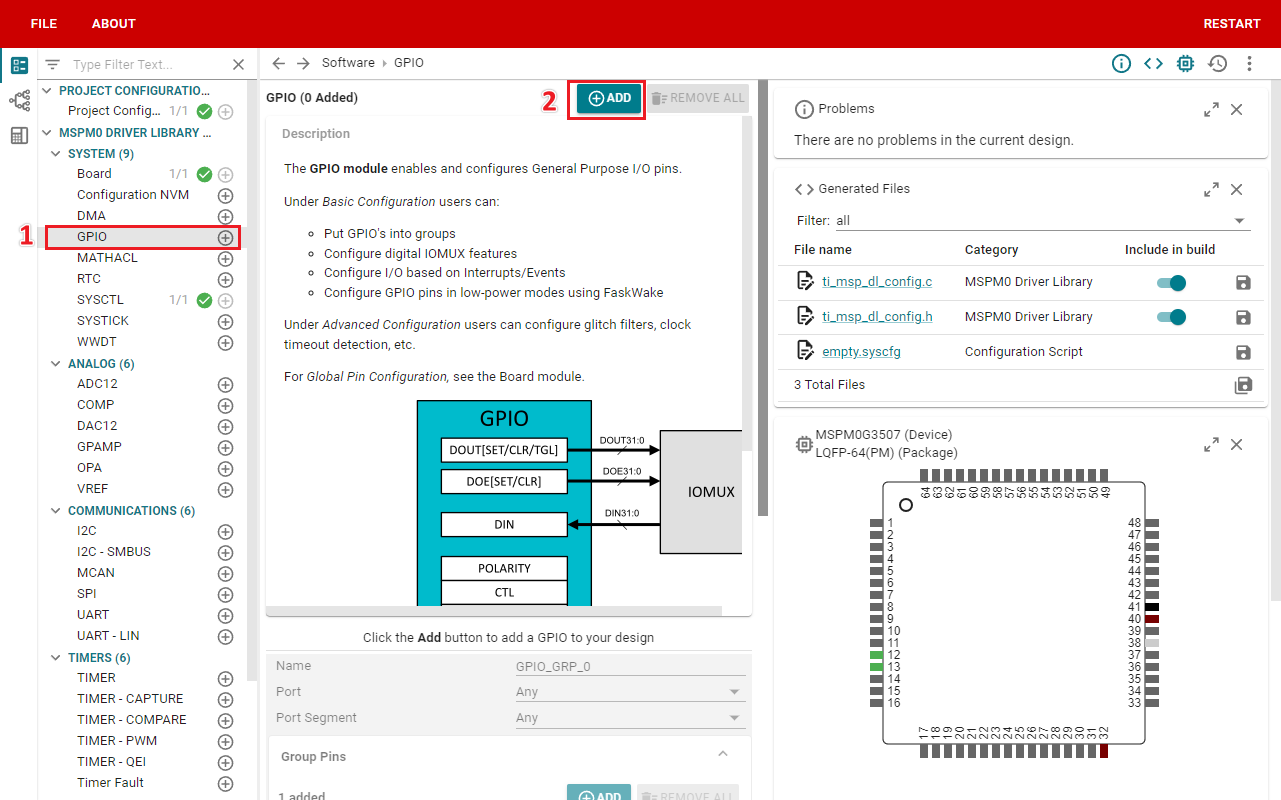
2. Parameter settings
2.1 Set port parameters
Set GPIO parameters and name the pin LED1
From the LED schematic, we can see that the port where LED1 is located is PB2, so set the Port to PORTB.
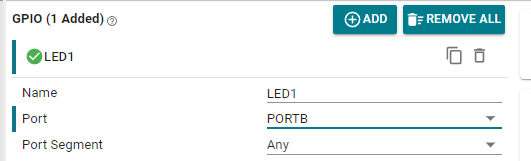
Parameter description:
Name: Custom name of the GPIO instance. By default, the name starts with a numeric suffix of "0"; we can customize the name to reflect the purpose of the module (for example, name the GPIO "LED1" so that we know that this pin is specifically used to control LED1).
Port: The port where the GPIO instance is located. The LED is connected to the GPIOB2 pin, so only PORTB can be selected.
Port Segment: Set the pull-up and pull-down resistors on the port. Note that it is the pull-up and pull-down of the port, which sets the entire GPIOB port.
2.2 Set pin parameters
Set the pin to output mode, set the pin to output low level by default, set the pin to pull-down mode, set the pin to GPIOB_2 pin, and do not enable interrupt events.
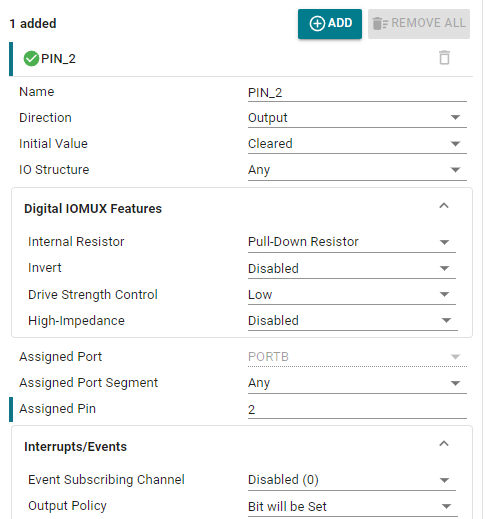
Parameter description:
Name: User-defined pin name, set to PIN_2.
Direction: Set the pin mode, input and output. Here we control the LED light and select the output mode.
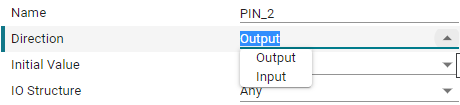
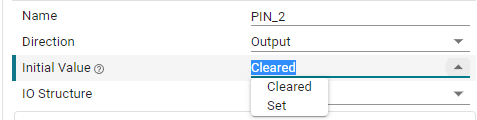
Initial Value: Set the initial state of the pin. It can only be set when configured as output mode. There are two options, clear and set. Clear means output low level, set means output high level.
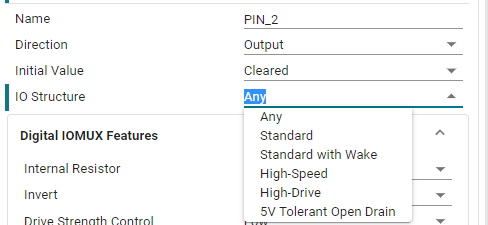
IO Structure: Set the IO structure. There are multiple options, default (Any), standard (Standard), wake up (Standard with Wake), high speed (High-Speed) and can tolerate 5V (5V Tolerant Open Drain) structure.
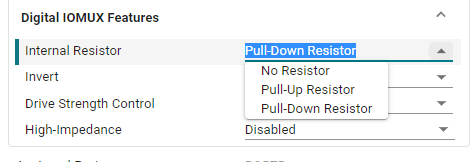
Internal Resistor: Set the pull-up and pull-down resistors of the pin. There are three options: no setting, pull-up setting, and pull-down setting. Here, the pull-down resistor is selected according to the connection method of the LED light.
Assigned Pin: Set the pin number. Fill in the corresponding pin number for the pin to be controlled. For example, if the LED in the development board is connected to GPIOB2, fill in 2.
2.3 Save and update the configuration file
Click SAVE to save the configuration in SYSCONFIG, then turn off SYSCONFIG and return to keil.
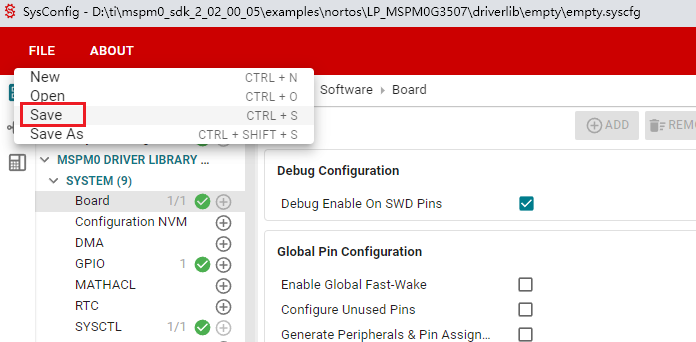
Select Yes to All in the pop-up window
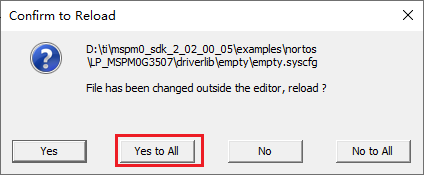
After that, we can see that the empty.syscfg file is updated with the parameters we set.
We also need to confirm whether the .c and .h files are updated. Compile directly, and the compilation will be automatically updated to keil. If there is no update, we can also copy the file content in SYSCONFIG.
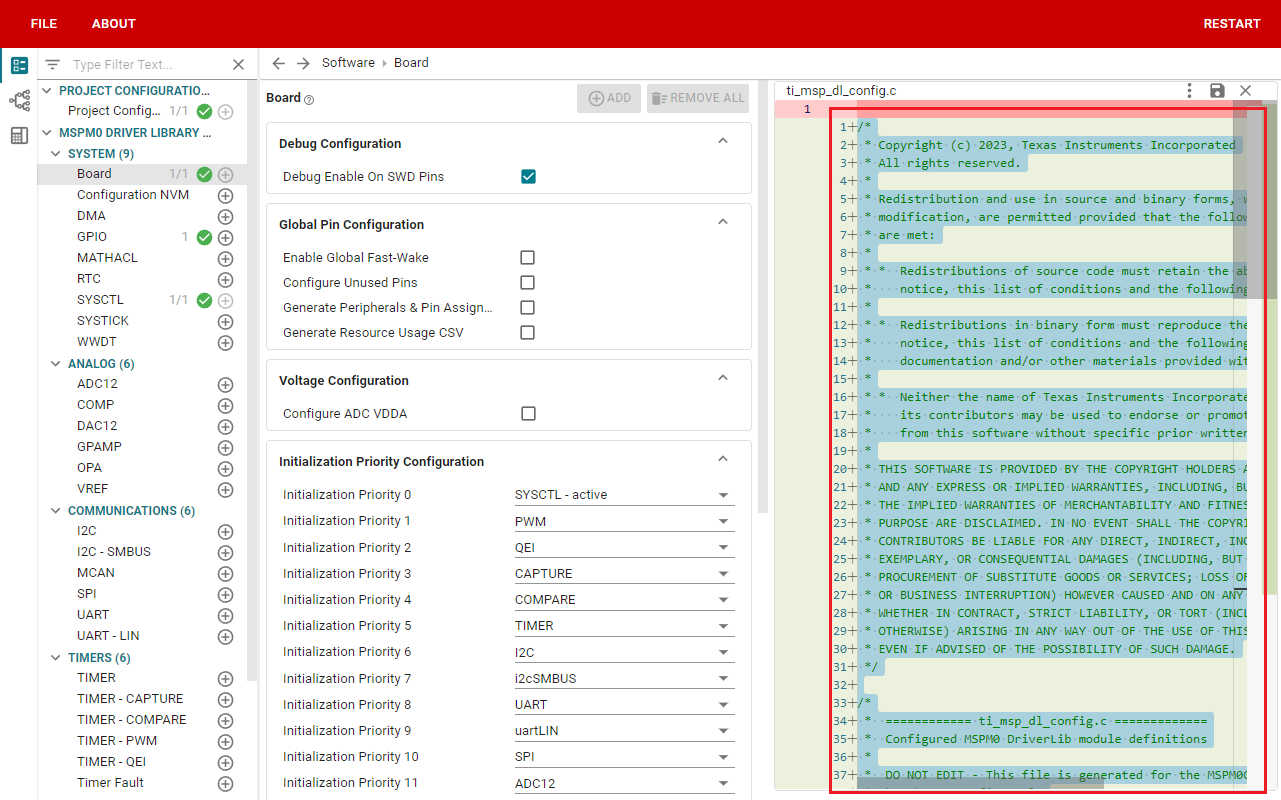
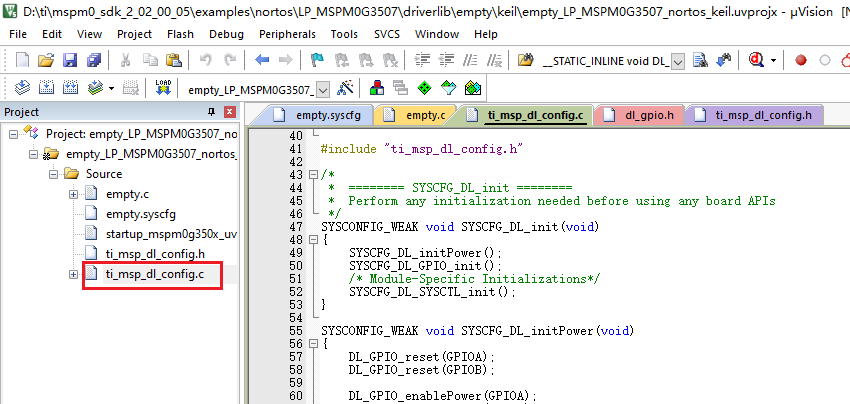
.h file is the same as above, you can copy the file content in SYSCONFIG.
3. Write the program
In the empty.c file, write the following code
x#include "ti_msp_dl_config.h"//自定义延时(不精确) Custom delay (not precise)void delay_ms(unsigned int ms){ unsigned int i, j; // 下面的嵌套循环的次数是根据主控频率和编译器生成的指令周期大致计算出来的, // 需要通过实际测试调整来达到所需的延时。 // The number of nested loops below is roughly calculated based on the master control frequency and the instruction cycle generated by the compiler,and needs to be adjusted through actual testing to achieve the required delay. for (i = 0; i < ms; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 8000; j++) { // 仅执行一个足够简单以致于可以预测其执行时间的操作 // Perform only one operation that is simple enough to predict its execution time __asm__("nop"); // "nop" 代表“无操作”,在大多数架构中,这会消耗一个或几个时钟周期 "nop" stands for "no operation", which on most architectures consumes one or a few clock cycles } }}int main(void){ SYSCFG_DL_init(); while (1) { DL_GPIO_clearPins(LED1_PORT,LED1_PIN_2_PIN);//输出低电平 Output low level delay_ms(1000);//延时大概1S Delay about 1S DL_GPIO_setPins(LED1_PORT,LED1_PIN_2_PIN); //输出高电平 Output high level delay_ms(1000);//延时大概1S Delay about 1S }}4. Compile
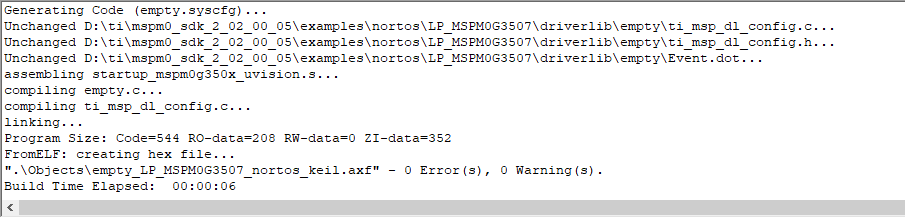
Click the Rebuild icon. The following prompt appears, indicating that the compilation is complete and there are no errors.
4. Program Analysis
- dl_gpio.h
xxxxxxxxxx/** * @brief Set a group of GPIO pins * * @param[in] gpio Pointer to the register overlay for the peripheral * @param[in] pins Pins to set high. Bitwise OR of @ref DL_GPIO_PIN. */__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_setPins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins){ gpio->DOUTSET31_0 = pins;}/** * @brief Clear a group of GPIO pins * * @param[in] gpio Pointer to the register overlay for the peripheral * @param[in] pins Pins to clear. Bitwise OR of @ref DL_GPIO_PIN. */__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_clearPins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins){ gpio->DOUTCLR31_0 = pins;}/** * @brief Toggle a group of GPIO pins * * @param[in] gpio Pointer to the register overlay for the peripheral * @param[in] pins Pins to toggle. Bitwise OR of @ref DL_GPIO_PIN. */__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_togglePins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins){ gpio->DOUTTGL31_0 = pins;}__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_setPins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins): This function outputs a high level for the control pin.
__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_clearPins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins): This function outputs a low level for the control pin.
__STATIC_INLINE void DL_GPIO_togglePins(GPIO_Regs* gpio, uint32_t pins): This function flips the level of the control pin. If it was originally a high level, it will become a low level. If it was originally a low level, it will become a high level.
- empty.c
xxxxxxxxxxint main(void){ SYSCFG_DL_init(); while (1) { DL_GPIO_clearPins(LED1_PORT,LED1_PIN_2_PIN);//输出低电平 Output low level delay_ms(1000);//延时大概1S Delay about 1S DL_GPIO_setPins(LED1_PORT,LED1_PIN_2_PIN); //输出高电平 Output high level delay_ms(1000);//延时大概1S Delay about 1S }}Set PB2 to output low level, delay about 1s, then output high level, and delay about 1s again. Repeat this process.
5. Experimental phenomenon
After the program is downloaded, you can see that the LED1 light on the MSPM0 development board is lit and flashes every about 1s.