ROS1 Use Cases
Aurora is a newly developed sensor for integrated positioning and mapping created by SLAMTEC that integrates laser, vision, inertial navigation and deep learning technologies. The sensor does not require external dependencies and can provide six-degree-of-freedom positioning capabilities for indoor and outdoor three-dimensional high-precision mapping machines as soon as it is turned on.
1. Development environment requirements
Based on the Ubuntu 20.04 operating system, with ROS1 software package and compiler Gcc9.
2. Download radar SDK
Download link:SLAMTEC Product Documents Download and Technical Support
Two versions of the SDK have been placed in the attachment. Use the corresponding version according to the gcc version of your environment.
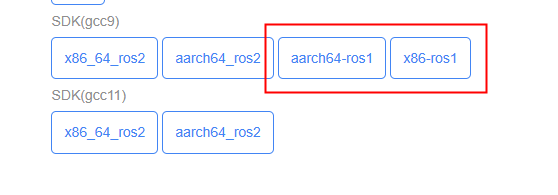
Aurora ROS1 SDK contains resources and codes that you may use during development. Its directory structure is organized as follows:
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
| docs | Reference Documents |
| src | Source Code |
| --slamware_ros_sdk | ROS SDK Source Code Package |
| --slamware_sdk | SDK Related Header Files and Library Files |
| --aurora_remote_public | Aurora Related Header Files and Library Files |
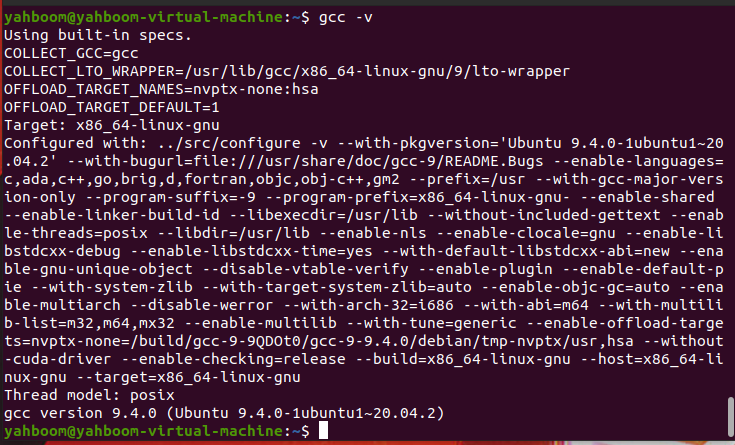
Terminal input, the following content can be used to view the gcc version
gcc -v
3. Hardware requirements
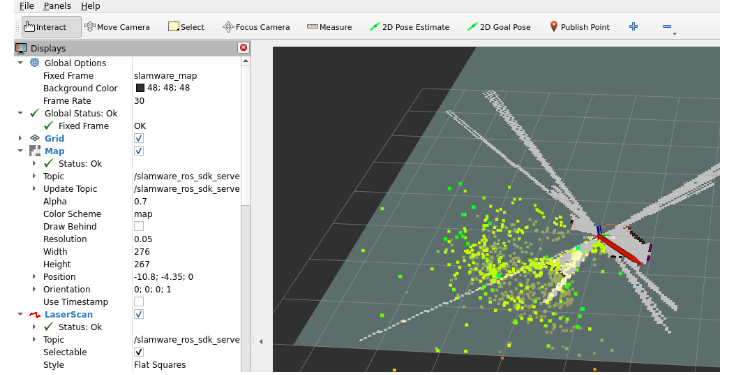
To use ROS1 SDK, you need an Auraro-based spatial mapping device, turn it on and configure the appropriate IP address, and the virtual machine needs to connect to the hotspot of the aurora radar. The slamware_ros_sdk_server_node node will try to connect to the device after it is started.
4. Environment setup
4.1. Create a workspace first
xxxxxxxxxxmkdir -p ~/ros_Ws/srccd ~/ros_ws/srcPut the sdk source code you just downloaded in the src working directory where the source code is stored,
4.2 Compile
xxxxxxxxxxcd ..catkin_makeIt is normal to have warnings when compiling slamware_sdk,

4.3 Configure the workspace system environment
xxxxxxxxxxsource devel/setup.bashIn order to automatically load the environment every time the terminal is started: add the following command to ~/.bashrc
xxxxxxxxxxecho "source ~/ros_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc4.4 Configure the system environment for dynamic libraries for image building
Since aurora_remote_public_lib is a dynamic library, you need to add the platform path to LD_LIBRARY_PATH. For example, if you place slamware_ros1_sdk_linux-x86_64-gcc9 in the ~/ros_ws/sec folder, you need to add the following command to ~/.bashrc
Note: If you download the SDK for the aarch64 environment, the corresponding name should be changed to slamware_ros1_sdk_linux-aarch64-gcc9.
xxxxxxxxxxexport LD_LIBRARY_PATH=~/ros_ws/src/aurora_ros1_sdk_linux_x86_gcc9/src/aurora_remote_public/lib/linux_x86_64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH4.5 Start the graph building node
If the Aurora device is in AP mode, connect to the Aurora WIFI and start the node
xxxxxxxxxxroslaunch slamware_ros_sdk slamware_ros_sdk_server_and_view.launch ip_address:=192.168.11.1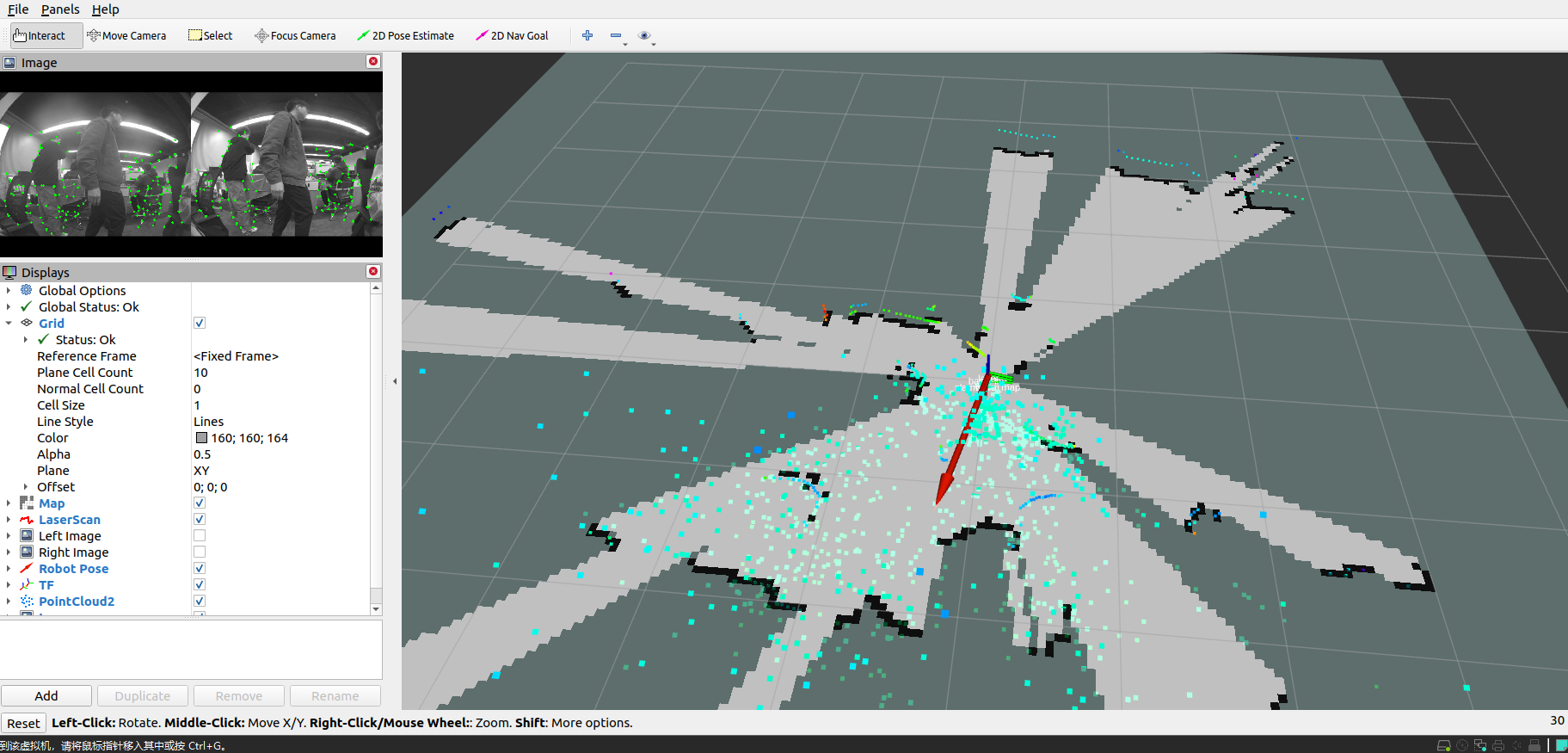
Raspberry Pi 5, X5, Jetson nano version:
If it is the Raspberry Pi desktop version and Jetson nano, x5 desktop version, after successfully booting up, connect the external monitor to the hotspot of Aurora radar to the motherboard, as shown below,
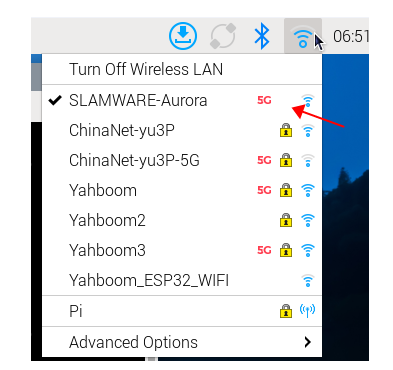
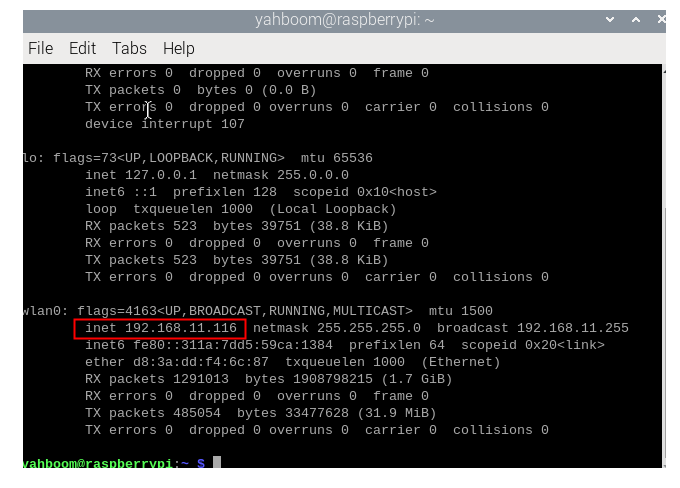
Then enter ifconfig in the terminal to view the ip address under the current hotspot, and then use this address for vnc remote desktop connection, (the premise is that the computer must also be connected to the hotspot emitted by Aurora radar)

Enter docker in advance and enter in the terminal
xxxxxxxxxxsh ros1_noetic.sh
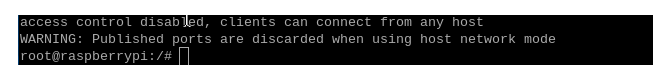
If the following interface appears, it means that you have successfully entered docker.
Then enter in the docker terminal,
x
ros2 launch slamware_ros_sdk slamware_ros_sdk_server_and_view.launch ip_address:=192.168.11.1If successful, you can view the map building screen.