Image scaling
In OpenCV, the function for image scaling is: cv2.resize(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, Size, fx, fy, interpolation)
Code path:
x~/dofbot_pro/dofbot_opencv/scripts/2.Transform/01_zoom_pic.ipynb
Parameter explanation:
| InputArray src | Input image |
|---|---|
| OutputArray dst | Output image |
| Size | Output image size |
| fx, fy | Scaling coefficients along the x-axis and y-axis |
| interpolation | Interpolation method |
Option interpolation method used:
| INTER_NEAREST | Nearest neighbor interpolation |
|---|---|
| INTER_LINEAR | Bilinear interpolation (default setting) |
| INTER_AREA | Resample using pixel area relations. |
| INTER_CUBIC | Bicubic interpolation of 4x4 pixel neighborhood |
| INTER_LANCZOS4 | Lanczos interpolation of 8x8 pixel neighborhood |
Note:
The output size format is (width, height)
The default interpolation method is: bilinear interpolation
The main code is as follows:
x# 1 load 2 info 3 resize 4 checkimport cv2import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Python 2D drawing library
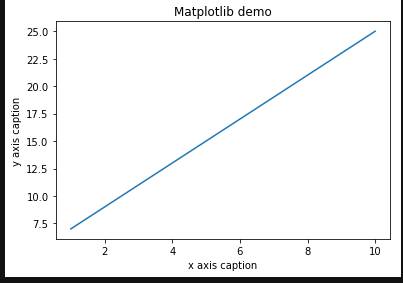
# Read the original imageimg = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg')# Print the image sizeprint(img.shape)# Assign the image height and width to x, y respectivelyx, y = img.shape[0:2]
# Scale to half of the original size, the output size format is (width, height)img_test1 = cv2.resize(img, (int(y / 2), int(x / 2)))# cv2.imshow('resize0', img_test1)# cv2.waitKey()
# Nearest neighbor interpolation scaling
# Scale to one-fourth of the originalimg_test2 = cv2.resize(img, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25, interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)# cv.imshow('resize1', img_test2)# cv.waitKey()# cv.destroyAllWindows()img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)dst1 = cv2.cvtColor(img_test1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)dst2 = cv2.cvtColor(img_test2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# Display original imageplt.imshow(img)plt.show()After execution, you can see that the image is 800*800
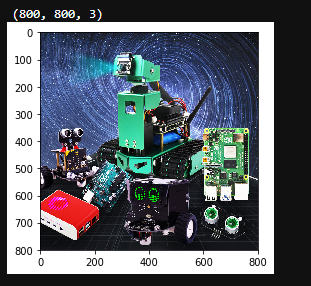
xxxxxxxxxx# Display zoom 1/2plt.imshow(dst1)plt.show()After execution, you can see that the image is 400*400, which is half the size
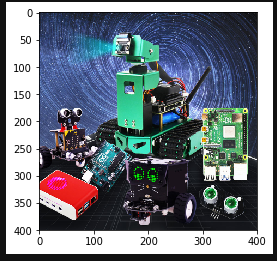
xxxxxxxxxx# Display zoom 1/4 Neighbor interpolation method zoomplt.imshow(dst2)plt.show()After execution, you can see that the image is 200*200, which is one quarter the size
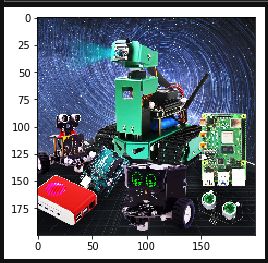
Next, let's talk about matplotlib: Python's 2D drawing library.
Reference tutorial: https://www.runoob.com/numpy/numpy-matplotlib.html
xxxxxxxxxximport numpy as npfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltx = np.arange(1,11)y = 2 * x + 5plt.title("Matplotlib demo")plt.xlabel("x axis caption")plt.ylabel("y axis caption")plt.plot(x,y)plt.show()