1. MoveIt2 configuration
Note: The factory image of this course has been configured. If you use the factory image system, you can skip the moveit configuration course.
1.1. Install MoveIt2
xxxxxxxxxxsudo apt install ros-humble-moveit*
The Jetson Orin series motherboard can run Moveit2 related cases directly on the motherboard, and the overall fluency is acceptable!
Open another terminal.
1.2. Start the assistant
Start MoveIt Setup Assistant:
xxxxxxxxxxros2 launch moveit_setup_assistant setup_assistant.launch.py
For the first time, you can choose to create a new MoveIt configuration package. For later simple modifications, you can choose to compile the existing MoveIt software package:
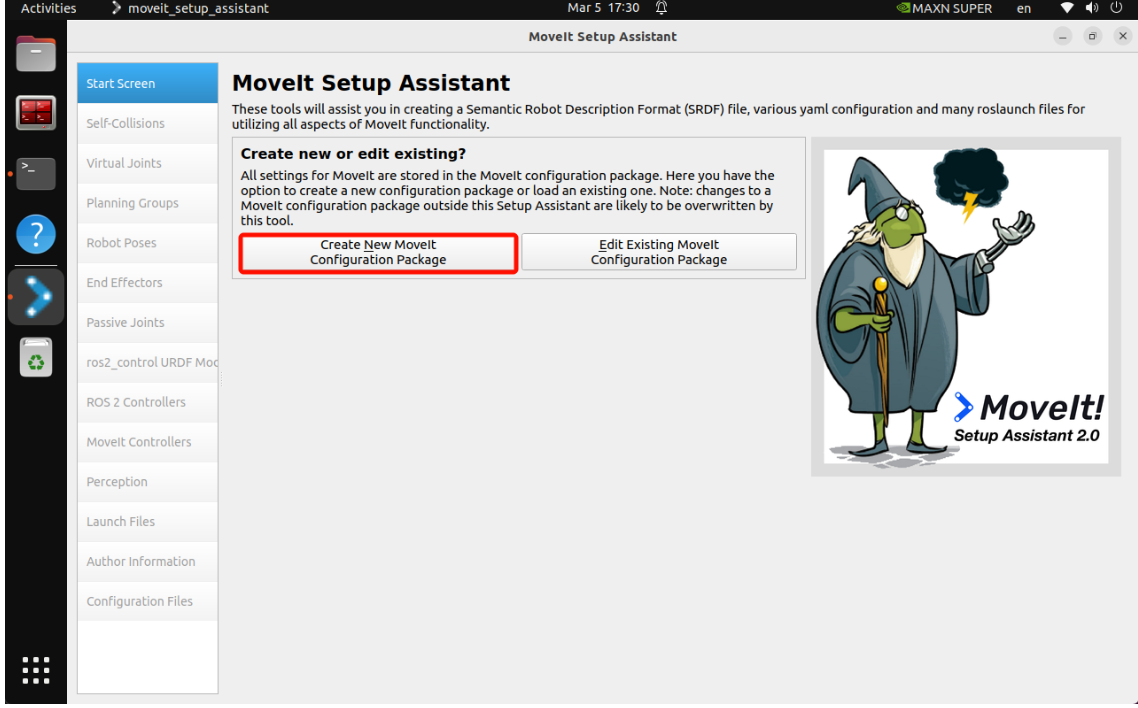
To create a new MoveIt configuration package, you need to import the robot's URDF model: Simply importing the URDF model file into the MoveIt assistant will result in an error. You need Use the compiled software package (jetcobot_description) URDF file path
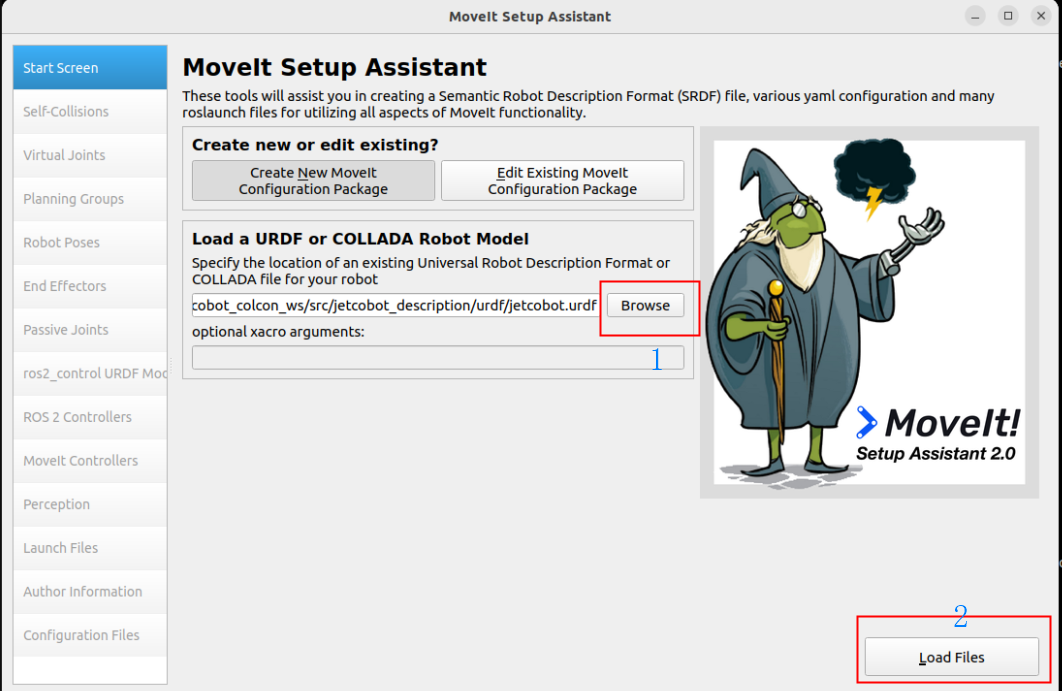
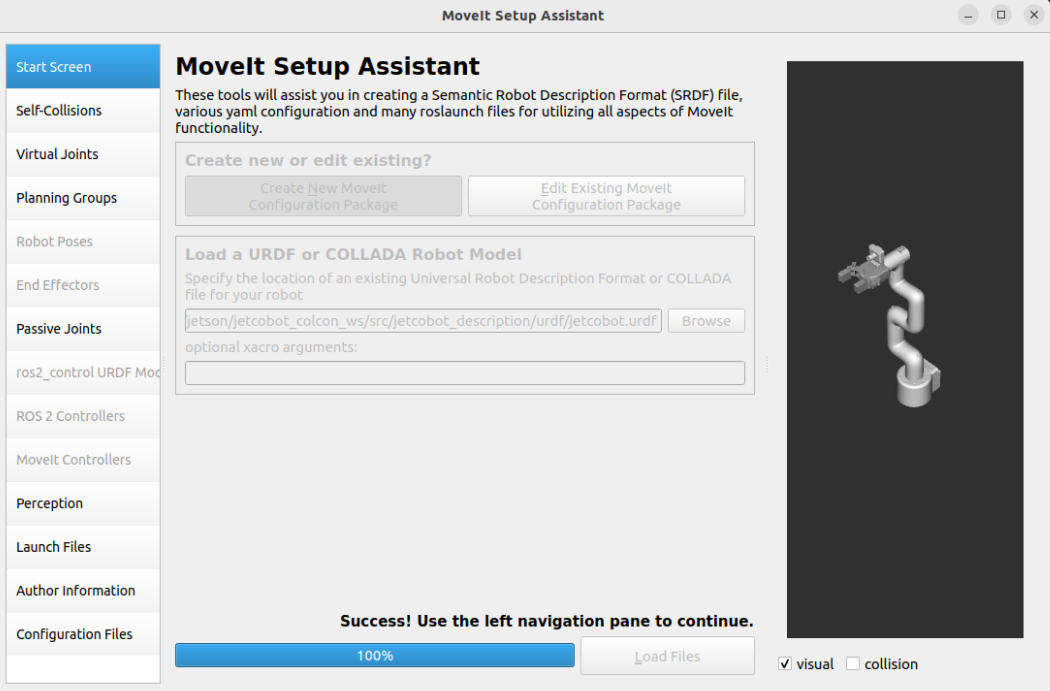
After selecting the URDF file, click Load File, and the MoveIt assistant will display the robot model:
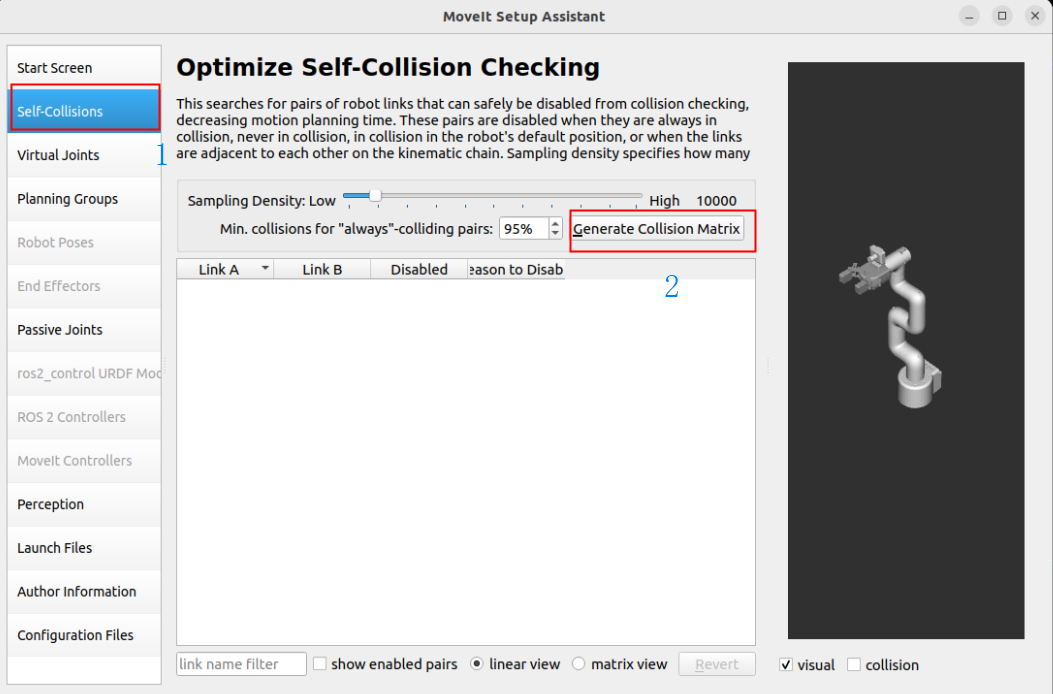
1.3, Collision Detection
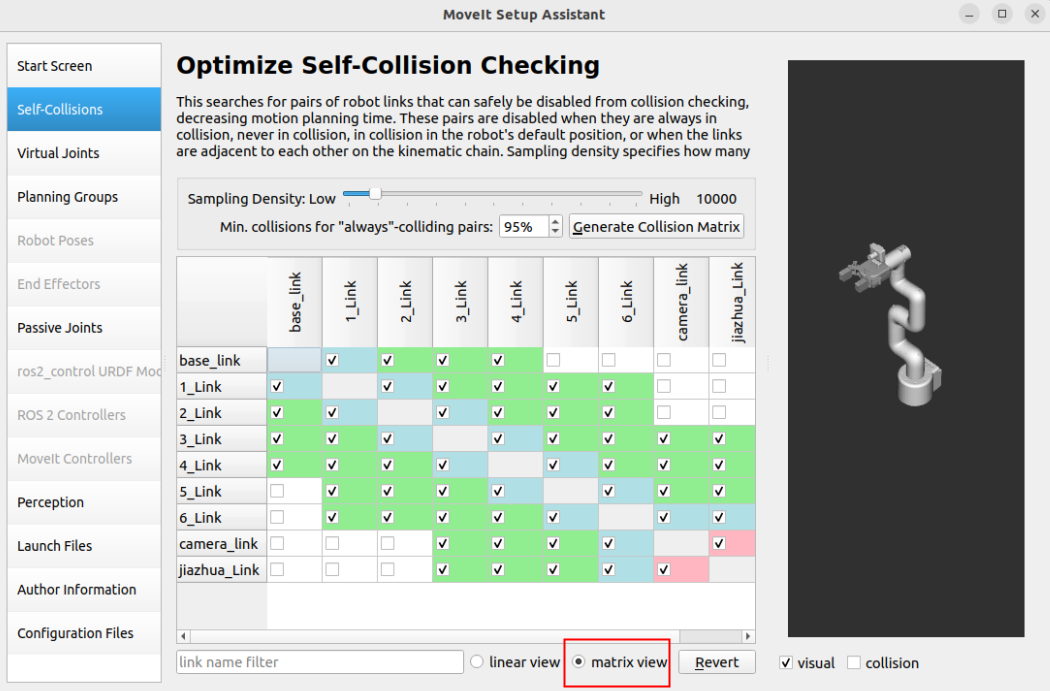
The self-collision matrix is a function used to optimize motion planning. Its main function is to generate a matrix to describe whether collisions may occur between the various links in the robot model.
This matrix can help the motion planner avoid unnecessary collision detection when planning the path, thereby improving planning efficiency.
The self-collision matrix can be automatically generated by clicking the MoveIt Setup Assistant option:
1.4. Virtual joints
A virtual joint is a tool used to define the relationship between a robot model and the outside world.
Virtual joints are usually used to describe the connection between the robot base and a fixed reference system (such as the world coordinate system).
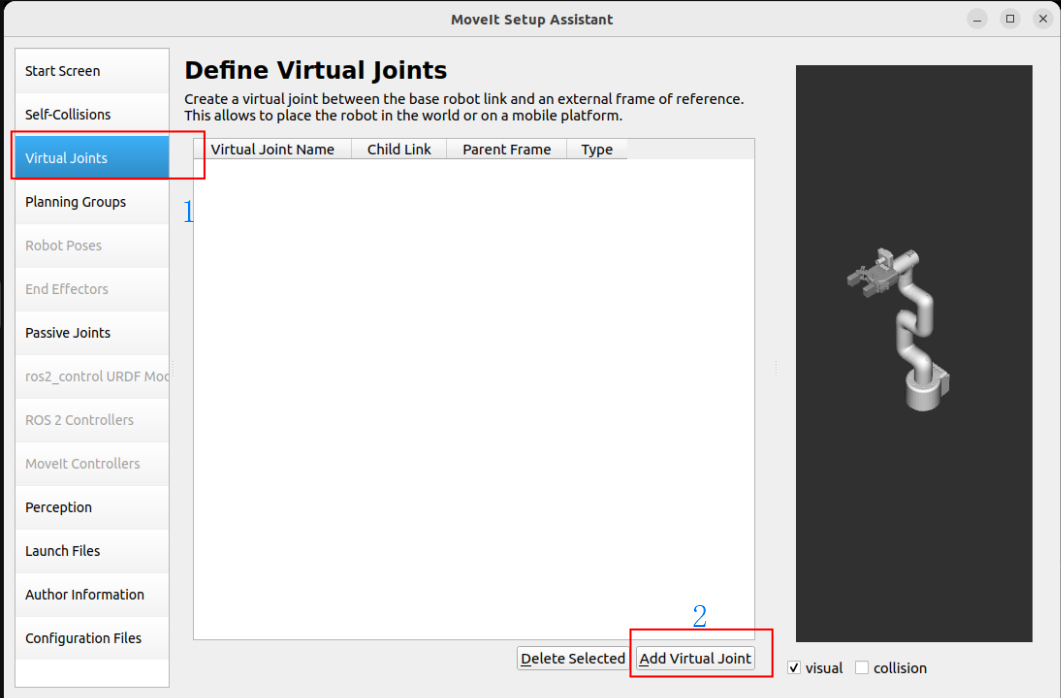
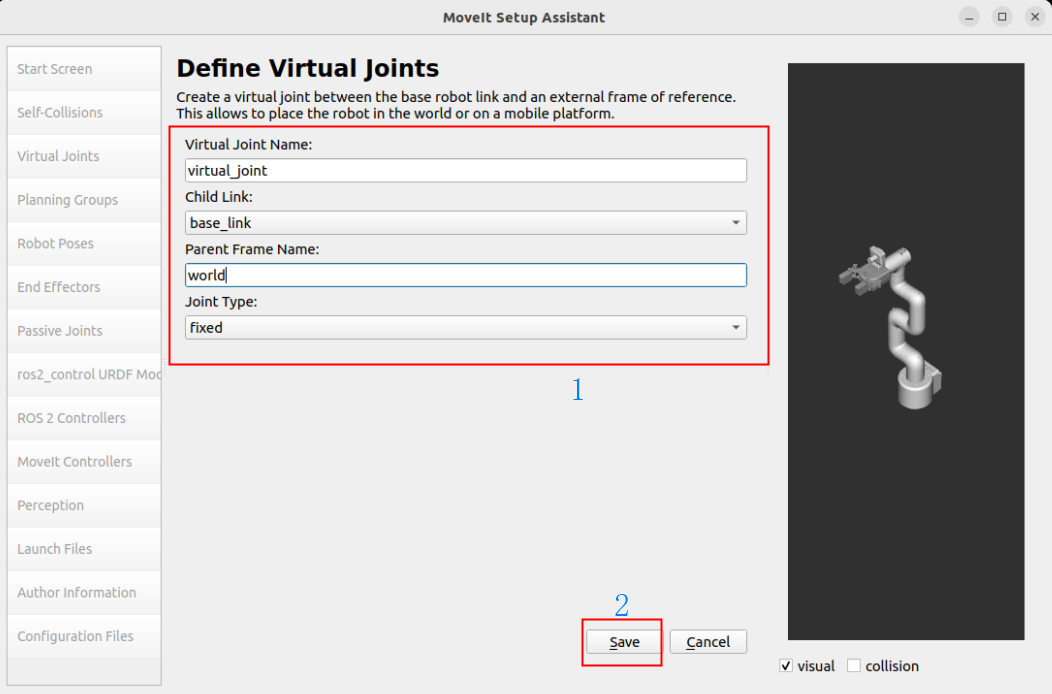
Fix the robot base link base_link and world:
Virtual Joint Name: virtual_joint
Child Link: base_link
Parent Frame Name: world
Joint Type: fixed
1.5, Motion Planning Group
The planning group is a key step in configuring the robot motion planning.
The planning group defines which joints and links in the robot can move together and how to plan their motion.
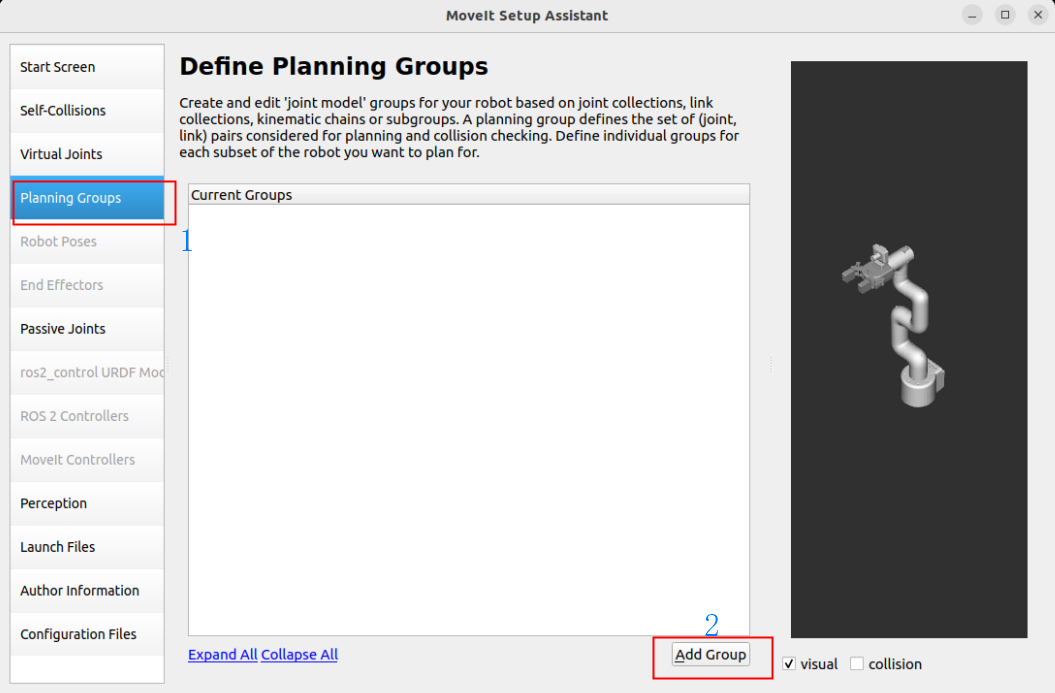
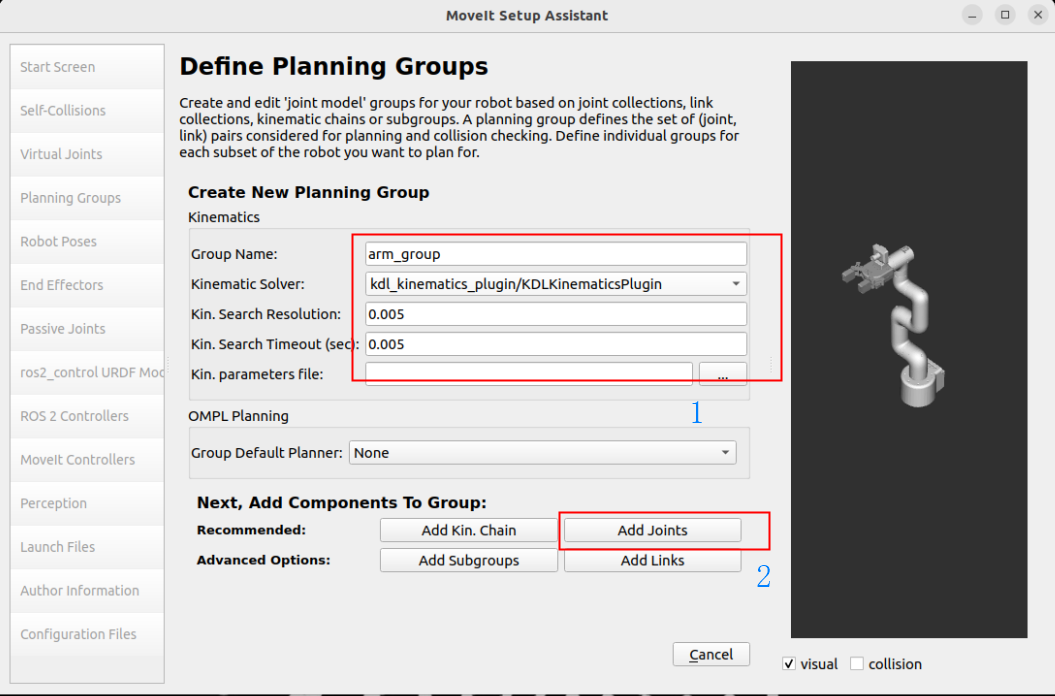
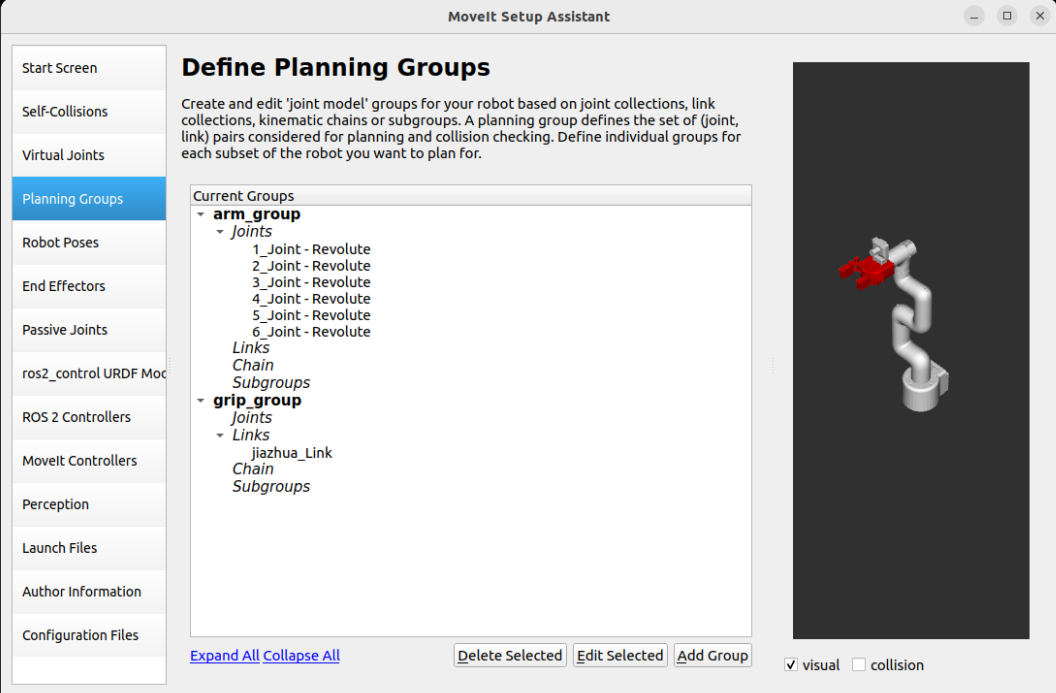
Planning robot arm group: arm_group
Group Name: arm_group
Kinematic Solver: kdl_kinematics_plugin/KDLKinematicsPlugin
Kin. Search Resolution (sampling density of joint space): 0.005
Kin. Search Timeout (solution time): 0.005
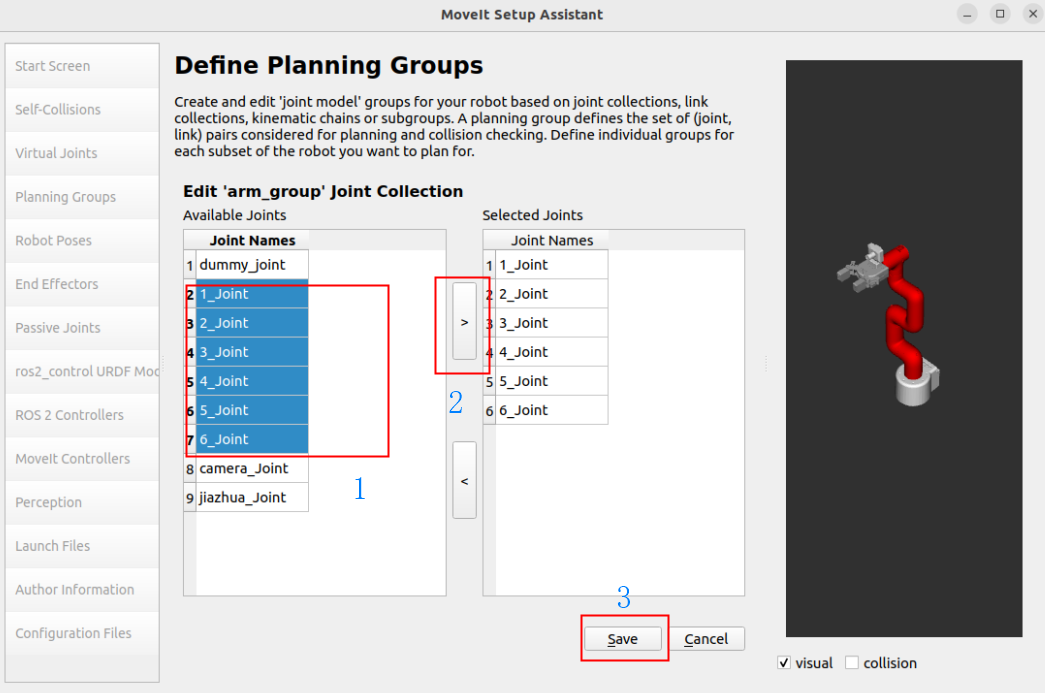
Add Joints: Select the joints of the robot arm
Joints: 1_Joint, 2_Joint, 3_Joint, 4_Joint, 5_Joint, 6_Joint
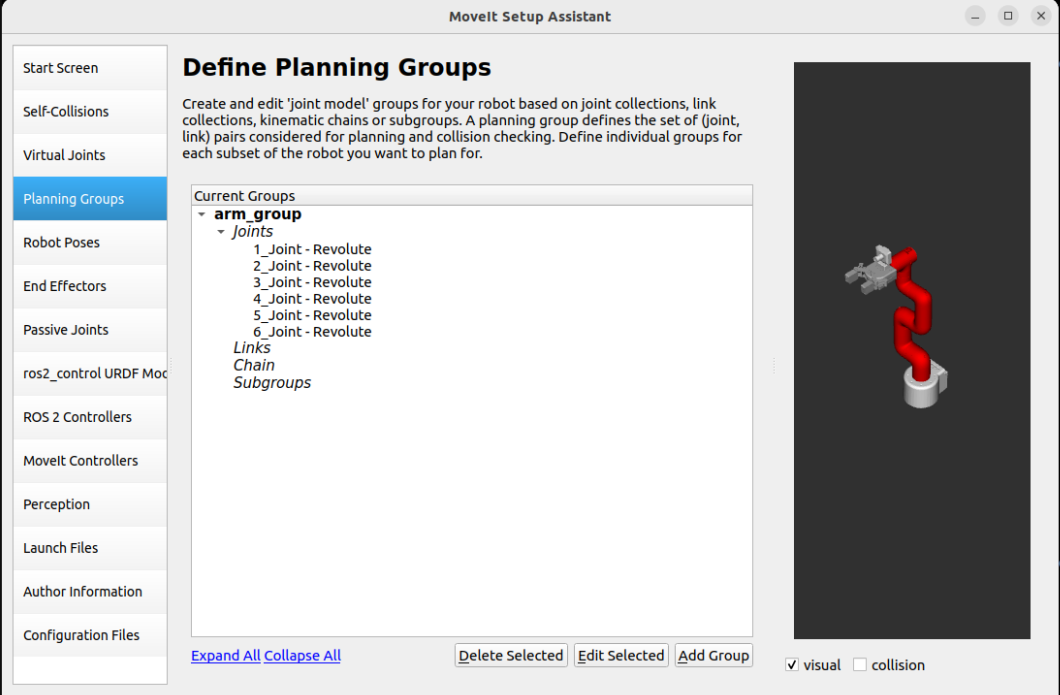
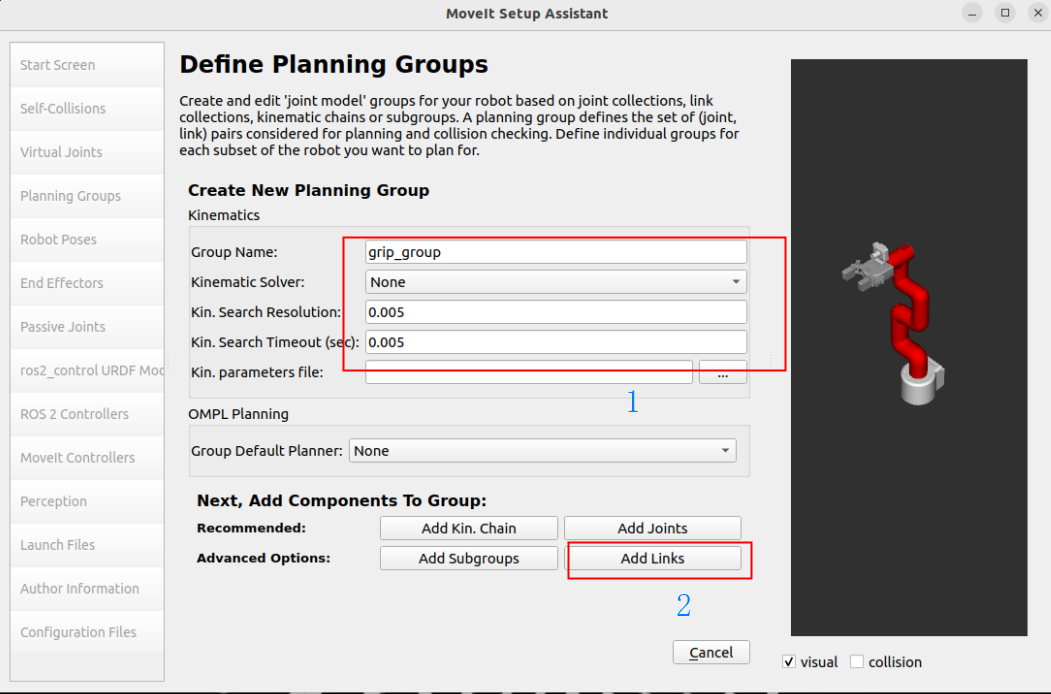
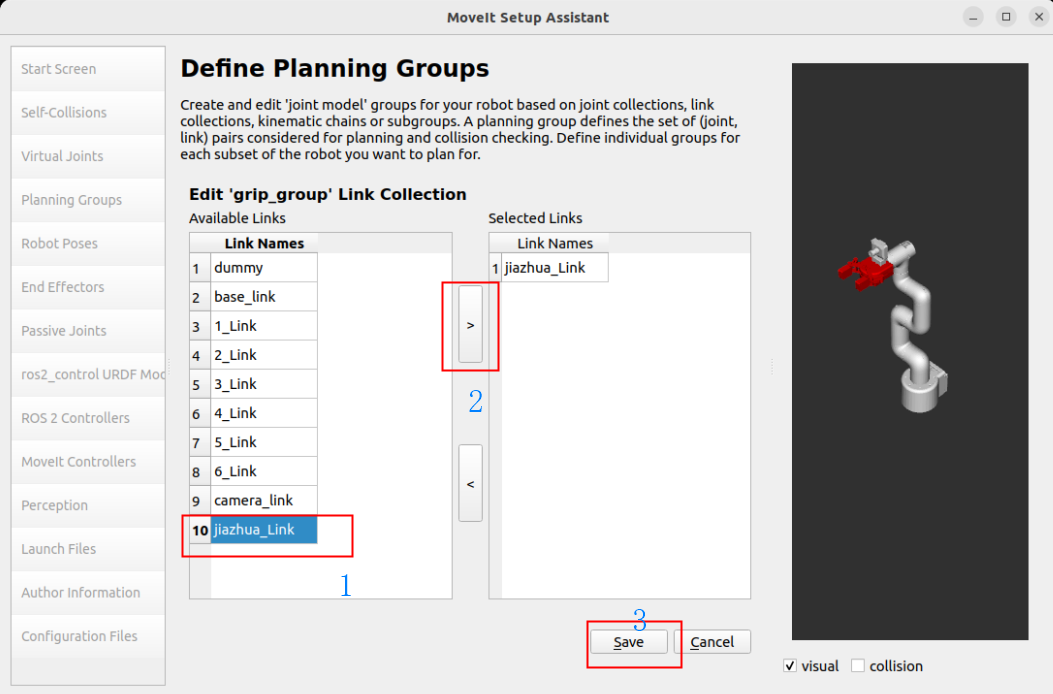
Plan gripper group: grip_group
Group Name: grip_group
Kinematic Solver: None
Kin. Search Resolution: 0.005
Kin. Search Timeout (solving time): 0.005
1.6. Robot position
Set three sets of predefined robot arm positions to the robot configuration:
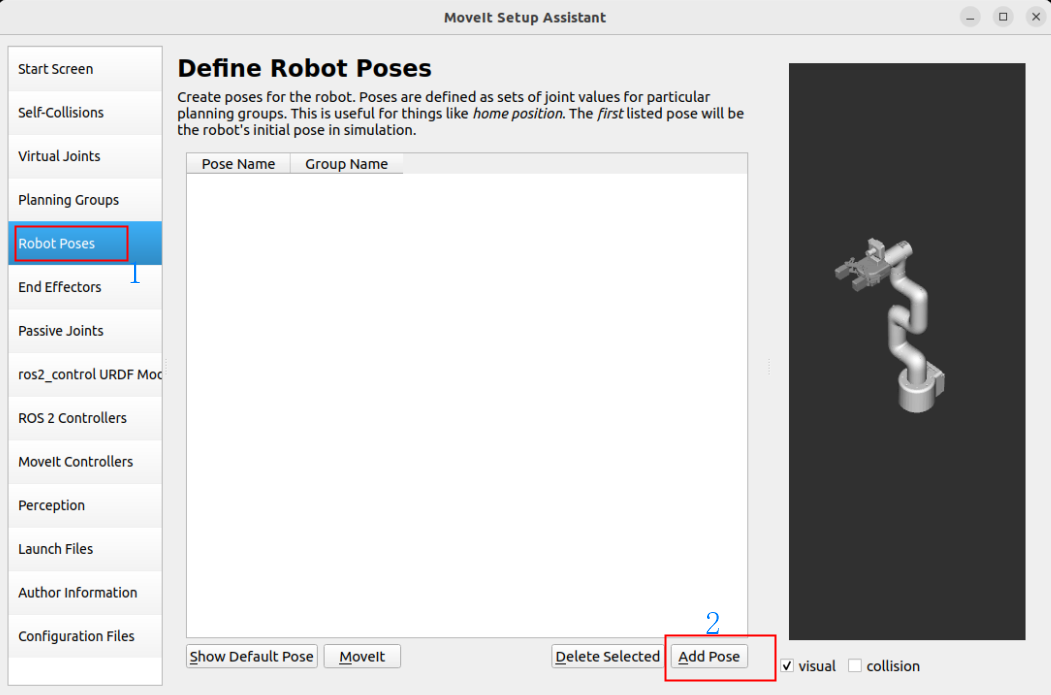
You can manually move the slider to set the state of each joint: up, down, init
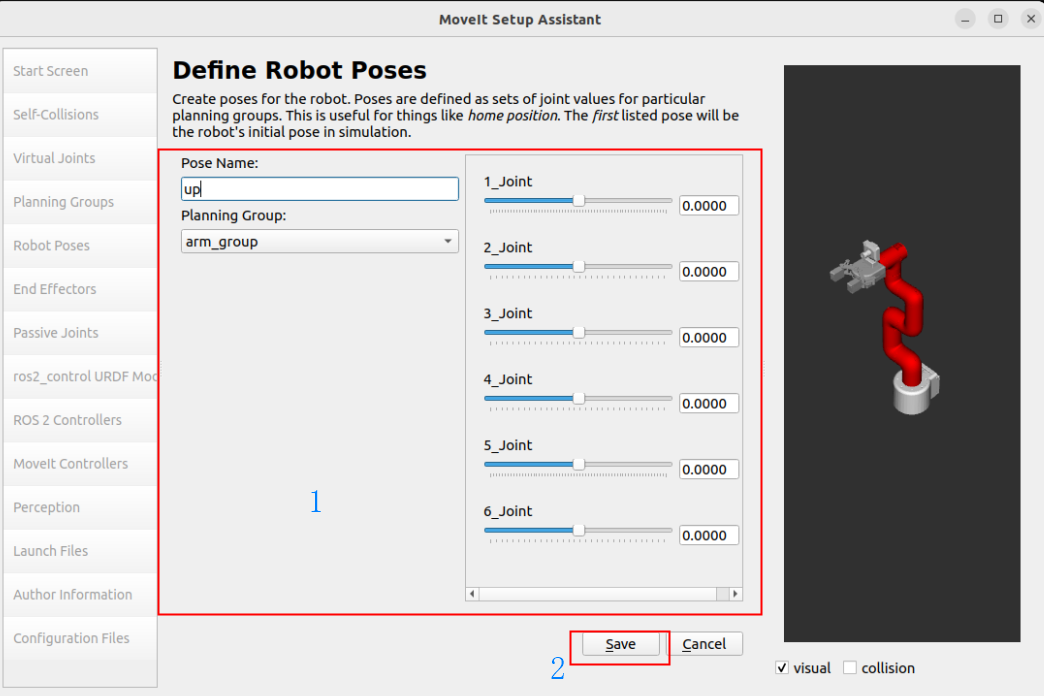
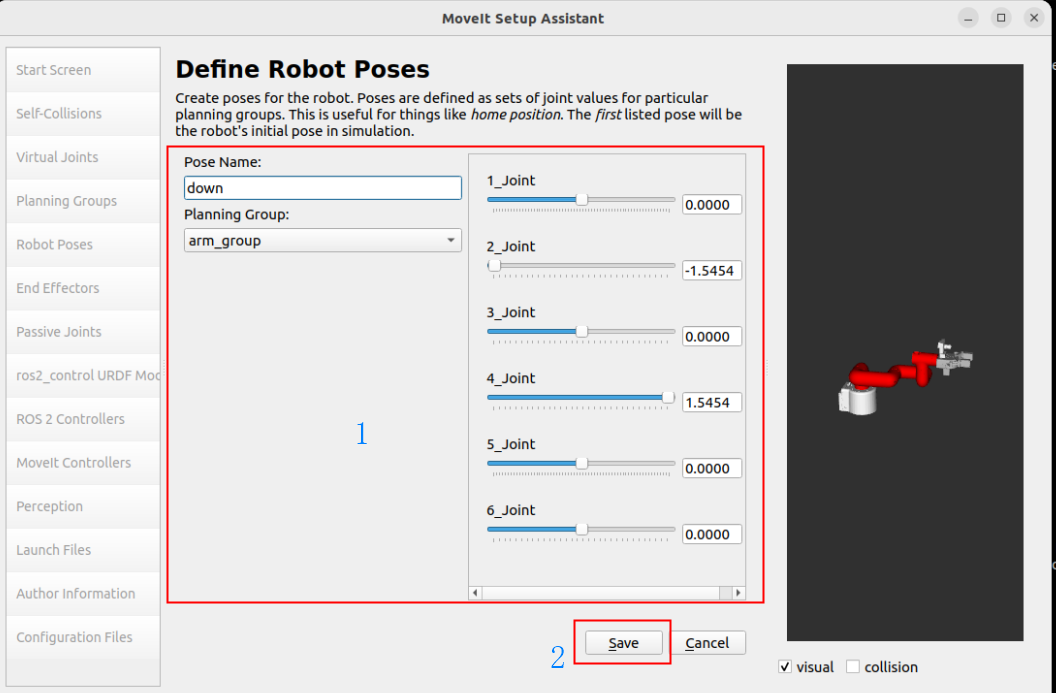
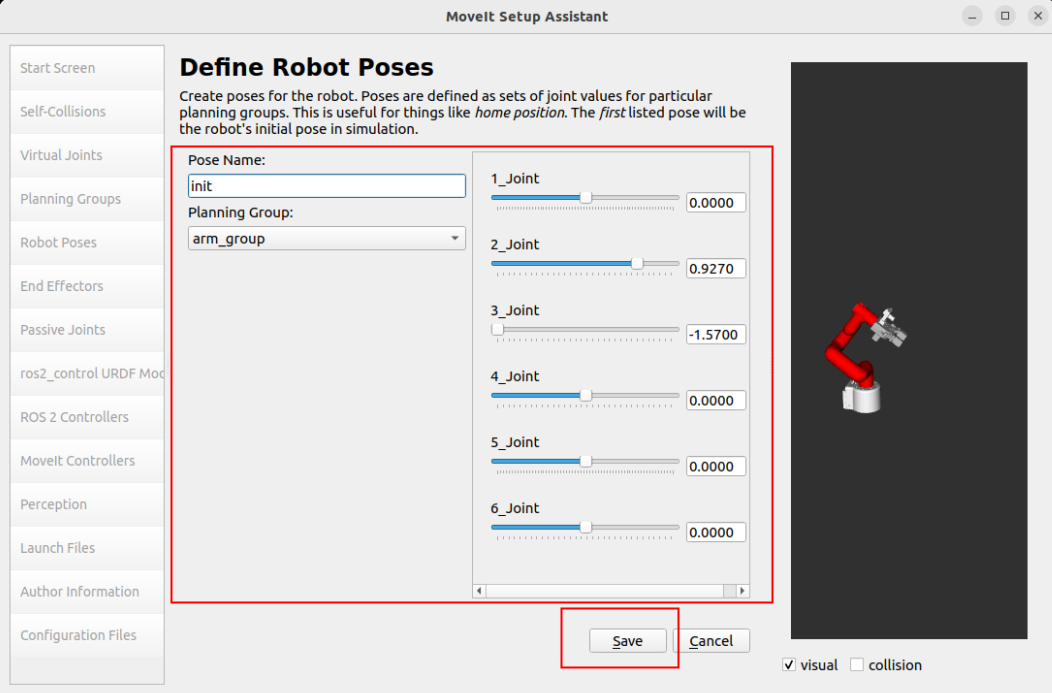
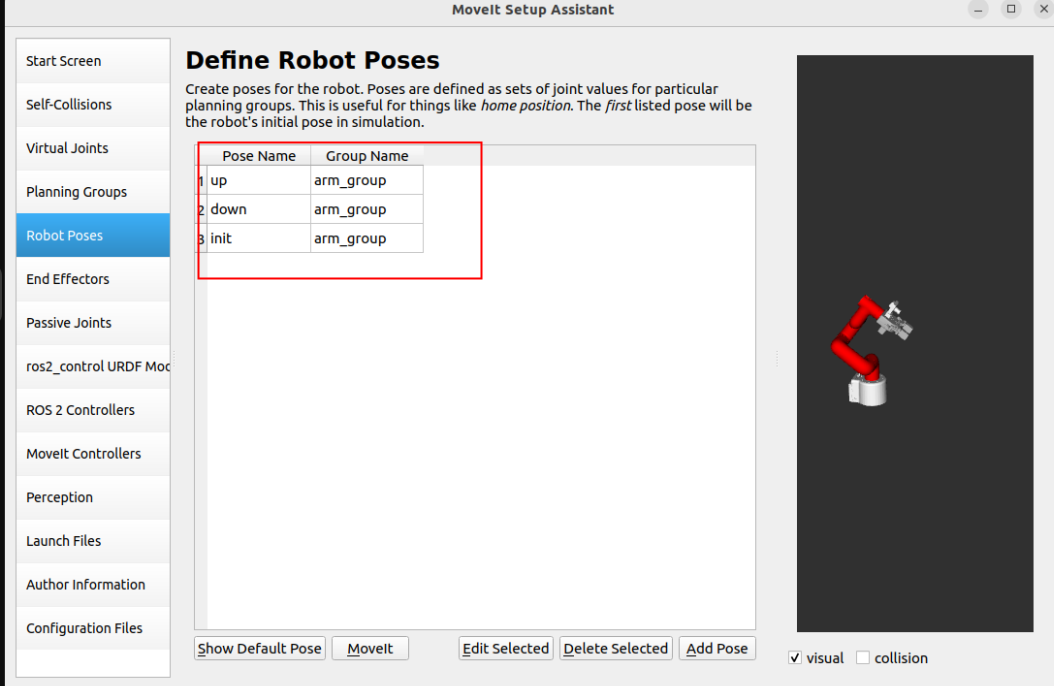
1.7. End Effector
Set the gripper group as the end effector:
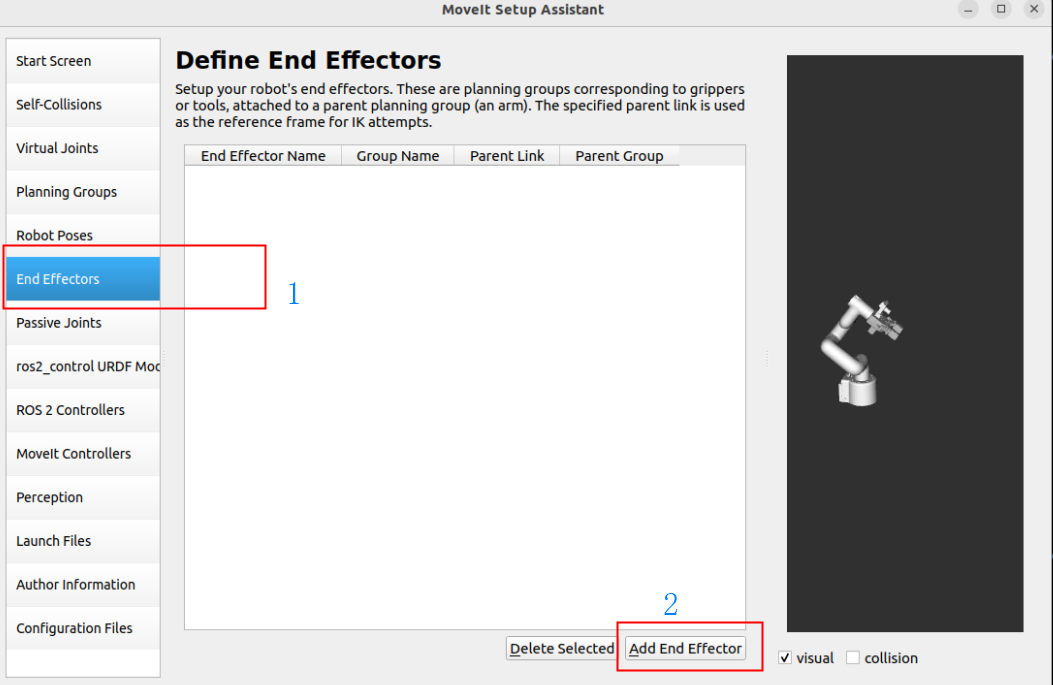
End Effector: gripper
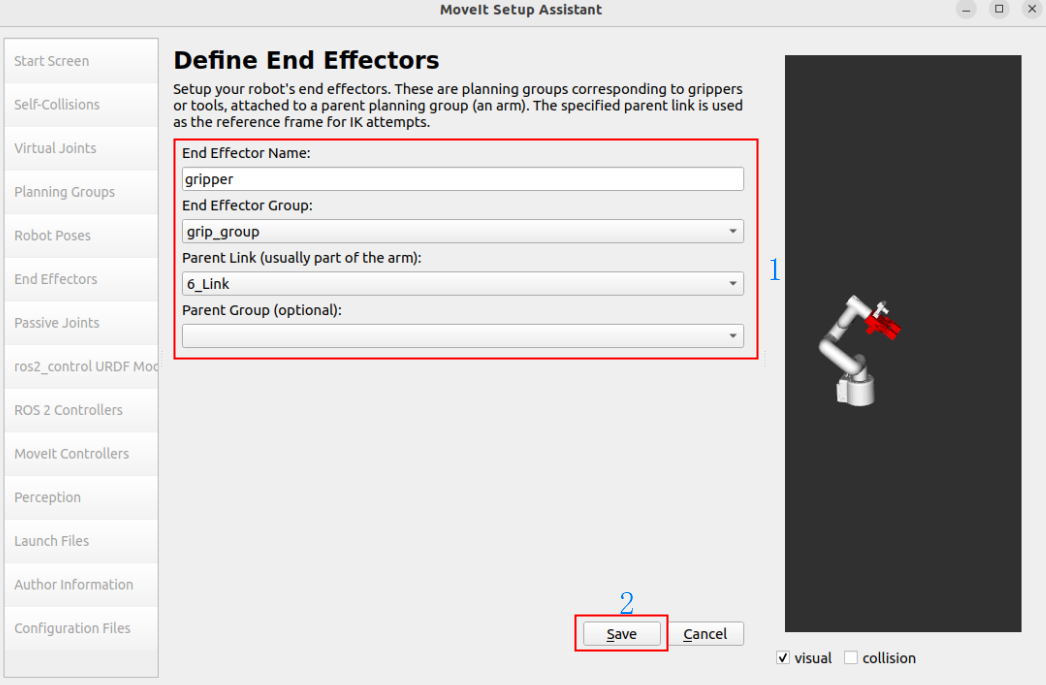
End Effector Name: gripper
End Effector Group: gripp_group
Parent Link: Arm5_Link
Parent Group: None
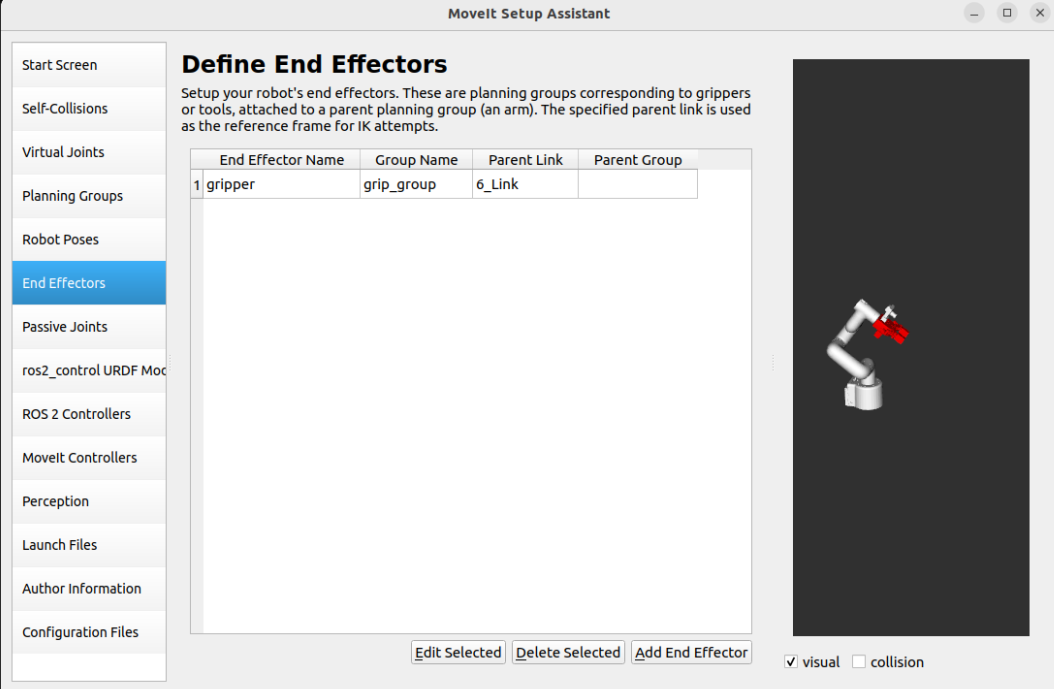
1.8. Passive Joints
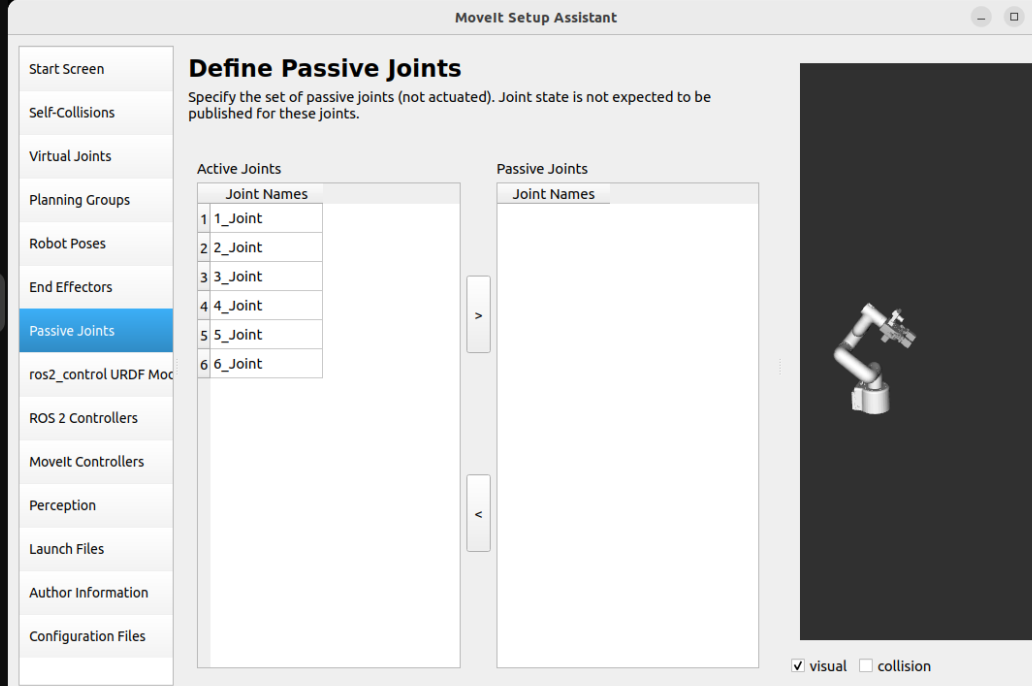
Passive joints are non-actuated joints that cannot be directly controlled: if the robot arm does not have a passive joint, it will be skipped directly.
1.9, URDF file
The MoveIt Setup Assistant automatically sets up the command interface and state interface for each joint: use the default generated information.
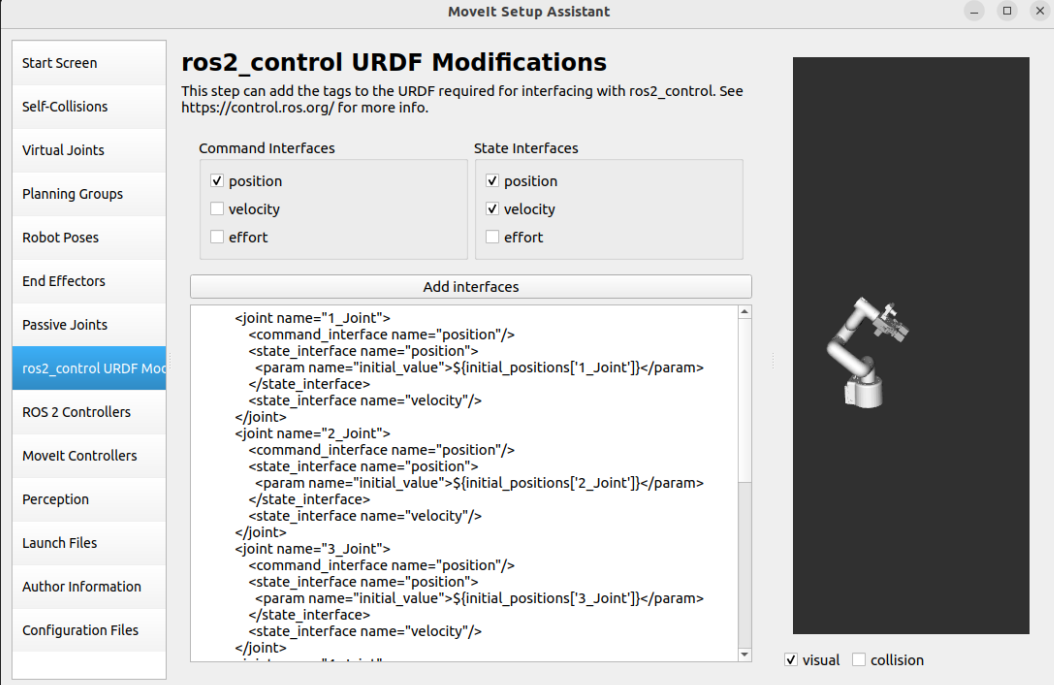
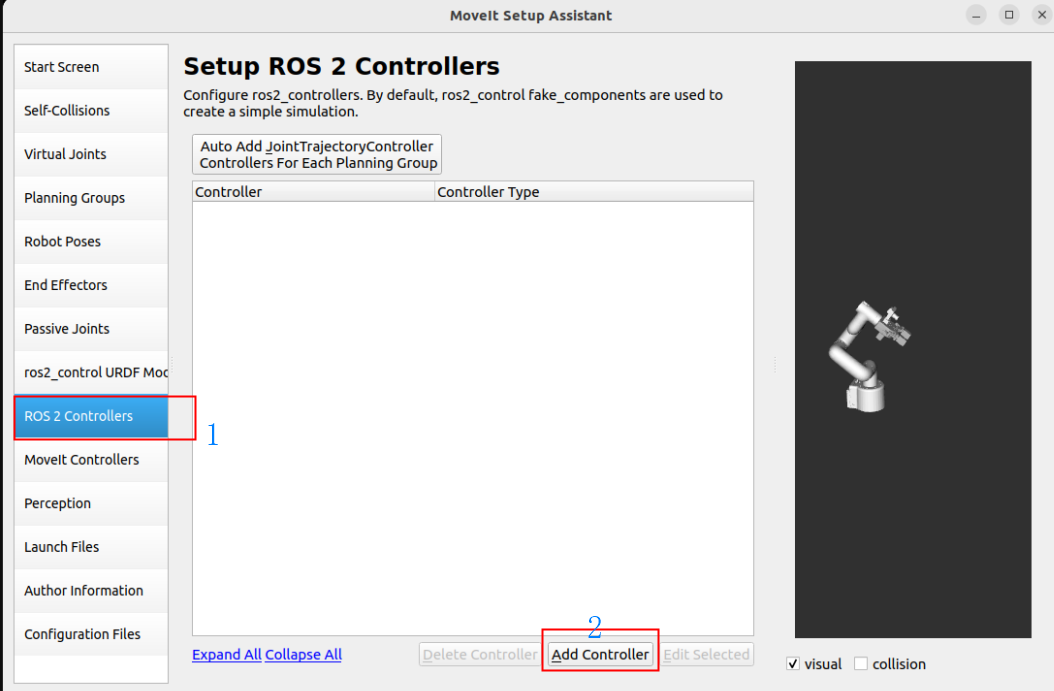
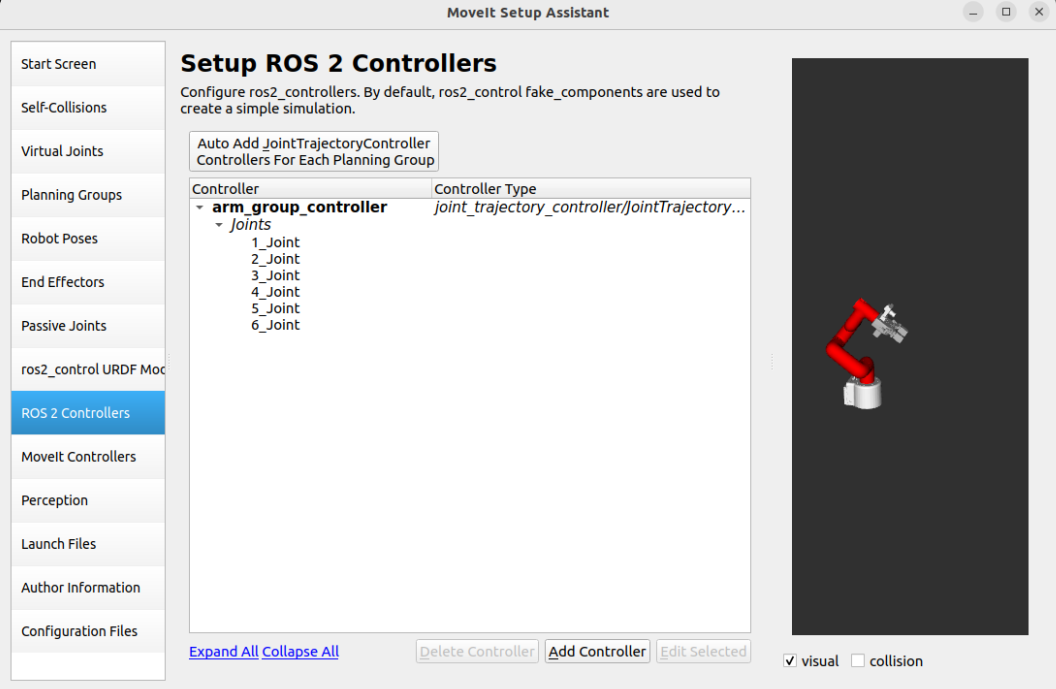
1.10, ROS2 Controllers
ROS2 Controllers is a framework for real-time robot control that can be used to automatically generate simulation controllers to drive robot joints.
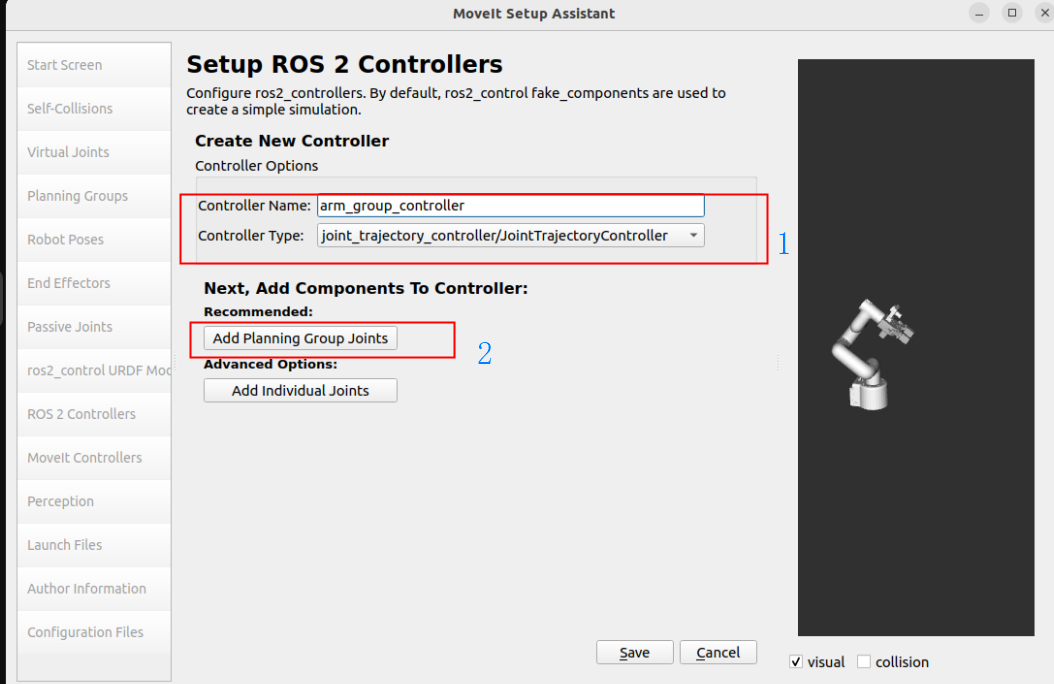
Add robot arm controller:
Controller Name: arm_group_controller
Controller Type: joint_trajectory_controller/JointTrajectoryController
Add Planning Group Joints: arm_group
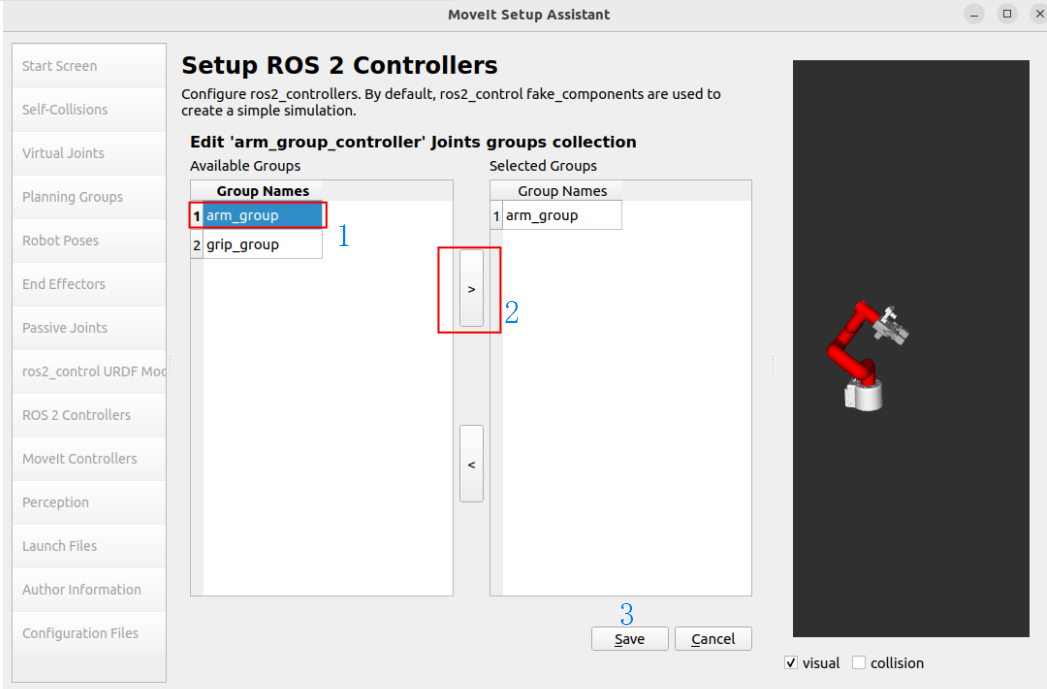
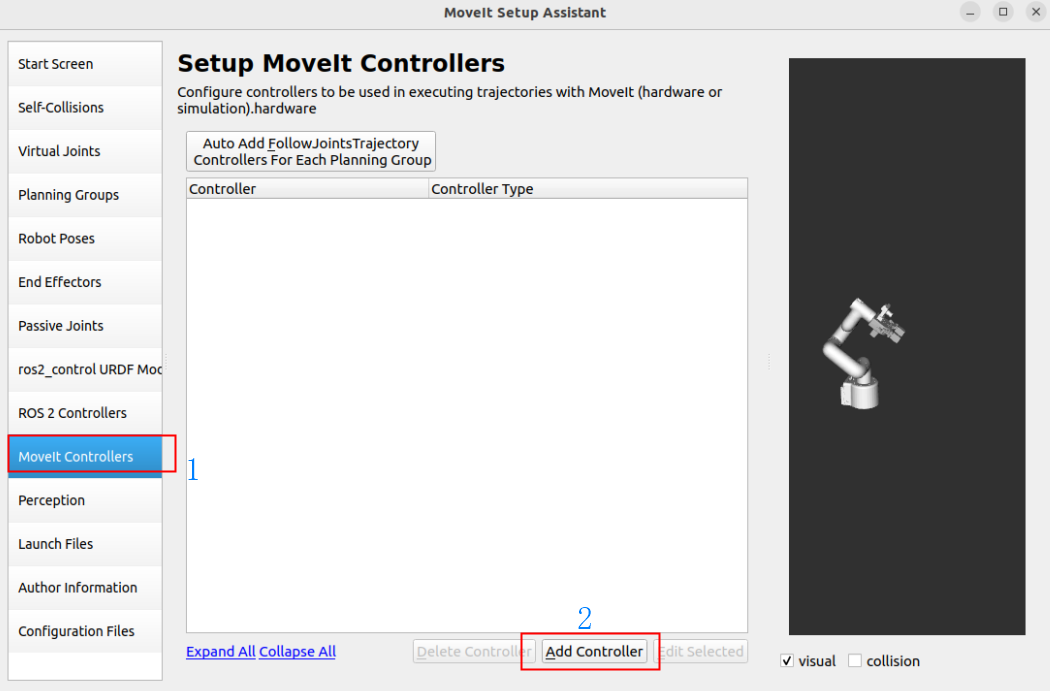
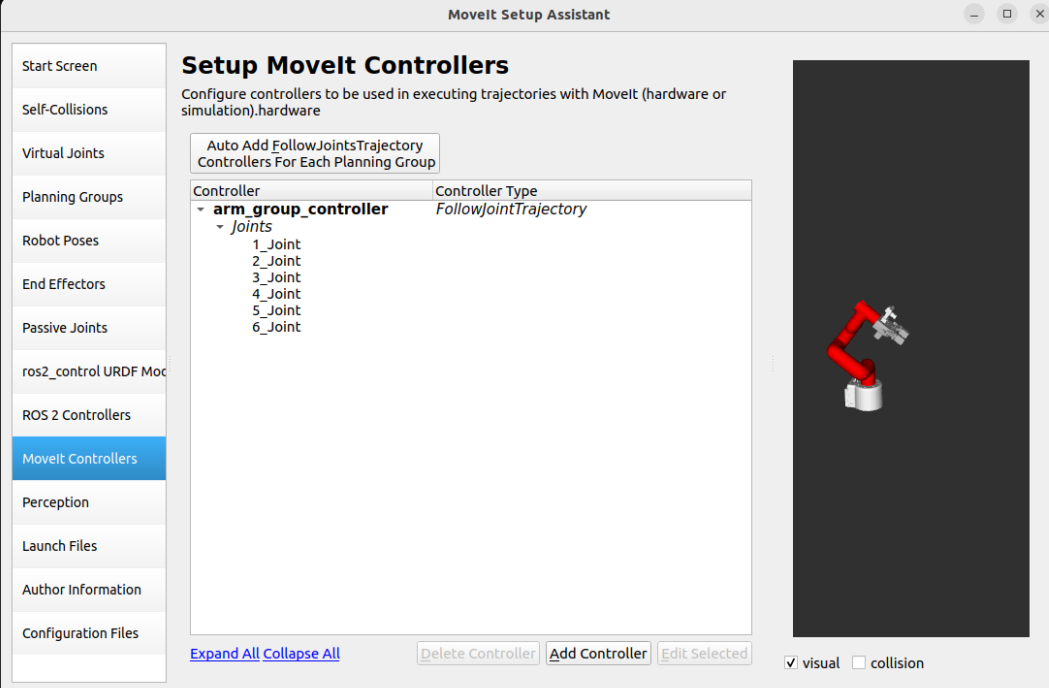
1.11, MoveIt Controllers
MoveIt requires a trajectory controller with the FollowJointTrajectoryAction interface to execute the planned trajectory, which sends the generated trajectory to the robot ROS2 controller.
Added MoveIt Controllers need to ensure that the controller name matches the name configured in ROS2 Controllers.
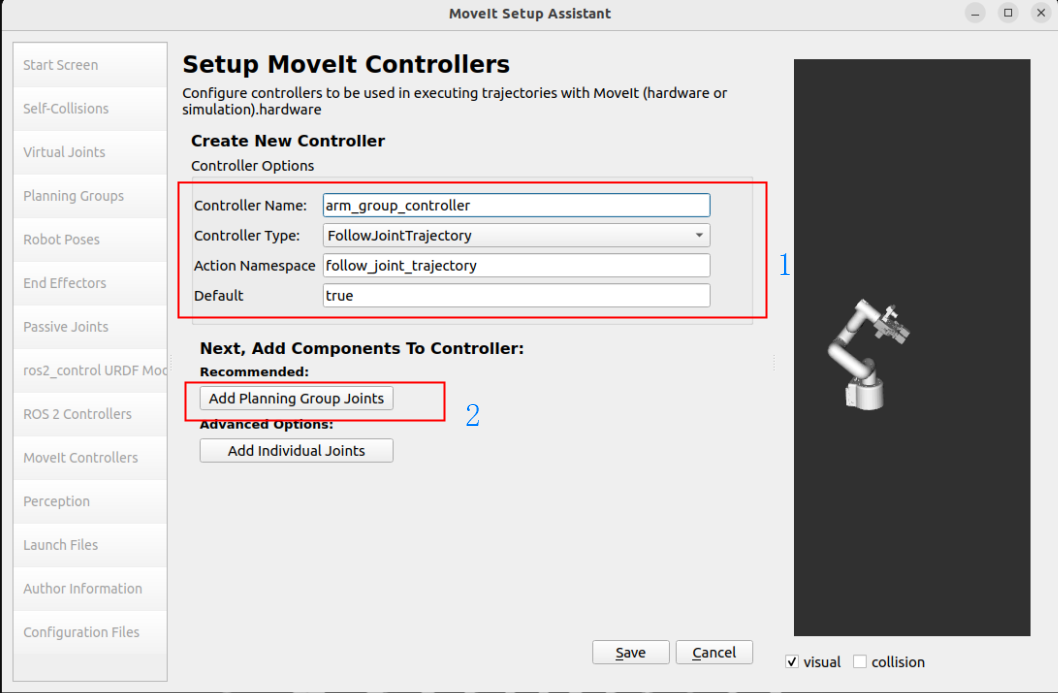
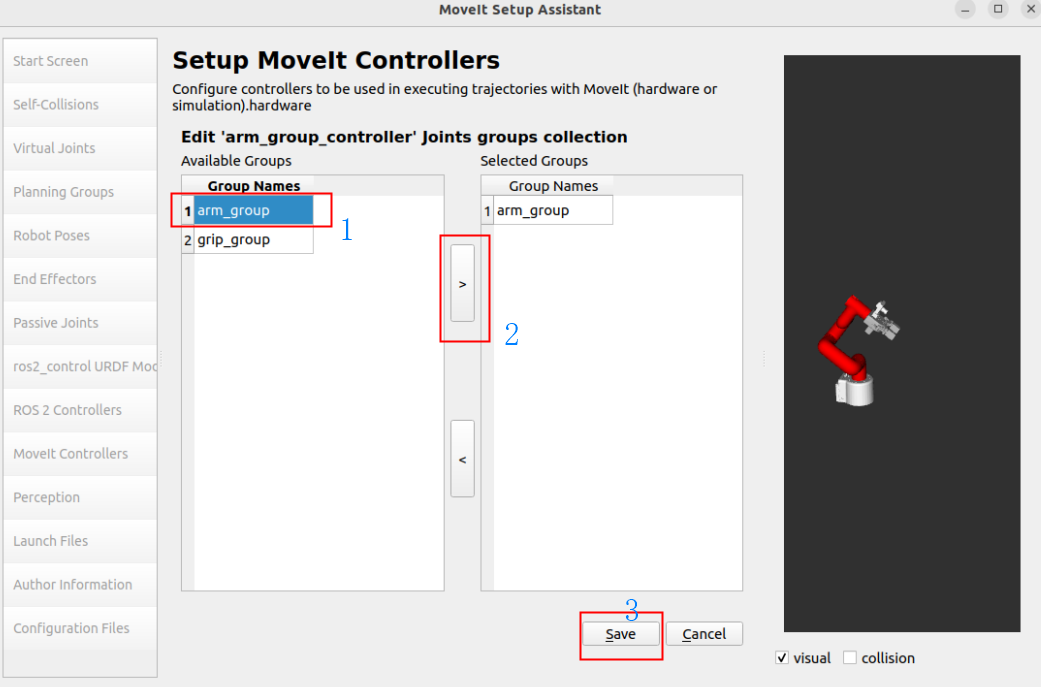
Add robot arm controller:
Controller Name: arm_group_controller
Controller Type: FollowJointTrajectory
Add Planning Group Joints: arm_group
1.12. Sensors
Configure the settings of the 3D sensor used by the robot: No configuration is required.
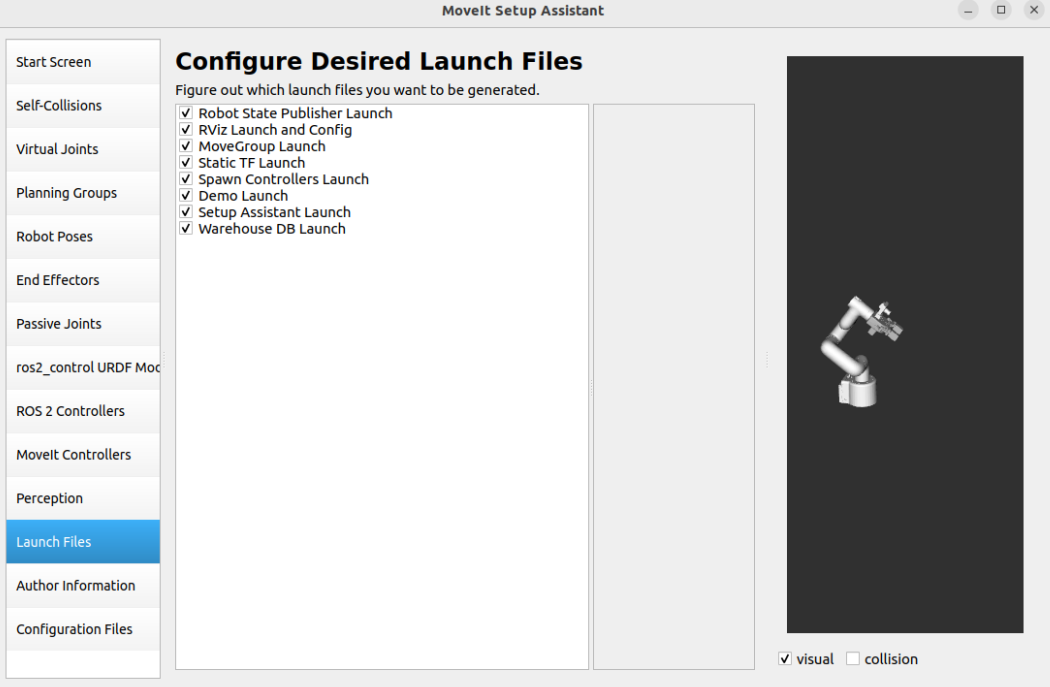
1.13. Startup File
Configure the automatically generated startup file: Use the default options.
1.14. Author Information
Add author information for package generation:
1.15. Generate configuration
Generate configuration files to the specified folder:
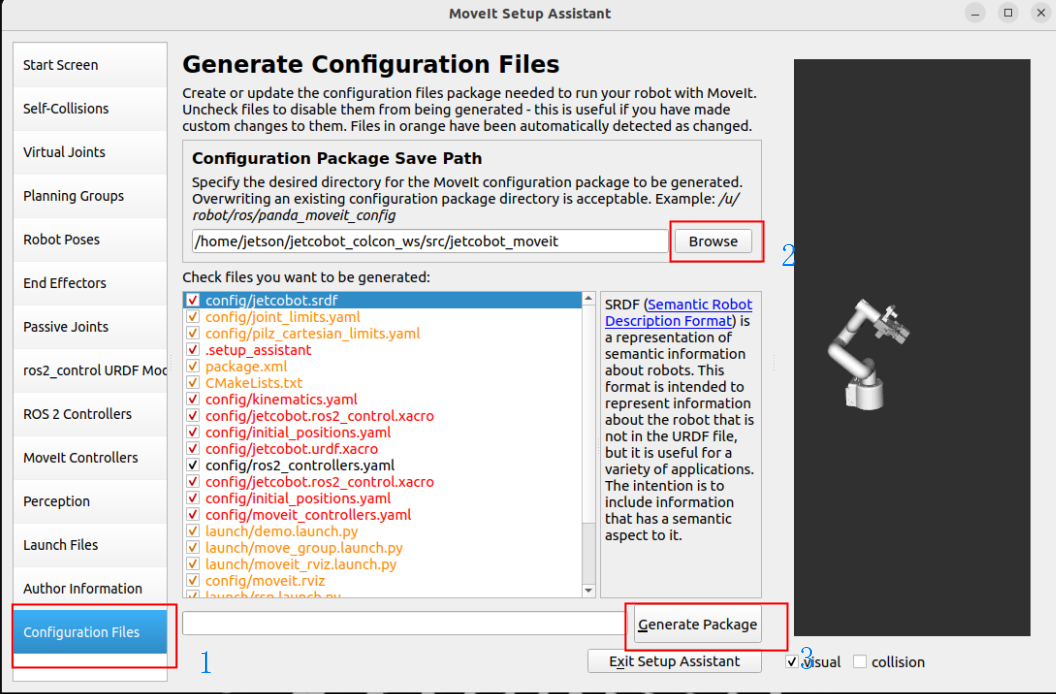
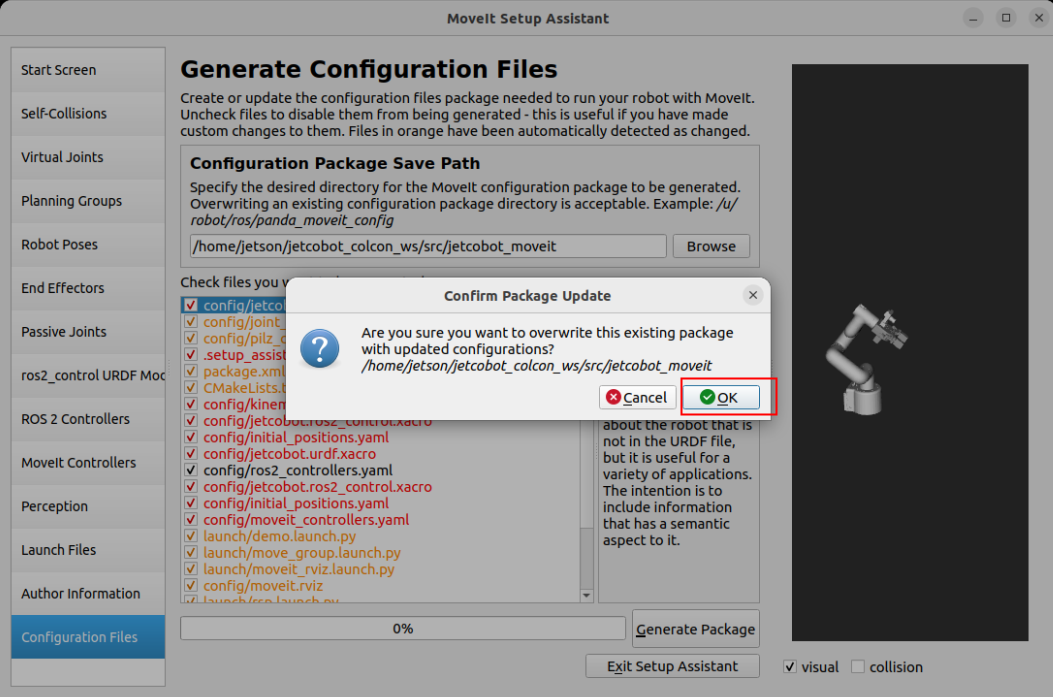
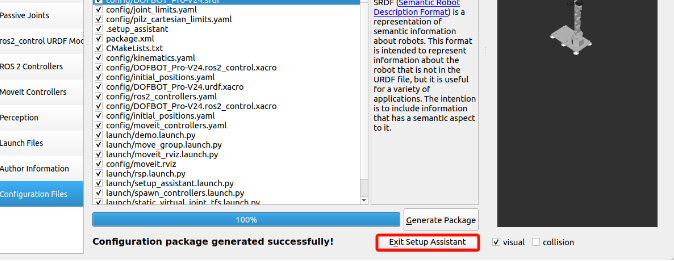
2. Configuration files
Enter the dofbot_pro_moveit folder:
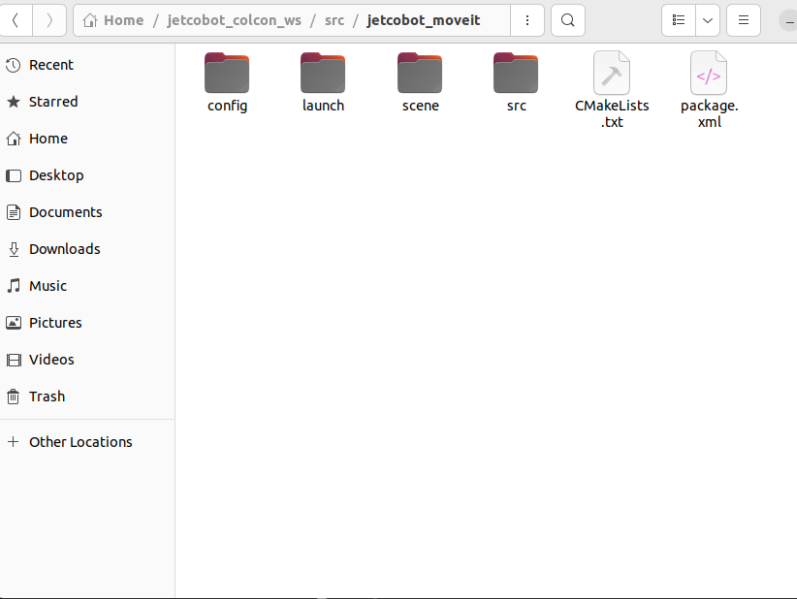
3. Configuration verification
MoveIt Setup The configuration file generated by Assistant needs to be modified to remove the warnings at startup and the problem of model not loading.
3.1, modify the configuration file
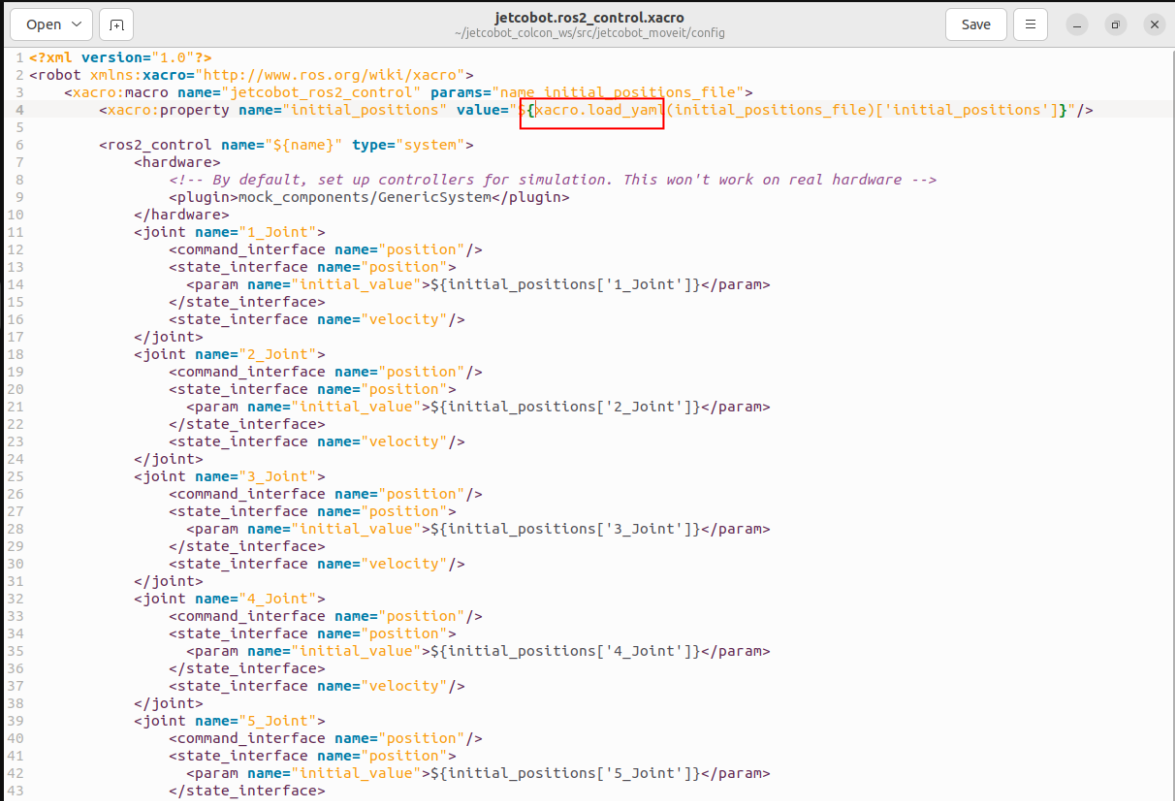
Modify the jetcobot.ros2_control.xacro file: modify the function of loading yaml
xxxxxxxxxxload_yaml(initial_positions_file)['initial_positions']Change toxacro.load_yaml(initial_positions_file)['initial_positions']
3.2, compile the software package
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/jetcobot_colcon_ws/colcon buildsource install/setup.bash
3.3、Start MoveIt
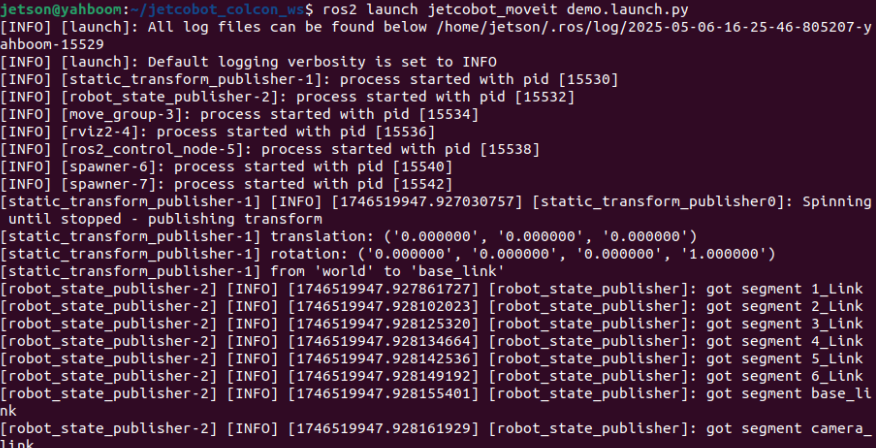
xxxxxxxxxxros2 launch jetcobot_moveit demo.launch.py
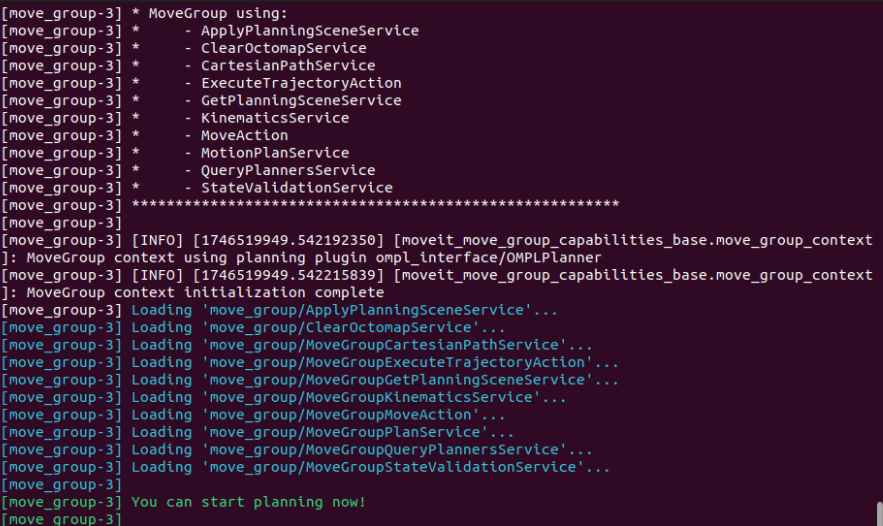
Starting the simulation is slow. When the terminal displays You can start planning now! or the robot arm displays a trackball (the trackball is a newly added sphere on the robot arm), the loading is complete.
References
MoveIt2 Humble: https://moveit.picknik.ai/humble/index.html
MoveIt2: https://moveit.picknik.ai/main/index.html