LVGL Development Preparation
LVGL Development PreparationIntroduction to LVGLLVGL's core advantageslv_binding_micropythonCore FeaturesApplicable scenariosLimitation of UseAdvantagesHow to learn lvgl on K230Quick Start
This tutorial is the necessary foundation for subsequent LVGL development
Although you can learn how to write lvgl without the optional screen, many touch-related functions cannot be used, and the learning experience will be poor
Introduction to LVGL
LVGL (Light and Versatile Graphics Library) is a free, open source graphics library designed specifically for embedded systems.
If you want to draw simple lines and graphics on K230, you can use the draw_xxxx series of graphics processing methods. For details, please refer to the previous tutorial. If you want to display some more complex graphics on K230 that can interact with the user (such as text boxes, buttons, progress bars, etc.)
Then we usually choose a GUI (Graphical User Interface) library to implement it. LVGL is a very useful GUI library.
LVGL's core advantages
Low resource usage
- Minimum memory requirement is only 64KB ROM and 16KB RAM
- Suitable for resource-constrained MCU platforms
- Components can be introduced on demand to optimize resource usage
Cross-platform compatibility
- Supports almost all mainstream MCU platforms
- Strong portability and well-designed hardware abstraction layer
- Support multiple operating systems: FreeRTOS, RT-Thread, etc.
Development efficiency
- Developed in C language, with a gentle learning curve (it also supports other languages, such as Micropython, which we will mention later)
- API design is simple and intuitive
- Rich sample code and documentation support
lv_binding_micropython
Github link lvgl/lv_binding_micropython: LVGL binding for MicroPython
Note: Github is often inaccessible, which is normal. Not reading the content of this link will not affect the subsequent learning.
In the previous article, we talked about LVGL. The original LVGL is actually a C language project and cannot be programmed using Micropython. As more and more embedded scenarios are programmed using Micropython, the lv_binding_micropython project was born.
lv_binding_micropython is an open source project that binds LVGL to MicroPython, allowing developers to develop LVGL graphical interfaces using the Python language. The following are the main features:
Core Features
- Ease of use
- Developing LVGL using Python syntax
- Lowers the threshold for using LVGL
- Support rapid prototyping
- Fully functional
xxxxxxxxxx# Example code# Note that this is pseudo code and cannot be run directly on K230# 示例代码# 注意,这个是伪代码,不能直接在K230上运行import lvgl as lvscr = lv.obj() # 创建屏幕对象 Create a screen objectbtn = lv.btn(scr) # 创建按钮 Create a buttonbtn.center() # 居中按钮 Center buttonlabel = lv.label(btn) # 创建标签 Create a labellabel.set_text("Button") # 设置文本 Set the textApplicable scenarios
- Rapid prototyping
- Education and Teaching
- Simple graphical interface development
- Non-performance critical applications
Limitation of Use
- Performance overhead
- There is a certain performance loss compared to the C language version
- Relatively larger memory usage
- Hardware requirements
- Requires more Flash and RAM
- It is recommended to use an MCU with a main frequency exceeding 100MHz
Advantages
- High development efficiency
- Easy debugging
- Reduced code size
- Suitable for quick verification
How to learn lvgl on K230
LVGL is a relatively complex component library. Our tutorial is difficult to cover all the content, so it is necessary to read the official documentation.
The lvgl library in the K230 firmware uses version v8.3
The official documentation link is as follows: Welcome to the documentation of LVGL! — LVGL documentation
If the link is invalid, you can find LVGL.pdf in our development board documentation, which is an offline version of the document backup
The official tutorial is mainly written in C language. Although there are parts written in Micropython, there are inconsistencies between the writing in the document and the actual call , such as differences in function names and calling methods. To solve this problem, I printed out the real constant writing and function names of LVGL in the K230 firmware and put them in the development board data. You need to combine the official document and the actual supported calling writing (0. Development board data/ Other third-party documents/ lvgl_.txt) to develop and learn.
Quick Start
Complete code file [Source code summary / 12.Lvgl / 01.start.py]
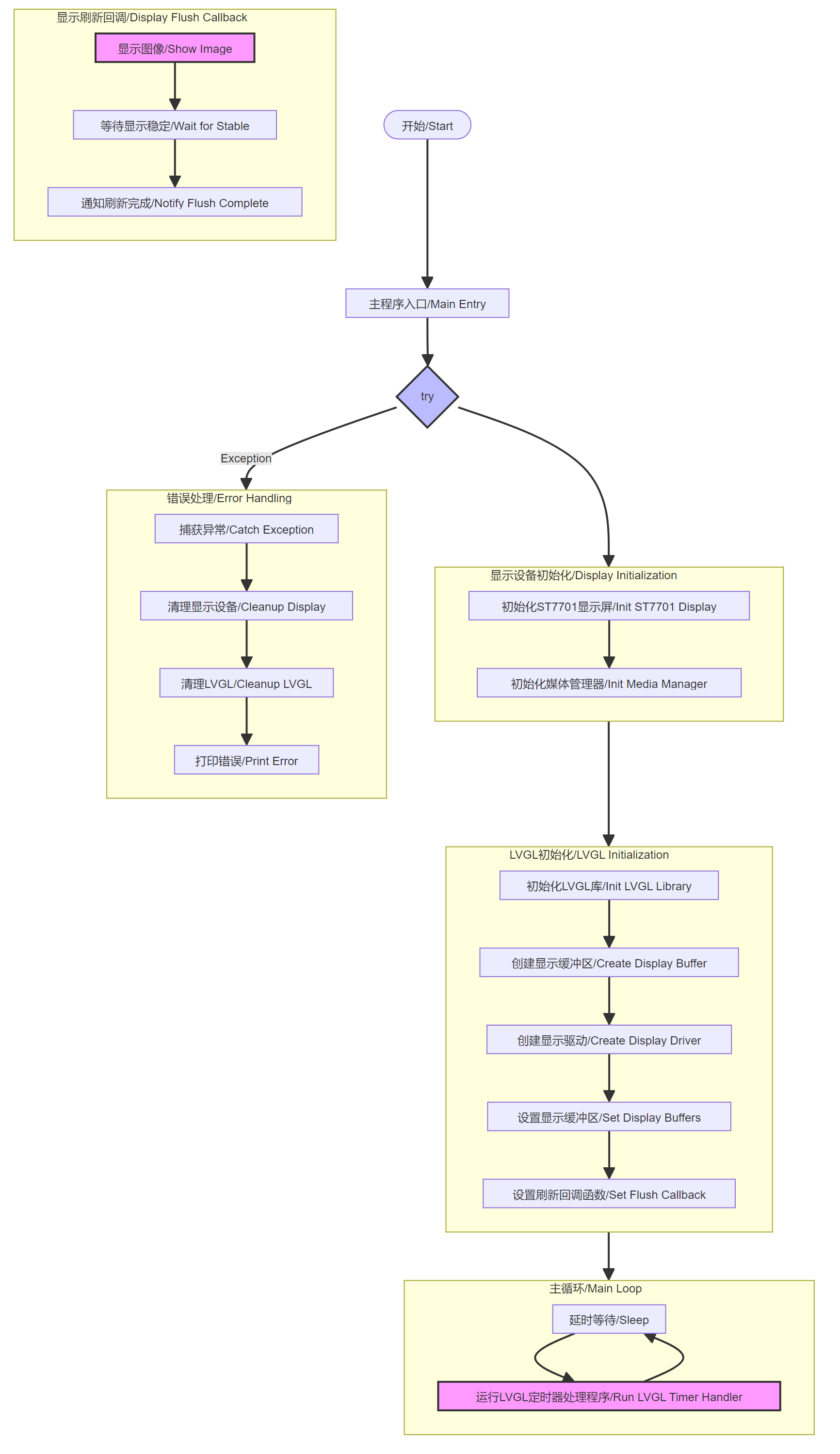
The following is an example of the basic structure of a lvgl code
xxxxxxxxxximport lvgl as lvfrom media.display import *import time # 显式导入time模块 / Explicitly import time module# 显示屏分辨率配置 / Display resolution configurationDISPLAY_WIDTH = 640 # 显示屏宽度 / Display widthDISPLAY_HEIGHT = 480 # 显示屏高度 / Display heightdef disp_drv_flush_cb(disp_drv, area, color): """ 显示驱动刷新回调函数 Display driver flush callback function Args: disp_drv: 显示驱动对象 / Display driver object area: 刷新区域 / Refresh area color: 颜色数据 / Color data """ global disp_img1 Display.show_image(disp_img1) # 显示图像缓冲区 / Show image buffer time.sleep(0.01) # 适当延时确保显示稳定 / Small delay to ensure stable display disp_drv.flush_ready() # 通知LVGL刷新完成 / Notify LVGL that flush is completedef display_init(): """ 显示设备初始化函数 Display device initialization function """ # 初始化ST7701显示屏 / Initialize ST7701 display Display.init( Display.ST7701, width=DISPLAY_WIDTH, height=DISPLAY_HEIGHT, to_ide=True # 启用IDE显示功能 / Enable IDE display function ) # 初始化媒体管理器 / Initialize media manager MediaManager.init()def lvgl_init(): """ LVGL初始化函数 LVGL initialization function """ global disp_img1 # 初始化LVGL库 / Initialize LVGL library lv.init() # 创建显示缓冲区 / Create display buffer disp_img1 = image.Image( DISPLAY_WIDTH, DISPLAY_HEIGHT, image.BGRA8888 # 使用BGRA8888颜色格式 / Use BGRA8888 color format ) # 创建显示驱动 / Create display driver disp_drv = lv.disp_create(DISPLAY_WIDTH, DISPLAY_HEIGHT) # 设置显示缓冲区 / Set display buffers disp_drv.set_draw_buffers( disp_img1.bytearray(), None, # 单缓冲模式 / Single buffer mode disp_img1.size(), lv.DISP_RENDER_MODE.DIRECT # 直接渲染模式 / Direct rendering mode ) # 设置刷新回调函数 / Set flush callback disp_drv.set_flush_cb(disp_drv_flush_cb) def display_deinit(): os.exitpoint(os.EXITPOINT_ENABLE_SLEEP) time.sleep_ms(50) # deinit display Display.deinit() # release media buffer MediaManager.deinit() def lvgl_deinit(): global disp_img1 lv.deinit() del disp_img1 def main(): """ 主函数 Main function """ try: # 初始化显示设备和LVGL / Initialize display device and LVGL display_init() lvgl_init() print("LVGL initialization completed") # LVGL主循环 / LVGL main loop while True: # 运行LVGL定时器处理程序 / Run LVGL timer handler period = lv.timer_handler_run_in_period(1) time.sleep_ms(period) except Exception as e: display_deinit() lvgl_deinit() print(f"Error occurred: {e}")if __name__ == "__main__": main()The basic structure includes the following main parts:
Display device initialization:
- Initialize the ST7701 display
- Set the display resolution
- Initialize the Media Manager
LVGL initialization:
- Initialize the LVGL library
- Creating and configuring a display buffer
- Set up display driver and callback function
Main loop:
- Run the LVGL timer handler
- Error checking and handling
Display refresh callback:
- Displaying images
- Wait for the display to stabilize
- Notification refresh completed
Cleaning process:
- Display device cleanup
- Media Manager Cleanup
- LVGL Cleanup
- Buffer deletion
These steps are essential for using lvgl on K230. Although the code looks a lot, basically no modification is required. Just copy it every time you write a new LVGL program.
When we run this code example, we can see that a white background appears on the K230 screen and no error message appears, which means that lvgl initialization is successful.
In the following chapters, we will introduce several commonly used components of LVGL.