7. Perspective Transformation
7.1. Perspective Transformation
Perspective transformation is also called projection transformation. The affine transformation we often talk about is a special case of perspective transformation. The purpose of perspective transformation is to transform objects that are straight lines in reality into straight lines in the image. Perspective transformation can map a rectangle to an arbitrary quadrilateral.
cv2. warpPerspective(src, M, dsize[,flag, [,borderMode[,borderValue]]])
src: source image
M: 3X3 transformation matrix
dsize: output image size.
flags: interpolation method, default INTER_LINEAR (bilinear interpolation), when WARP_INVERSE_MAP, it means that M is an inverse transformation, which can achieve an inverse transformation from the target dst to src.
borderMode: border type. The default is BORDER_CONSTANT. When the value is BORDER_TRANSPARENT, the values in the target image are not changed, and these values correspond to the outliers in the original image.
borderValue: Boundary value, default is 0.
Like affine transformation, OpenCV still provides a function cv2.getPerspectiveTransform() to provide the transformation matrix above.
The function is as follows:
cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(matSrc, matDst)
matSrc: Four vertex coordinates of the input image.
matDst: Four vertex coordinates of the output image.
7.2. Actual effect display
Code path:
/home/pi/DOGZILLA_Lite_class/4.Open Source CV/B.Geometric_Transformations/07_Perspective_Transformation.ipynb
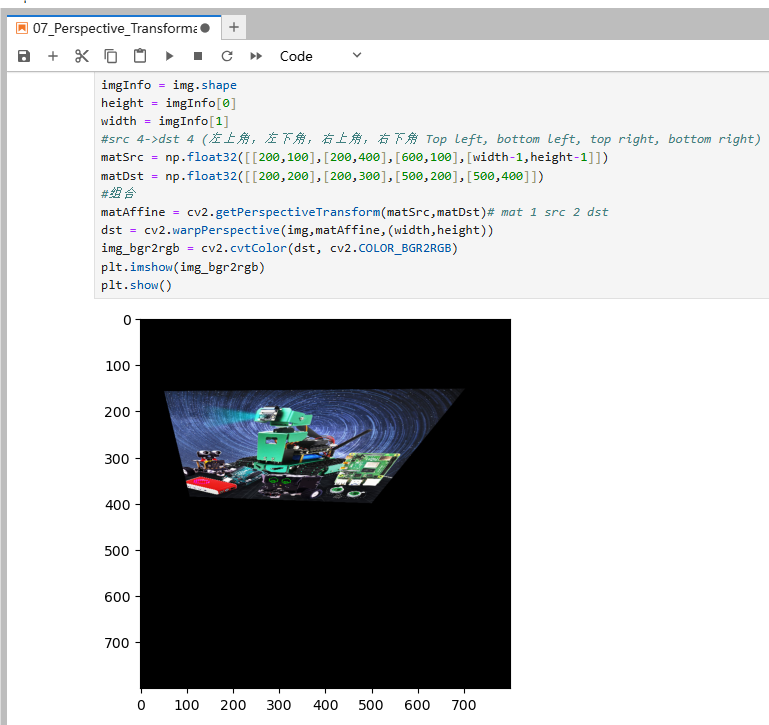
ximport cv2import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimg = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',1)imgInfo = img.shapeheight = imgInfo[0]width = imgInfo[1]#src 4->dst 4 (左上角,左下角,右上角,右下角 Top left, bottom left, top right, bottom right)matSrc = np.float32([[200,100],[200,400],[600,100],[width-1,height-1]])matDst = np.float32([[200,200],[200,300],[500,200],[500,400]])#组合matAffine = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(matSrc,matDst)# mat 1 src 2 dstdst = cv2.warpPerspective(img,matAffine,(width,height))img_bgr2rgb = cv2.cvtColor(dst, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb)plt.show()