1. Grayscale processing
1.1. Grayscale processing
The process of converting a color image into a grayscale image is the grayscale processing of the image. The color of each pixel in a color image is determined by the three components of R, G, and B, and each component can take values 0-255, so that a pixel can have a range of more than 16 million (256256256=1677256) colors. A grayscale image is a special color image with the same three components of R, G, and B. The range of variation of one pixel is 256. Therefore, in digital image processing, images of various formats are generally converted into grayscale images to reduce the amount of calculation for subsequent images. The description of grayscale images, like color images, still reflects the distribution and characteristics of the overall and local chromaticity and highlight levels of the entire image.
- Image grayscale processing
Grayscale processing is the process of converting a color image into a grayscale image. Color images are divided into three components of R, G, and B, which respectively show various colors such as red, green, and blue. Grayscale is the process of making the R, G, and B components of the color equal. Pixels with large grayscale values are brighter (the maximum pixel value is 255, which is white), and vice versa, they are darker (the minimum pixel value is 0, which is black).
The core idea of image grayscale is R = G = B, and this value is also called grayscale value.
Image grayscale algorithm
1) Maximum value method: Make the converted R, G, and B values equal to the largest of the three values before conversion, that is: R=G=B=max(R, G, B). The grayscale image converted by this method is very bright.
2) Average value method: The converted R, G, and B values are the average values of R, G, and B before conversion. That is: R=G=B=(R+G+B)/3. The grayscale image produced by this method is relatively soft.
3) Weighted average method: According to certain weights, the values of R, G, and B are weighted averaged, that is: 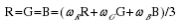 are the weights of R, G, and B respectively, and different values are used to form different grayscale images. Since the human eye is most sensitive to green, followed by red, and the least sensitive to blue, a grayscale image that is easier to recognize will be obtained.
are the weights of R, G, and B respectively, and different values are used to form different grayscale images. Since the human eye is most sensitive to green, followed by red, and the least sensitive to blue, a grayscale image that is easier to recognize will be obtained.
In OpenCV, cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) is used to grayscale the image.
1.2 Actual effect display
Source code path:
/home/pi/DOGZILLA_Lite_class/4.Open Source CV/C.Image_Processing_Text_Drawing/01_Grayscale_Processing.ipynb
x#方法1 imread Method 1: imread#注意:有时第一次运行图片不会显示出来,第二次才会显示出来 #Note: Sometimes the image will not appear on the first run, but will appear on the second run import cv2import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimg0 = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',0) img1 = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',1)# print(img0.shape)# print(img1.shape)# cv2.imshow('src',img0)# cv2.waitKey(0)#原始图像 The original image# img_bgr2rgb1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb1)#灰色图像 Gray Imageimg_bgr2rgb0 = cv2.cvtColor(img0, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb0)plt.show()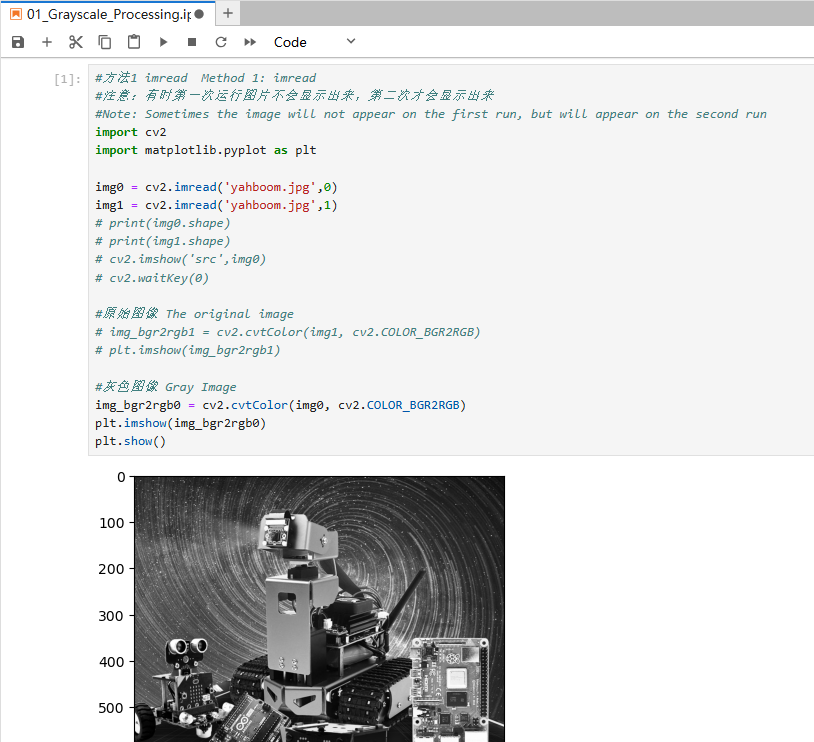
xxxxxxxxxx#方法2 cvtColor Method 2 cvtColor#注意:有时第一次运行图片不会显示出来,第二次才会显示出来#Note: Sometimes the image will not appear on the first run, but will appear on the second runimport cv2import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimg = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',1)dst = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 颜色空间转换 1 data 2 BGR gray. Color space conversion 1 data 2 BGR gray#cv2.imshow('dst',dst)#cv2.waitKey(0)#原始图像 The original image# img_bgr2rgb1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb1)#灰色图像 Gray Imageimg_bgr2rgb0 = cv2.cvtColor(dst, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb0)plt.show()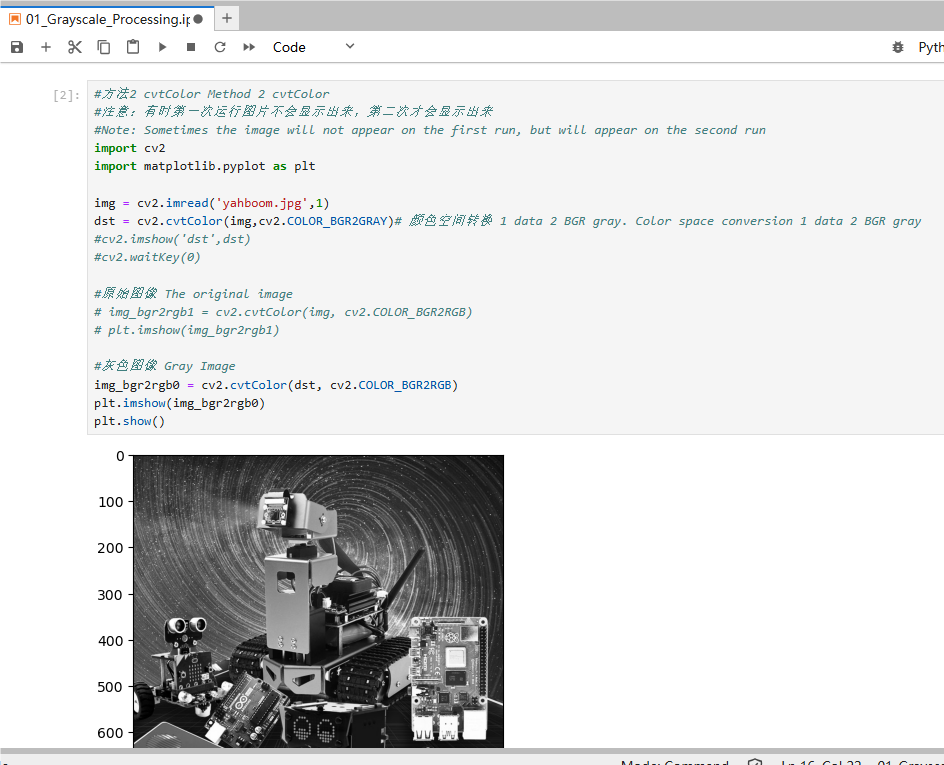
xxxxxxxxxx#方法3 平均值法 Method 3: Average value methodimport cv2import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimg = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',1)imgInfo = img.shapeheight = imgInfo[0]width = imgInfo[1]# RGB R=G=B = gray (R+G+B)/3dst = np.zeros((height,width,3),np.uint8)for i in range(0,height): for j in range(0,width): (b,g,r) = img[i,j] gray = (int(b)+int(g)+int(r))/3 dst[i,j] = np.uint8(gray)#cv2.imshow('dst',dst)#cv2.waitKey(0)#原始图像 original image# img_bgr2rgb1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb1)#灰色图像 Gray Imageimg_bgr2rgb0 = cv2.cvtColor(dst, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb0)plt.show()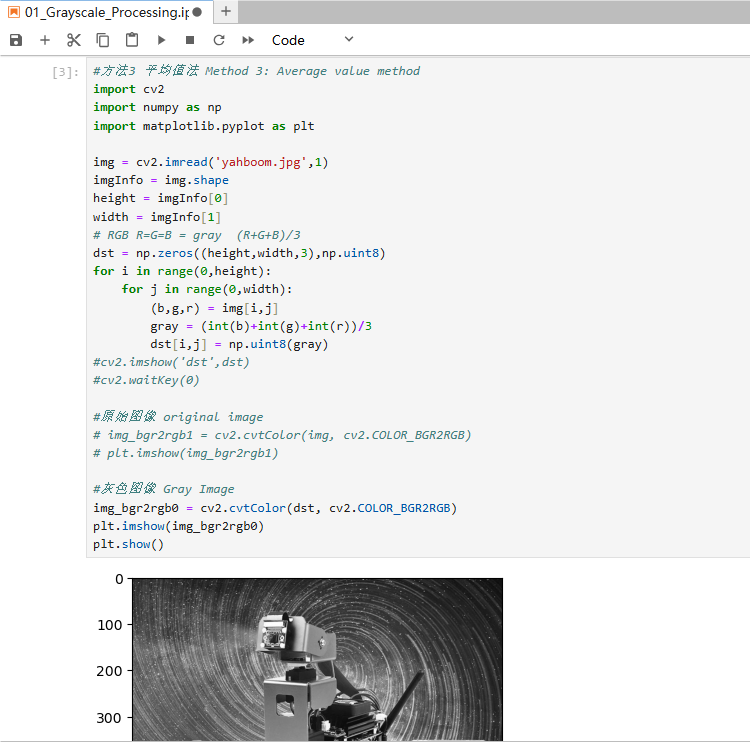
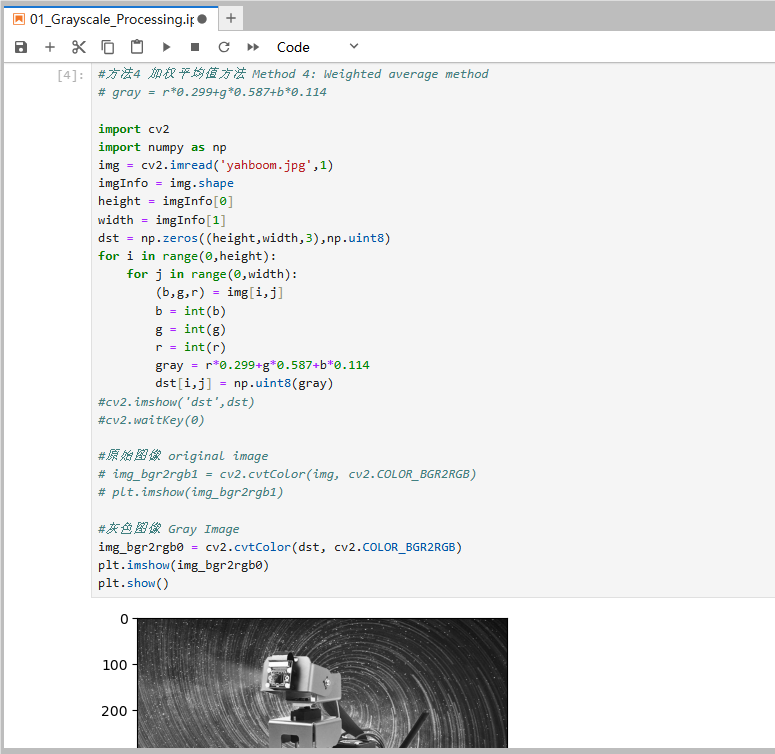
xxxxxxxxxx#方法4 加权平均值方法 Method 4: Weighted average method# gray = r*0.299+g*0.587+b*0.114 import cv2import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('yahboom.jpg',1)imgInfo = img.shapeheight = imgInfo[0]width = imgInfo[1]dst = np.zeros((height,width,3),np.uint8)for i in range(0,height): for j in range(0,width): (b,g,r) = img[i,j] b = int(b) g = int(g) r = int(r) gray = r*0.299+g*0.587+b*0.114 dst[i,j] = np.uint8(gray)#cv2.imshow('dst',dst)#cv2.waitKey(0)#原始图像 original image# img_bgr2rgb1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb1)#灰色图像 Gray Imageimg_bgr2rgb0 = cv2.cvtColor(dst, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)plt.imshow(img_bgr2rgb0)plt.show()