3. Install Rosmaster driver library
3. Install Rosmaster driver library3.1 Declaration before installing driver library3.2 Downloading the Python Driver Library File3.3 Transferring Files to Jetson Nano3.4 Starting Installation3.5 Importing Library Files3.6. How to use the driver library basics3.7 API Introduction
3.1 Declaration before installing driver library
The latest driver library has already been installed in the cart's factory image system, so you don't need to repeat the installation. If you are not using the factory image, or the driver library has been updated, you need to install the driver library.
The path to install the driver library from the factory system: ~/Software/py_install
Please refer to the following steps to install the driver library, and take the V1.5.8 version as an example.
3.2 Downloading the Python Driver Library File
The latest version of Rosmaster Python driver library is provided in this course material, named py_install.zip.
The zip contains the following files:
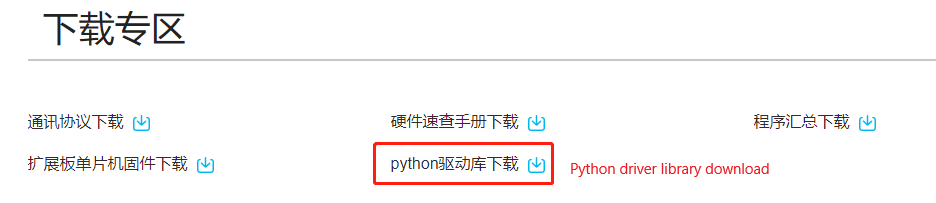
Or Yahboom official website in the Rosmaster material download area click [python driver library download] to download to the latest version of py_install.zip file.
3.3 Transferring Files to Jetson Nano
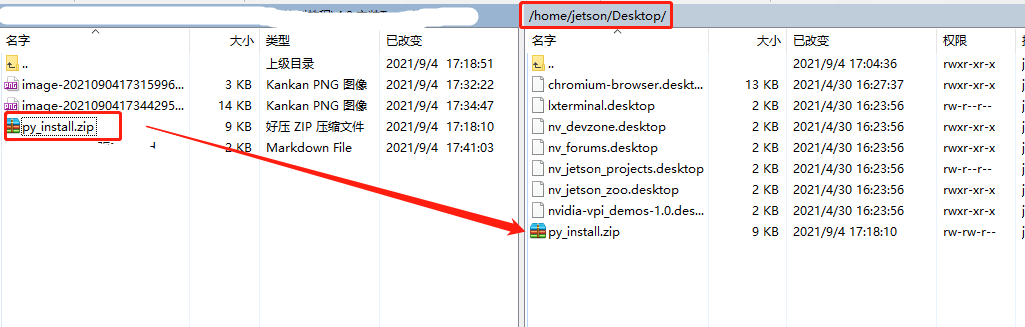
If you are using the browser that comes with Jetson Nano to download the file from the AWS website, please download the file to a user-operable path, such as the desktop.
If you are using the driver library zip file in the information, or using a computer browser to download the driver library file, you can drag the driver library zip file into the Jetson Nano desktop via WinSCP software.
The driver library file can be deleted after successful installation.
If you don't know how to use WinSCP to transfer files yet, please check the following web page for detailed installation and operation of WinSCP:
File Transfer (Jetson Nano 4 GB)
3.4 Starting Installation
Open the terminal of Jetson Nano and enter the following command to unzip it.
Go to the desktop and check if the file exists, the red box is the target file.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/Desktop && lsUnzip the file
xxxxxxxxxxunzip py_install.zip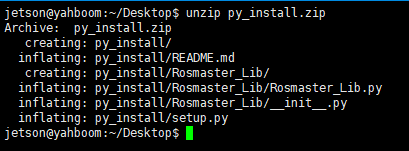
Note: The entire documentation is based on placing the py_install.zip archive on the Jetson Nano system desktop. If you have a different path where the zip is stored, please go to the corresponding directory according to the actual path.
Go to the folder of the driver library
xxxxxxxxxxcd py_installRun the install command and see the version number at the end to indicate successful installation. This command will overwrite the previously installed Rosmaster_Lib driver library.
xxxxxxxxxxsudo python3 setup.py install
3.5 Importing Library Files
The name of Rosmaster driver library is Rosmaster_Lib, use Rosmaster_Lib to import the library in the program.
xxxxxxxxxxfrom Rosmaster_Lib import Rosmaster
3.6. How to use the driver library basics
For details, please check the video tutorial of this lesson.
Source Path: Rosmaster/Samples/3.test_rosmaster.ipynb
3.7 API Introduction
The following API profiles of the driver libraries are introduced later in the control course to introduce the functional usage and parameter contents.
xxxxxxxxxx| __del__(self)|| __init__(self, car_type=1, com='/dev/myserial', delay=0.002, debug=False)| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.|| clear_auto_report_data(self)| # 清除单片机自动发送过来的缓存数据| # Clear the cache data automatically sent by the MCU|| create_receive_threading(self)| # 开启接收和处理数据的线程| # Start the thread that receives and processes data|| get_accelerometer_data(self)| # 获取加速度计三轴数据,返回a_x, a_y, a_z| # Get accelerometer triaxial data, return a_x, a_y, a_z|| get_battery_voltage(self)| # 获取电池电压值| # Get the battery voltage|| get_gyroscope_data(self)| # 获取陀螺仪三轴数据,返回g_x, g_y, g_z| # Get the gyro triaxial data, return g_x, g_y, g_z|| get_magnetometer_data(self)| # 获取磁力计三轴数据,返回m_x, m_y, m_z|| get_motion_data(self)| # 获取小车速度,val_vx, val_vy, val_vz| # Get the car speed, val_vx, val_vy, val_vz|| get_motion_pid(self)| # 获取小车的运动PID参数, 返回[kp, ki, kd]| # Get the motion PID parameters of the dolly and return [kp, ki, kd]|| get_motor_encoder(self)| # 获取四路电机编码器数据| # Obtain data of four-channel motor encoder|| get_uart_servo_angle(self, s_id)| # 读取总线舵机的角度,s_id表示要读取的舵机的ID号,s_id=[1-6]| # Read the Angle of the bus steering gear, s_id indicates the ID number of the steering gear to beread, s_id=[1-6]|| get_uart_servo_angle_array(self)| # 一次性读取六个舵机的角度[xx, xx, xx, xx, xx, xx],如果某个舵机错误则那一位为-1| # Read the angles of three steering gear [xx, xx, xx, xx, xx, xx] at one time. If one steering gearis wrong, that one is -1|| get_uart_servo_value(self, servo_id)| # 读取总线舵机位置参数, servo_id=[1-250], 返回:读到的ID,当前位置参数| # Read bus servo position parameters, servo_id=[1-250], return: read ID, current position parameters|| get_version(self)| # 获取底层单片机版本号,如1.1| # Get the underlying microcontroller version number, such as 1.1|| reset_flash_value(self)| # 重置小车flash保存的数据,恢复出厂默认值。| # Reset the car flash saved data, restore the factory default value|| set_auto_report_state(self, enable, forever=False)| # 单片机自动返回数据状态位,默认为开启,如果设置关闭会影响部分读取数据功能。| # enable=True,底层扩展板会每隔10毫秒发送一包数据,总共四包不同数据,所以每包数据每40毫秒刷新一次。enable=False,则不发送。| # forever=True永久保存,=False临时作用。| # The MCU automatically returns the data status bit, which is enabled by default. If the switch isclosed, the data reading function will be affected.| # enable=True, The underlying expansion board sends four different packets of data every 10 milliseconds, so each packet is refreshed every 40 milliseconds.| # If enable=False, the report is not sent.| # forever=True for permanent, =False for temporary|| set_beep(self, on_time)| # 蜂鸣器开关,on_time=0:关闭,on_time=1:一直响,| # on_time>=10:响xx毫秒后自动关闭(on_time是10的倍数)。| # Buzzer switch. On_time =0: the buzzer is off. On_time =1: the buzzer keeps ringing| # On_time >=10: automatically closes after xx milliseconds (on_time is a multiple of 10)|| set_car_motion(self, v_x, v_y, v_z)| # 小车运动控制,v_x=[-1.0, 1.0], v_y=[-1.0, 1.0], v_z=[-5.0, 5.0]| # Car movement control, v_x = [-1.0, 1.0], v_y = [-1.0, 1.0], v_z = [-5.0, 5.0]|| set_car_run(self, state, speed, adjust=False)| # 控制小车向前、向后、向左、向右等运动。| # state=[0~6],=0停止,=1前进,=2后退,=3向左,=4向右,=5左旋,=6右旋| # speed=[-100, 100],=0停止。| # adjust=True开启陀螺仪辅助运动方向。=False则不开启。| # Control the car forward, backward, left, right and other movements.| # State =[0~6],=0 stop,=1 forward,=2 backward,=3 left,=4 right,=5 spin left,=6 spin right| # Speed =[-100, 100], =0 Stop.| # Adjust =True Activate the gyroscope auxiliary motion direction. If =False, the function is disabled.|| set_car_type(self, car_type)| # 设置小车类型| # Set car Type|| set_colorful_effect(self, effect, speed=255, parm=255)| # RGB可编程灯带特效展示。| # effect=[0, 6],0:停止灯效,1:流水灯,2:跑马灯,3:呼吸灯,4:渐变灯,5:星光点点,6:电量显示| # speed=[1, 10],数值越小速度变化越快。| # parm,可不填,作为附加参数。用法1:呼吸灯效果传入[0, 6]可修改呼吸灯颜色。| # RGB programmable light band special effects display.| # Effect =[0, 6], 0: stop light effect, 1: running light, 2: running horse light, 3: breathing light, 4: gradient light, 5: starlight, 6: power display| # Speed =[1, 10], the smaller the value, the faster the speed changes| # Parm, left blank, as an additional argument. Usage 1: The color of breathing lamp can be modified by the effect of breathing lamp [0, 6]|| set_colorful_lamps(self, led_id, red, green, blue)| # RGB可编程灯带控制,可单独控制或全体控制,控制前需要先停止RGB灯特效。| # led_id=[0, 13],控制对应编号的RGB灯;led_id=0xFF, 控制所有灯。| # red,green,blue=[0, 255],表示颜色RGB值。| # RGB programmable light belt control, can be controlled individually or collectively, before control need to stop THE RGB light effect.| # Led_id =[0, 13], control the CORRESPONDING numbered RGB lights; Led_id =0xFF, controls all lights.| # Red,green,blue=[0, 255], indicating the RGB value of the color.|| set_motor(self, speed_1, speed_2, speed_3, speed_4)| # 控制电机PWM脉冲,从而控制速度(未使用编码器测速)。speed_X=[-100, 100]| # Control PWM pulse of motor to control speed (speed measurement without encoder). speed_X=[-100, 100]|| set_pid_param(self, kp, ki, kd, forever=False)| # PID 参数控制,会影响set_car_motion函数控制小车的运动速度变化情况。默认情况下可不调整。| # kp ki kd = [0, 10.00], 可输入小数。| # forever=True永久保存,=False临时作用。| # 由于永久保存需要写入芯片flash中,操作时间较长,所以加入delay延迟时间,避免导致单片机丢包的问题。| # 临时作用反应快,单次有效,重启单片后数据不再保持。| # PID parameter control will affect the set_CAR_motion function to control the speed change of thecar. This parameter is optional by default.| # KP ki kd = [0, 10.00]| # forever=True for permanent, =False for temporary.| # Since permanent storage needs to be written into the chip flash, which takes a long time to operate, delay is added to avoid packet loss caused by MCU.| # Temporary effect fast response, single effective, data will not be maintained after restarting the single chip|| set_pwm_servo(self, servo_id, angle)| # 舵机控制,servo_id:对应ID编号,angle:对应舵机角度值| # servo_id=[1, 4], angle=[0, 180]| # Servo control, servo_id: corresponding, Angle: corresponding servo Angle value|| set_pwm_servo_all(self, angle_s1, angle_s2, angle_s3, angle_s4)| # 同时控制四路PWM的角度,angle_sX=[0, 180]| # At the same time control four PWM Angle, angle_sX=[0, 180]|| set_uart_servo(self, servo_id, pulse_value, run_time=500)| # 控制总线舵机。servo_id:[1-255],表示要控制的舵机的ID号, id=254时, 控制所有已连接舵机。| # pulse_value=[96,4000]表示舵机要运行到的位置。| # run_time表示运行的时间(ms),时间越短,舵机转动越快。最小为0,最大为2000| # Control bus steering gear. Servo_id :[1-255], indicating the ID of the steering gear to be controlled. If ID =254, control all connected steering gear.| # pulse_value=[96,4000] indicates the position to which the steering gear will run.| # run_time indicates the running time (ms). The shorter the time, the faster the steering gear rotates. The minimum value is 0 and the maximum value is 2000|| set_uart_servo_angle(self, s_id, s_angle, run_time=500)| # 设置总线舵机角度接口:id:7-9, angle: 7:[0, 225], 8:[30, 270], 9:[30, 180], 设置舵机要运动到的角度。| # 设直立向上夹紧状态,三个舵机都为180度,7/8号顺时针(向下)转为减,逆时针(向上)转为增,夹子松开为减,夹紧为增。| # run_time表示运行的时间(ms),时间越短,舵机转动越快。最小为0,最大为2000| # Set bus steering gear Angle interface: ID :7-9, Angle :7 :[0, 225], 8:[30, 270], 9:[30, 180], setsteering gear to move to the Angle.| # Set up the vertical clamping state, the three steering gear are 180 degrees, 7/8 clockwise (down)to decrease, counterclockwise (up) to increase, clip release to decrease, clamping to increase.| # run_time indicates the running time (ms). The shorter the time, the faster the steering gear rotates. The minimum value is 0 and the maximum value is 2000|| set_uart_servo_angle_array(self, angle_s=[90, 90, 90, 90, 90, 180], run_time=500)| # 同时控制机械臂所有舵机的角度。| # Meanwhile, the Angle of all steering gear of the manipulator is controlled|| set_uart_servo_id(self, servo_id)| # 设置总线舵机的ID号,servo_id=[1-250]。| # 运行此函数前请确认只连接一个总线舵机,否则会把所有已连接的总线舵机都设置成同一个ID,造成控制混乱。| # Set the bus servo ID, servo_id=[1-250].| # Before running this function, please confirm that only one bus actuator is connected. Otherwise,all connected bus actuators will be set to the same ID, resulting in confusion of control|| set_uart_servo_offset(self, servo_id)| # 设置机械臂的中位偏差,servo_id=0~6, =0全部恢复出厂默认值| # Run the following command to set the mid-bit deviation of the manipulator: servo_id=0 to 6, =0 Restore the factory default values|| set_uart_servo_torque(self, enable)| # 关闭/打开总线舵机扭矩力, enable=[0, 1]。| # enable=0:关闭舵机扭矩力,可以用手转动舵机,但命令无法控制转动;| # enable=1:打开扭矩力,命令可以控制转动,不可以用手转动舵机。| # Turn off/on the bus steering gear torque force, enable=[0, 1].| # enable=0: Turn off the torque force of the steering gear, the steering gear can be turned by hand, but the command cannot control the rotation;| # enable=1: Turn on torque force, command can control rotation, can not turn steering gear by hand