4. ROS2 service communication
Service communication is one of the ROS2 node communication methods, it is different from topic communication, service communication has a feedback mechanism, it will feedback the result of the service. Therefore, service communication is mostly used in programs that need feedback results, such as the small turtle routine, which calls the Spawn service to generate a turtle, and prints out the turtle's name after the service is completed (after the turtle is generated). The next step is to explain how to use the Python language to realize the service communication between nodes.
1. Create a new function package
Create a new feature package in the src of the previously created workspace directory by typing, in the terminal.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_ws/srcros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python service_pkg
3. Write server-side python file
3.1, Program source code
Create a new file named server_demo.py.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_ws/src/service_pkg/service_pkggedit server_demo.py
Copy the following section into the file.
xxxxxxxxxx#导入相关的库文件 # Import the relevant library filesimport rclpyfrom rclpy.node import Nodefrom example_interfaces.srv import AddTwoIntsclass Service_Server(Node): def __init__(self,name): super().__init__(name) #创建一个服务端,使用的是create_service函数,传入的参数分别是: #服务数据的数据类型、服务的名称,服务回调函数(也就是服务的内容) # Create a server, using the create_service function, with the parameters passed in being: # the data type of the service data, the name of the service, the service callback function (that is, the content of the service) self.srv = self.create_service(AddTwoInts, '/add_two_ints', self.Add2Ints_callback) #这里的服务回调函数的内容是把两个整型数相加,然后返回相加的结果 #The content of the service callback function here is to add two integers together and return the result of the addition def Add2Ints_callback(self,request,response): response.sum = request.a + request.b print("response.sum = ",response.sum) return responsedef main(): rclpy.init() server_demo = Service_Server("publisher_node") rclpy.spin(server_demo)Focus on the service callback function, Add2Ints_callback, here you need to pass in the parameters in addition to self, there is the request and response, request is the parameters needed by the service, response is the service feedback results. request.a and request.b is the request part of the content, response.sum is the response part of the content, here first look at the AddTwoInts this type of data is how, you can use the following command to see. content, response.sum is the response part of the content, here first look at the AddTwoInts this type of data is how, you can use the following commands to see.
xxxxxxxxxxros2 interface show example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts
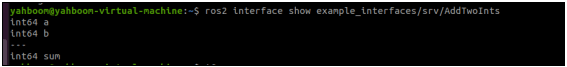
A part of the data of this type is divided into two parts, the upper part represents the request, the lower part represents the response. then the respective fields and their respective variables, such as int64 a, int64 b, all in the then pass the parameter is, you need to specify the value of a, b is how much. Similarly, the result of the feedback also needs to specify what the value of sum is.
3.2 Modifying the setup.py file
Terminal input.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_ws/src/service_pkggedit setup.py
Find the location shown below.
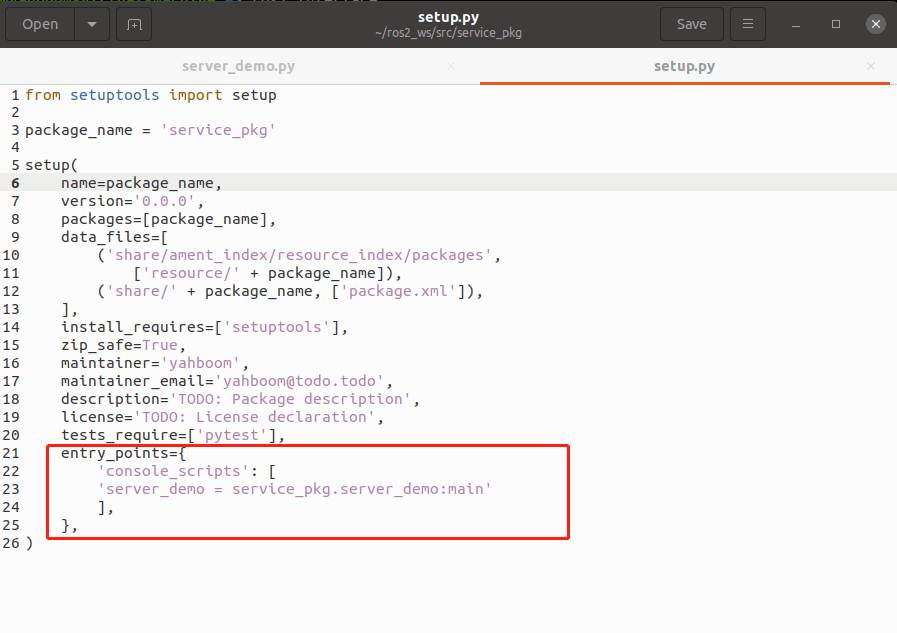
Add the following to 'console_scripts': [].
xxxxxxxxxx'server_demo = service_pkg.server_demo:main'
3.3. Compile workspace
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_wscolcon build
After the compilation is complete, refresh the environment variables in the workspace.
xxxxxxxxxxsource ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
3.4. Run the program
Terminal input,
xxxxxxxxxxros2 run service_pkg server_demo
After running, there is no feedback data because the service is not called, you can call the service from the command line, first query what services are currently available, terminal input, the
xxxxxxxxxxros2 service list
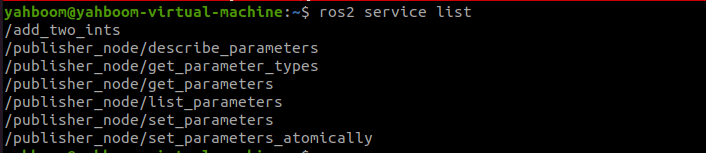
/add_two_ints is the service we need to invoke, which is done with the following command, terminal input, the
xxxxxxxxxxros2 service call /add_two_ints example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts "{a: 1,b: 4}"
Here we assign the value of a to 1 and the value of b to 4, that is, we call the service to compute the sum of 1 and 4.
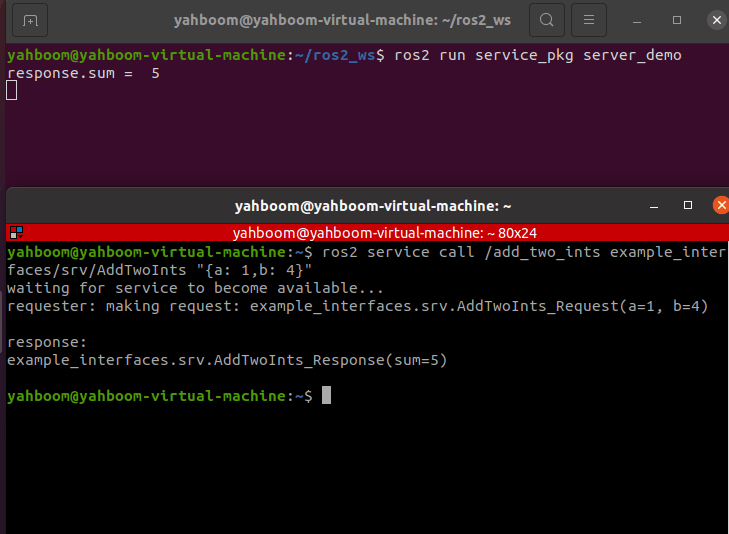
As you can see from the above figure, after calling the service, the result returned is 5, and the terminal running the server also prints the value returned.
4. Write the client-side python file
4.1, Program Source Code
Create a new file named client_demo.py.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_ws/srcservice_pkg/service_pkggedit client_demo.py
Copy the following into the inside.
xxxxxxxxxx#导入相关的库 #Import related librariesimport rclpyfrom rclpy.node import Nodefrom example_interfaces.srv import AddTwoIntsclass Service_Client(Node): def __init__(self,name): super().__init__(name) #创建客户端,使用的是create_client函数,传入的参数是服务数据的数据类型、服务的话题名称 # Create the client, using the create_client function, the parameters passed in are the data type of the service data, the topic name of the service self.client = self.create_client(AddTwoInts,'/add_two_ints') # 循环等待服务器端成功启动 # Loop for successful server-side startup while not self.client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=1.0): print("service not available, waiting again...") # 创建服务请求的数据对象 # Create data objects for service requests self.request = AddTwoInts.Request() def send_request(self): self.request.a = 10 self.request.b = 90 #发送服务请求 # Send a service request self.future = self.client.call_async(self.request) def main(): rclpy.init() #节点初始化 #Node initialization service_client = Service_Client("client_node") #创建对象 #Creating Objects service_client.send_request() #发送服务请求 # Send a service request while rclpy.ok(): rclpy.spin_once(service_client) #判断数据是否处理完成 # Determine if data processing is complete if service_client.future.done(): try: #获得服务反馈的信息并且打印 # Get service feedback and print response = service_client.future.result() print("Result = ",response.sum) except Exception as e: service_client.get_logger().info('Service call failed %r' % (e,)) break4.2 Modifying the setup.py file
Terminal input.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_ws/src/topic_pkggedit setup.py
Find the location shown below.

Add the following to 'console_scripts': [].
xxxxxxxxxx'client_demo = service_pkg.client_demo:main'
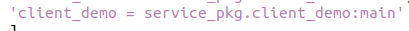
4.3. Compilation workspace
xxxxxxxxxxcd ~/ros2_wscolcon build
After the compilation is complete, refresh the environment variables in the workspace.
xxxxxxxxxxsource ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
4.4. Run the program
Terminal input
xxxxxxxxxx#启动服务端 #Start the serverros2 run service_pkg server_demo#启动客户端 #Start the clientros2 run service_pkg client_demo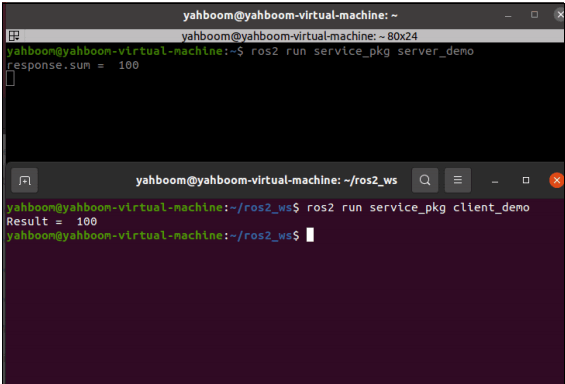
First run the server, then run the client, the client provides a=10, b=90, the server does the summation and gets the result as 100, the result is printed in both terminals.