Robot state estimation
Note: The ROS_DOMAIN_ID of the Raspberry Pi and the microROS control board need to be consistent. You can check [MicroROS Control Board Parameter Configuration] to set the microROS control board ROS_DOMAIN_ID. Check the tutorial [Connect MicroROS Agent] to determine whether the IDs are consistent.
1. Program function description
After the program is started, it will subscribe to imu and odom data, filter out part of the imu data, and then fuse it with the odom data. Finally, a fused odom data will be output to estimate the status of the robot. This data is mostly used in mapping and navigation. .
2.Start and connect to the agent
After successfully starting the Raspberry Pi, enter the following command to start the agent.
sh ~/start_agent_rpi5.sh
Then, turn on the car switch and wait for the car to connect to the agent. The connection is successful, as shown in the figure below.

3. Enter the car system docker
Open another terminal and enter the following command to enter docker.
xxxxxxxxxxsh ros2_humble.sh
When the following interface appears, you have successfully entered docker. Now you can control the car through commands.
4. Start the program
Enter the following command in the terminal.
xxxxxxxxxxros2 launch yahboomcar_bringup yahboomcar_bringup_launch.py
Enter the following command to view the communication diagram between nodes.
xxxxxxxxxxros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph
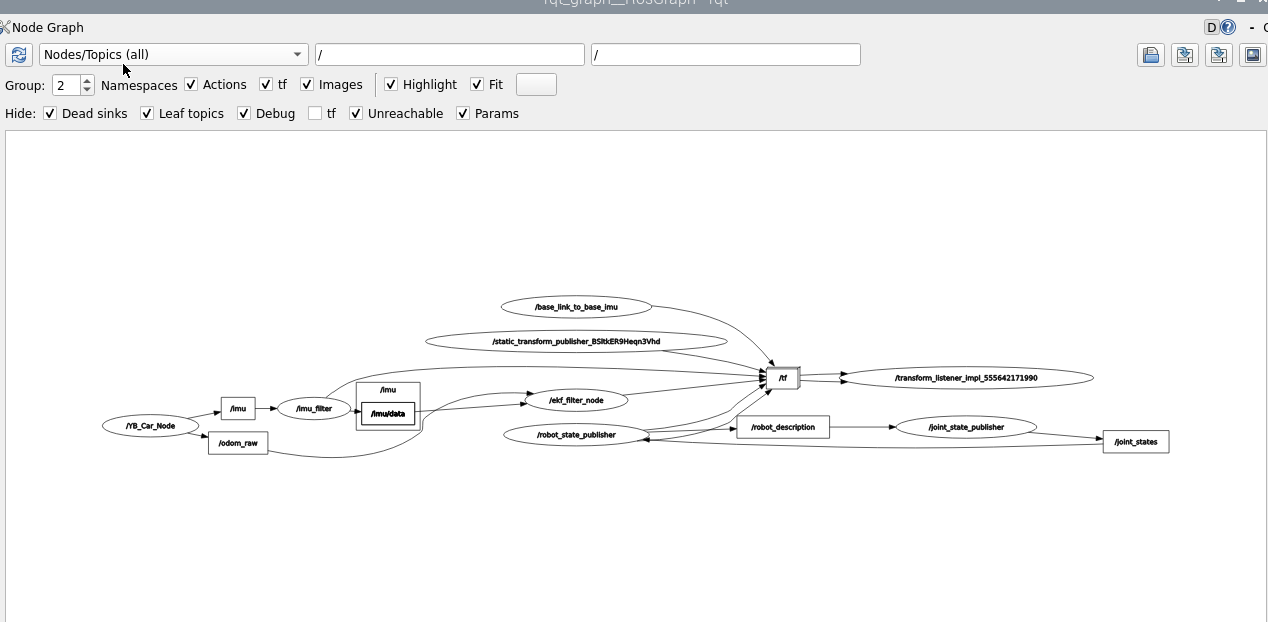
If it is not displayed at first, select [Nodes/Topics(all)], and then click the refresh button in the upper left corner.
The fused node is /ekf_filter_node. You can query the relevant information of this node and input it through the terminal.
xxxxxxxxxxros2 node info /ekf_filter_node
Combined with the node communication diagram above, it can be seen that the node subscribes to /imu/data and /odom_raw data, and then publishes a /odom data.
5. Parse launch file
launch file location(Take the supporting virtual machine as an example):
xxxxxxxxxx/root/yahboomcar_ws/src/yahboomcar_bringup/launchyahboomcar_bringup_launch.py
xfrom ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_path
from launch import LaunchDescriptionfrom launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgumentfrom launch.conditions import IfCondition, UnlessConditionfrom launch.substitutions import Command, LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Nodefrom launch_ros.parameter_descriptions import ParameterValue
import osfrom ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescriptionfrom launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
print("---------------------robot_type = x3---------------------")def generate_launch_description(): imu_filter_config = os.path.join( get_package_share_directory('yahboomcar_bringup'), 'param', 'imu_filter_param.yaml' )
imu_filter_node = IncludeLaunchDescription( PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join( get_package_share_directory('imu_filter_madgwick'), 'launch'), '/imu_filter.launch.py']) ) ekf_node = IncludeLaunchDescription( PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join( get_package_share_directory('robot_localization'), 'launch'), '/ekf.launch.py']) ) description_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription( PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join( get_package_share_directory('yahboomcar_description'), 'launch'), '/description_launch.py']) ) base_link_to_imu_tf_node = Node( package='tf2_ros', executable='static_transform_publisher', name='base_link_to_base_imu', arguments=['-0.002999', '-0.0030001','0.031701','0','0','0','base_link','imu_frame'] ) return LaunchDescription([ imu_filter_node, ekf_node, base_link_to_imu_tf_node, description_launch ])The launch file starts the following nodes.
imu_filter_node:Filter imu data nodes, mainly filter some imu data.
ekf_node:Fusion node, mainly fuses odom data and filtered imu data.
base_link_to_imu_tf_node:Publish a static change, mainly publishing the pose transformation of the imu module and the car
description_launch:Load the URDF model.