Docker command
Docker command1. View detailed information2. View the version number3. Pull the image4. Run the image4.1. View the running image4.2. View the running or stopped image5. Clean up images6. View local images7. Delete images8. Submit the image9. Stop the image10. Multiple terminals enter the same container
Docker engine includes Docker CLI, which provides command line tools for interacting with Docker daemon. This tutorial introduces the usage of common Docker commands.
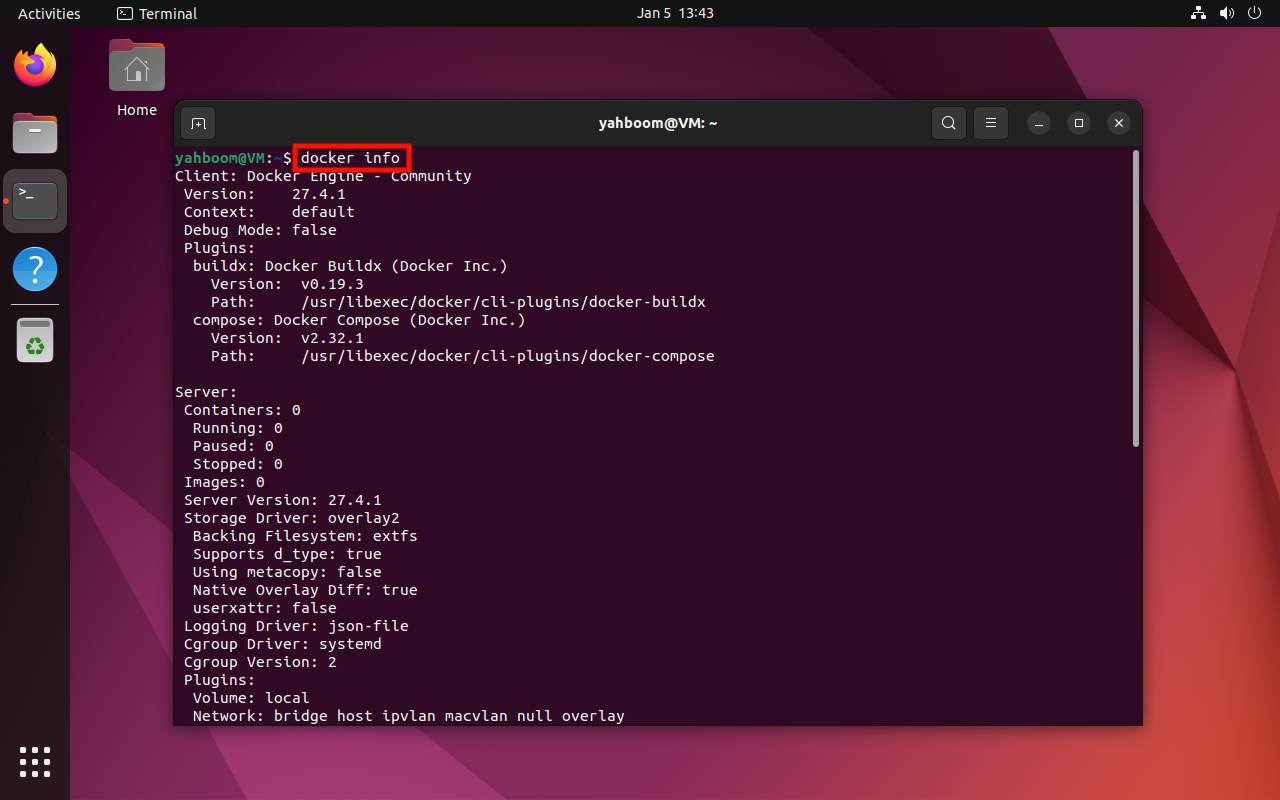
1. View detailed information
docker info
docker info
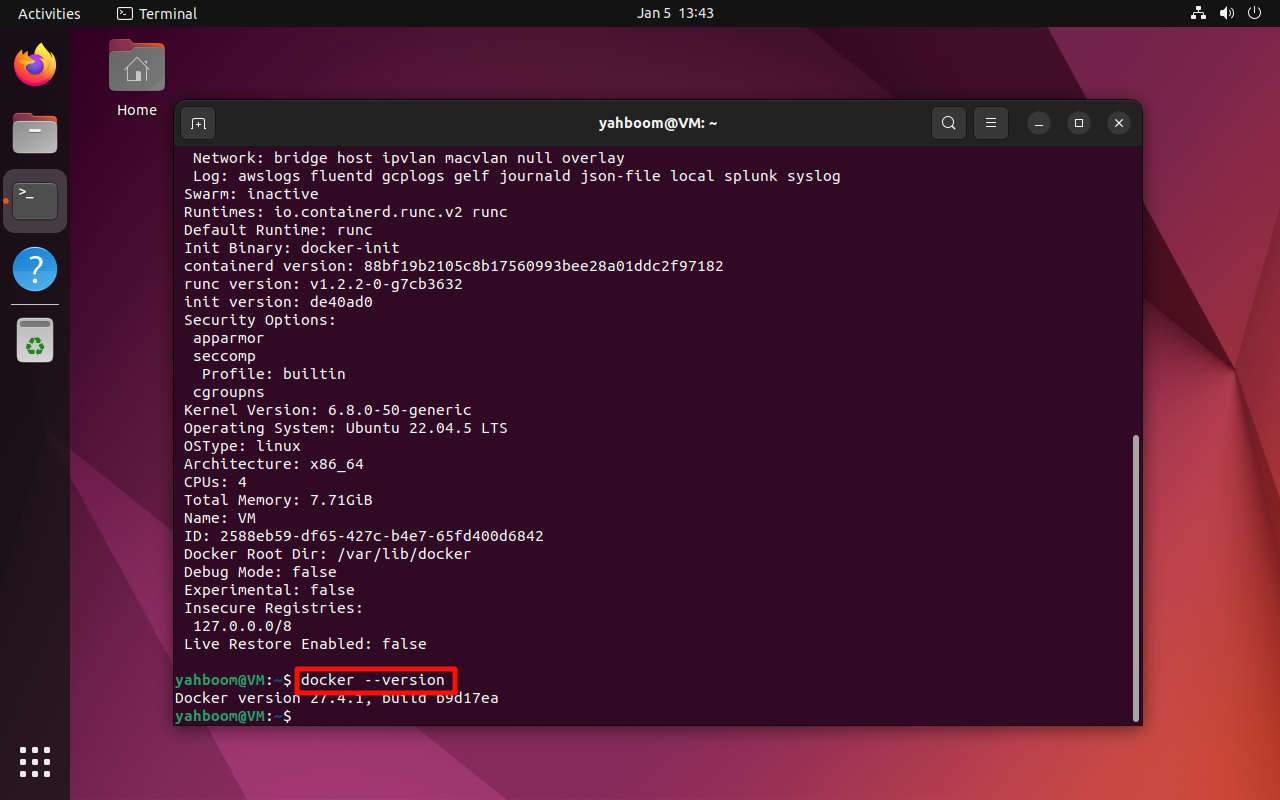
2. View the version number
docker --version
xxxxxxxxxxdocker --version
3. Pull the image
docker pull <image_name>
If no tag is specified, the image with the latest tag will be pulled by default.
xxxxxxxxxxdocker pull hello-world
docker pull <image_name>:
xxxxxxxxxxdocker pull ubuntu:18.04

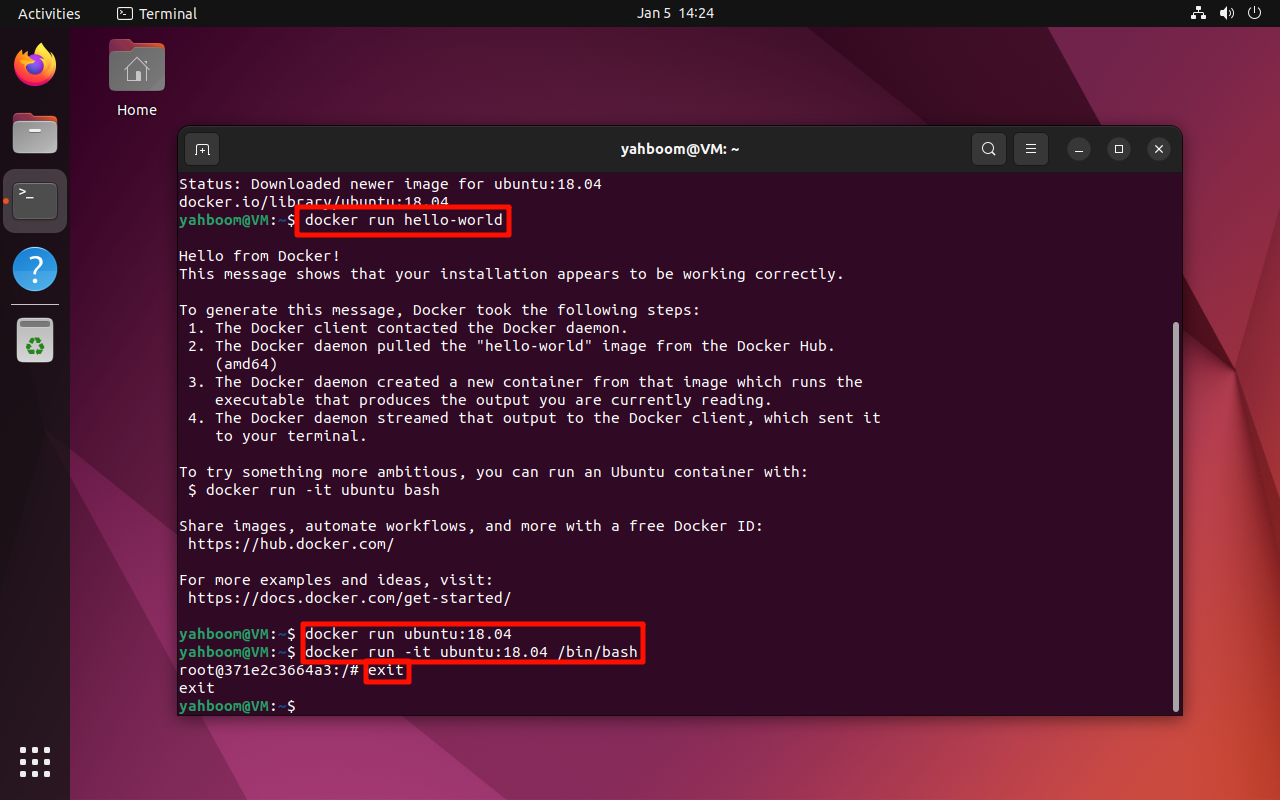
4. Run the image
If there is no image to be run locally, docker will automatically pull the corresponding image.
docker run <image_name>
xxxxxxxxxxdocker run hello-world
docker pull <image_name>:
Start the specified container and exit:
xxxxxxxxxxdocker run ubuntu:18.04
Start the specified container in interactive mode: Enter exit to exit
xxxxxxxxxxdocker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
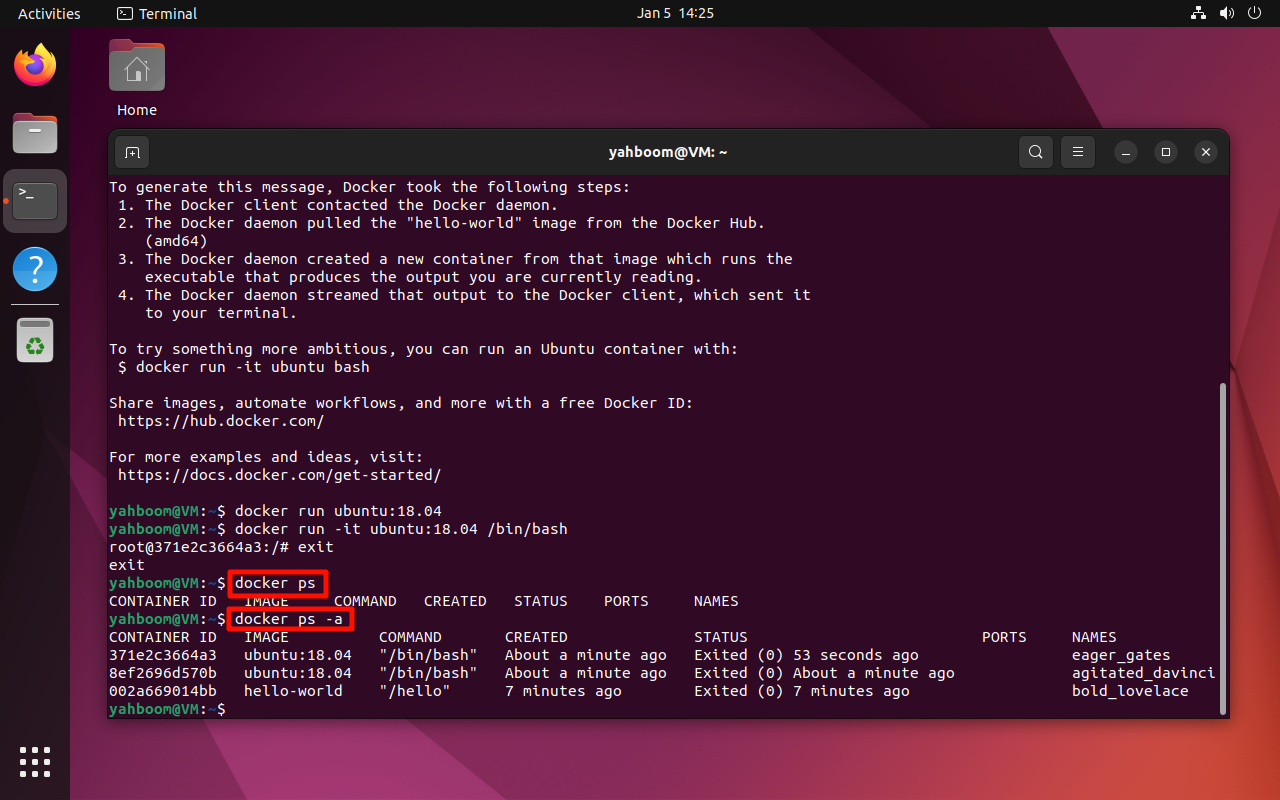
4.1. View the running image
docker ps
xxxxxxxxxxdocker ps
4.2. View the running or stopped image
xxxxxxxxxxdocker ps -a
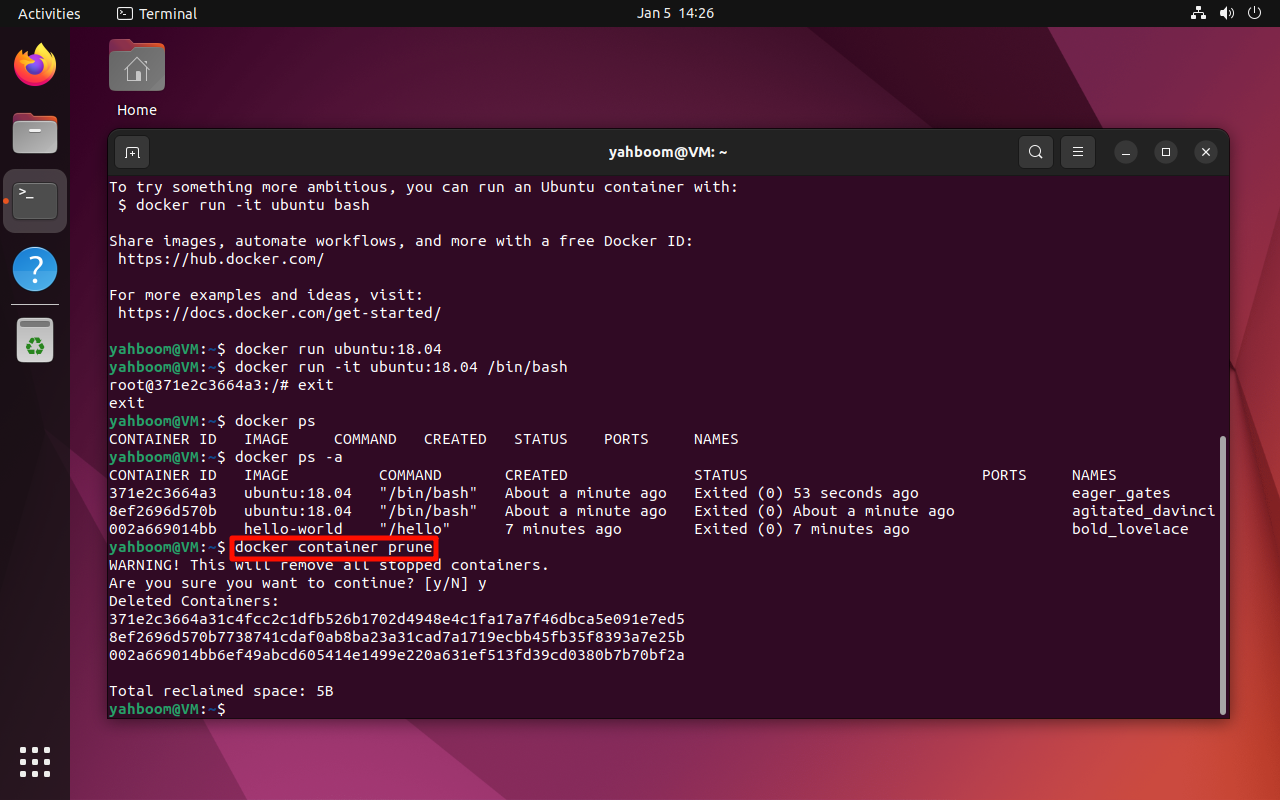
5. Clean up images
docker container prune
xxxxxxxxxxdocker container prune
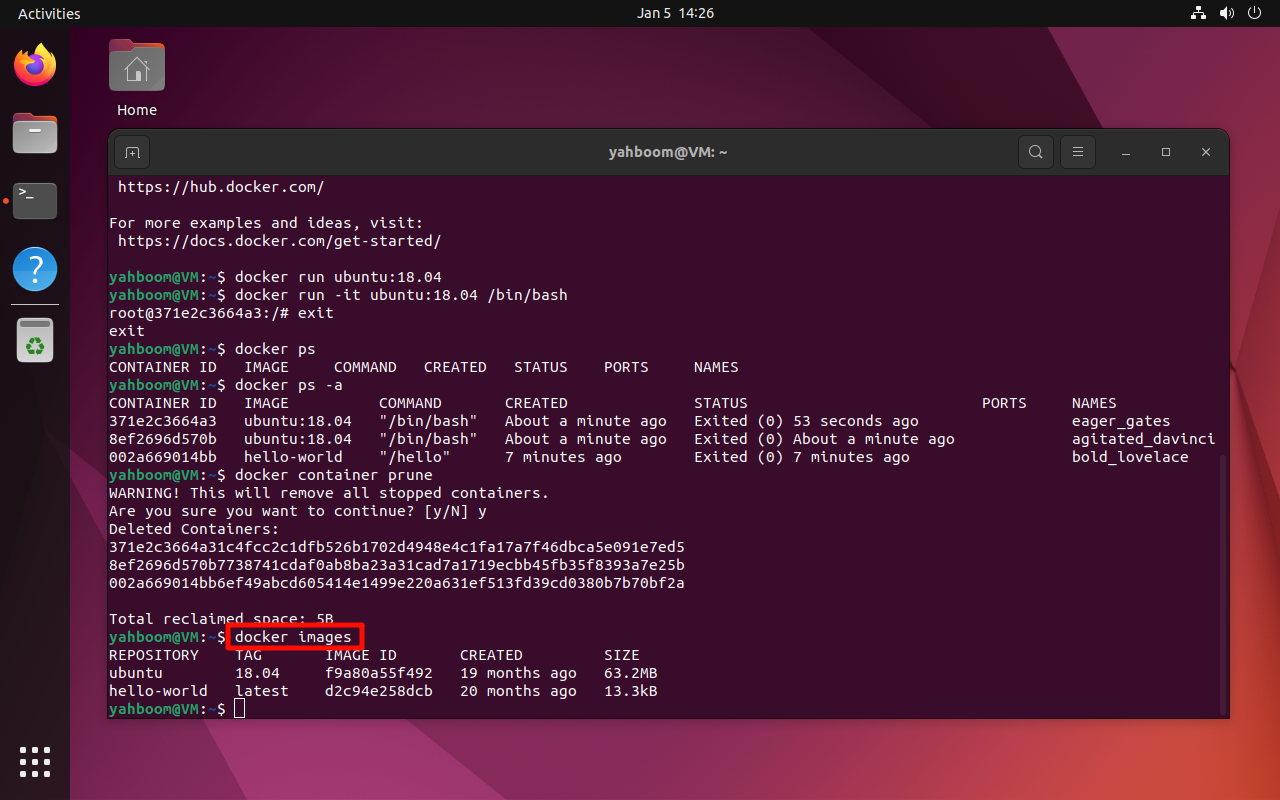
6. View local images
docker images
xxxxxxxxxxdocker images
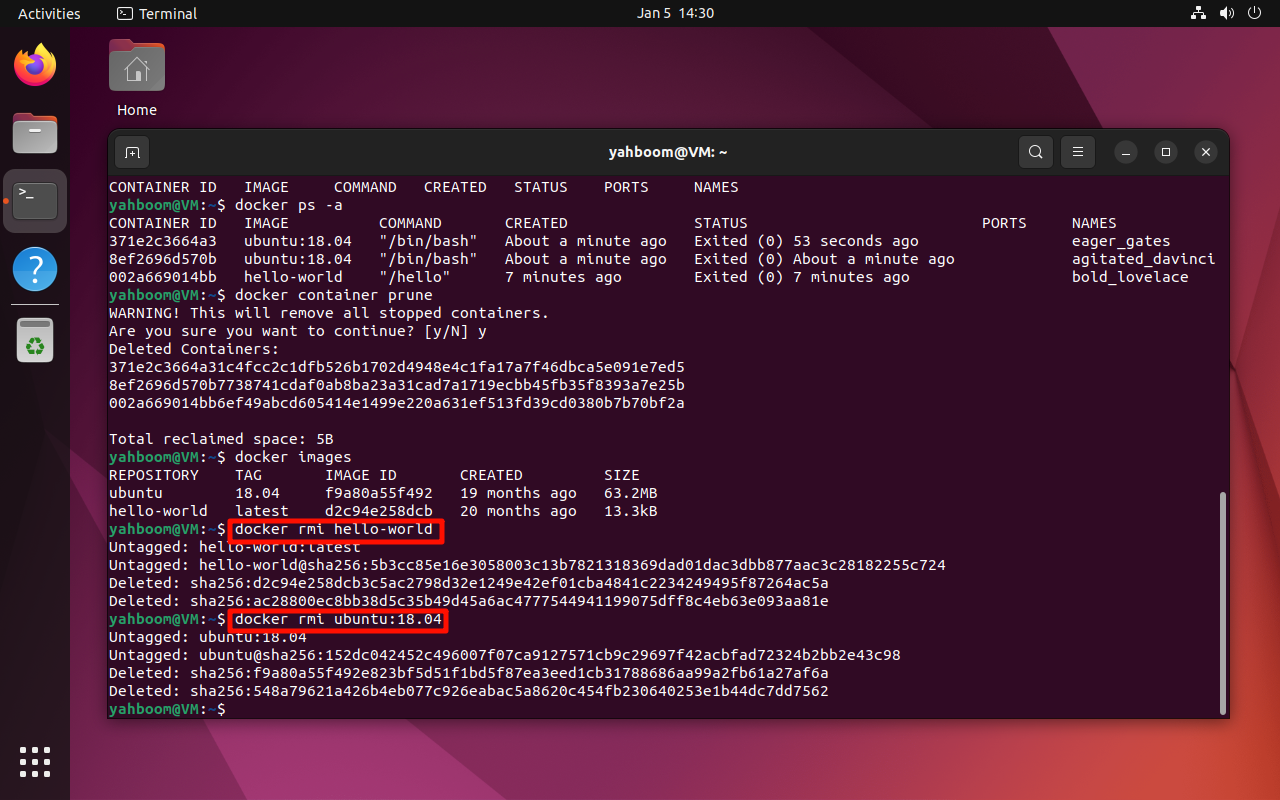
7. Delete images
Note: The image to be deleted needs to be stopped and cleaned up
docker rmi <image_name>
xxxxxxxxxxdocker rmi hello-world
docker rmi <image_name>:
xxxxxxxxxxdocker rmi ubuntu:18.04
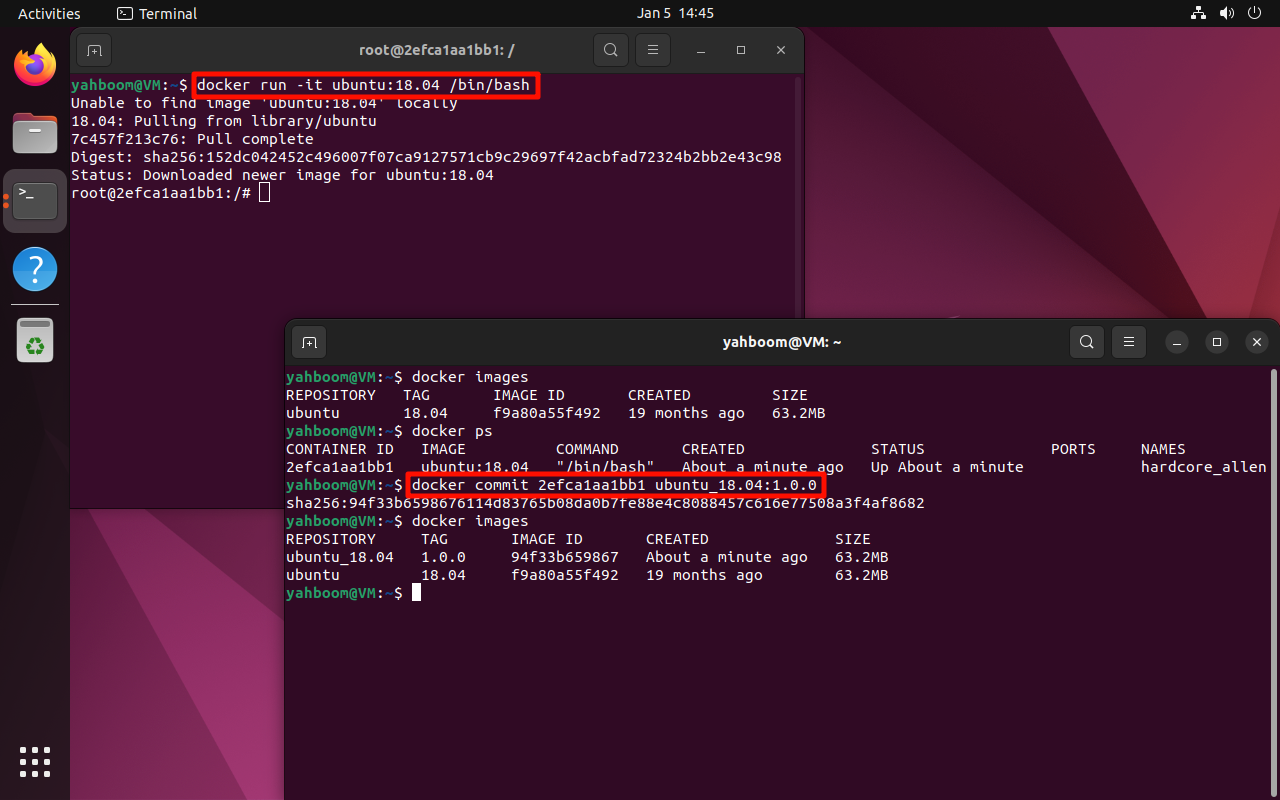
8. Submit the image
Pull and run the ubuntu:18.04 image in interactive mode
xxxxxxxxxxdocker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
docker commit
<image_name>:
Note: Modify according to the actual CONTAINER ID
xxxxxxxxxxdocker commit 2efca1aa1bb1 ubuntu_18.04:1.0.0
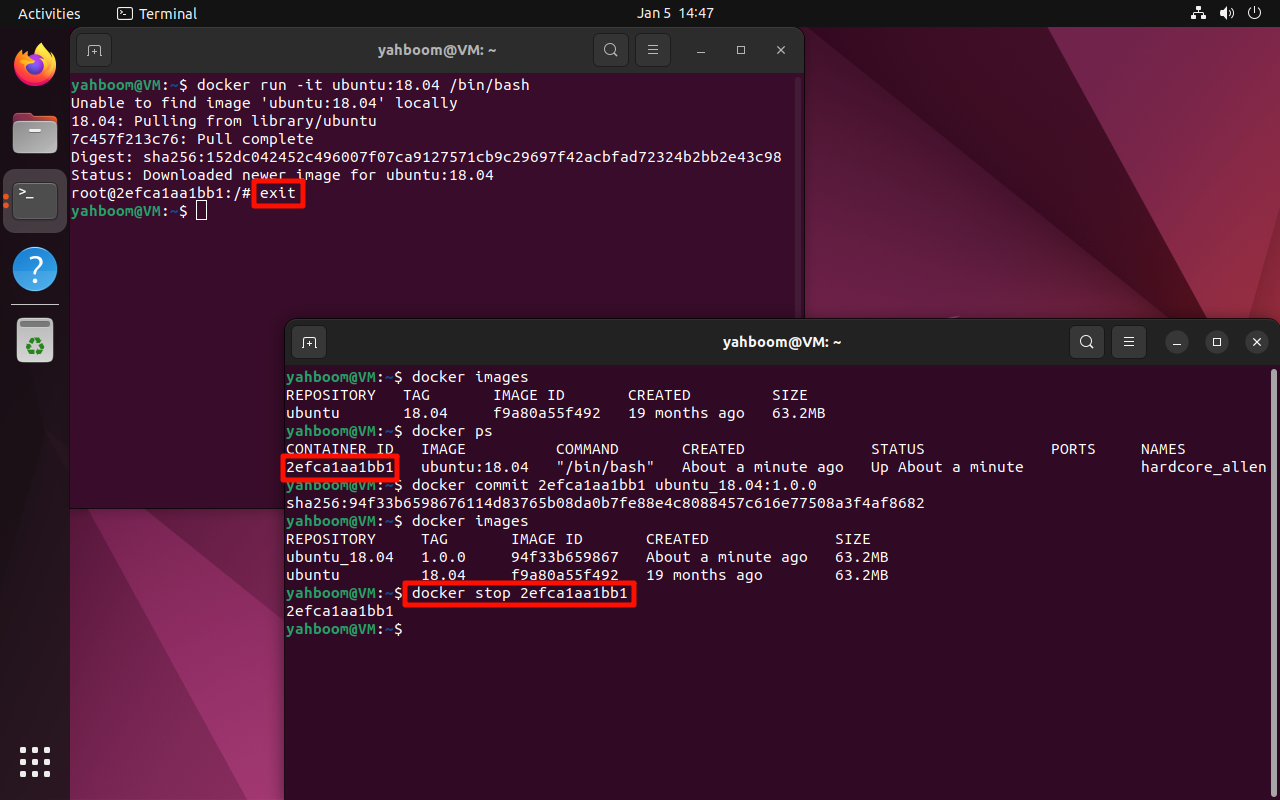
9. Stop the image
If you run the container in interactive mode and the terminal enters the container, you can enter exit in the container to stop the container;
If you close the container externally, you can use the docker stop command.
docker stop
Note: Modify according to the actual CONTAINER ID
xxxxxxxxxxdocker stop 2efca1aa1bb1
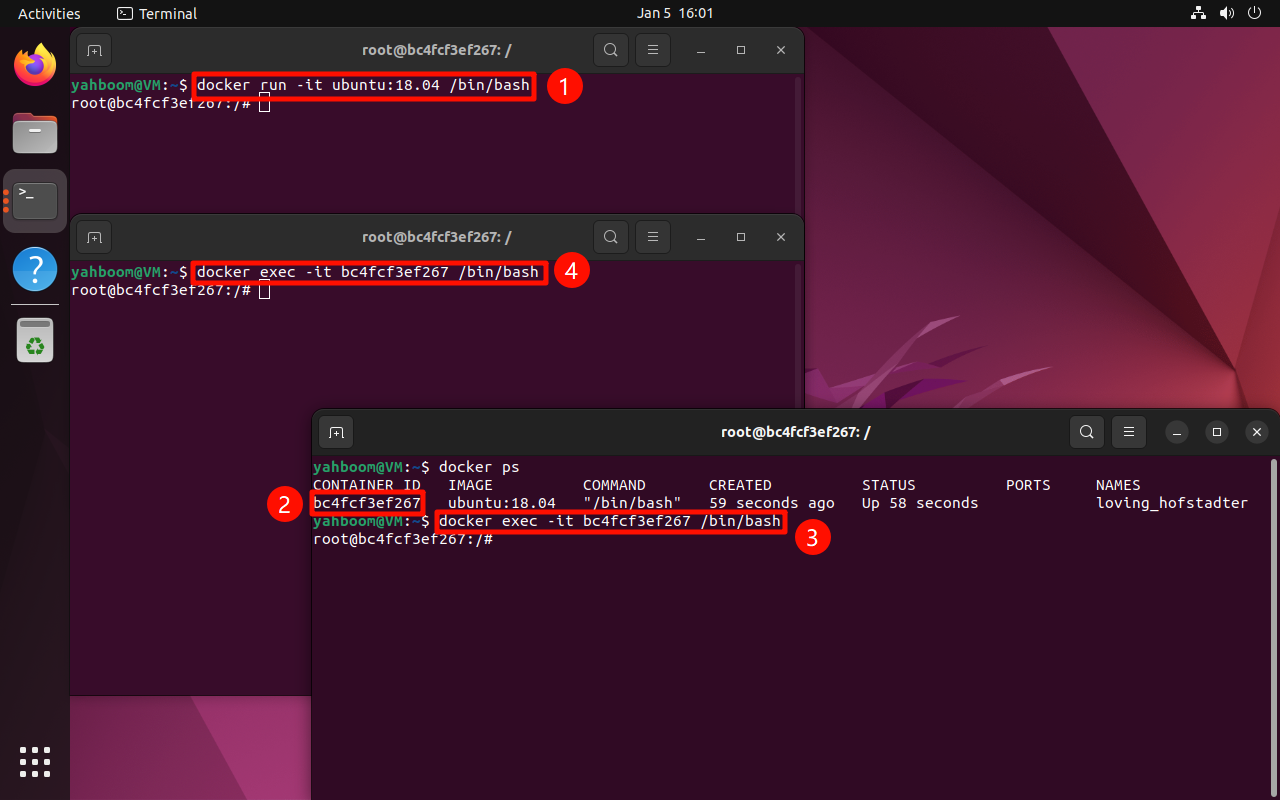
10. Multiple terminals enter the same container
Containers are isolated from each other. Directly using the command to run the image will start different containers; if you need to perform operations in the same container, you need to use the command to enter the same container.
Run the ubuntu:18.04 image in interactive mode:
xxxxxxxxxxdocker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
View the running container:
xxxxxxxxxxdocker ps
docker exec
Enter the running container in interactive mode: modify according to the actual CONTAINER ID
xxxxxxxxxxdocker exec -it bc4fcf3ef267 /bin/bash